International Banking Statistics of India: December 31, 2009* The article presents analysis of international liabilities and assets of banks in India, classified under Locational Banking Statistics (LBS) and consolidated international/foreign claims under Consolidated Banking Statistics (CBS), collected as per the reporting system of the Bank for International Settlements (BIS), for the quarter ended December 2009. The analysis of international liabilities/assets, based on LBS, has been undertaken by instrument, country and sector of customer/borrower, currency and country of incorporation of reporting bank; and the consolidated international claims, based on CBS, according to country and sector of borrower and residual maturity. Further, a broad comparison of international/foreign claims of BIS reporting banks vis-à-vis Indian banks has also been covered. Besides, the article details international/foreign claims derived from on-balance sheet items, viz., loans and deposits, holdings of securities as well as off-balance sheet items, viz., derivatives, guarantees and credit commitments on ultimate risk basis. Highlights Locational Banking Statistics – International Liabilities • The international liabilities (in Rupees) of banks in India, at end-December 2009 increased by 13.7 per cent over the position a year ago and by 0.8 per cent over the previous quarter. • The investment in the ADRs/ GDRs and equities of the banking sector by nonresidents registered a substantial growth over the position a year ago. • For the quarter ended December 2009, currency composition of the international liabilities revealed that the Indian Rupee continued to be the dominating currency. • The share of the international liabilities towards the non-bank sector was higher at 75.9 per cent compared to 69.3 per cent a year ago. Locational Banking Statistics – International Assets • At end-December 2009, the international assets (in Rupees) of banks in India declined marginally by 0.4 per cent over the position a year ago, while the assets increased by 1.7 per cent over the previous quarter. • The substantial decline in the nostro balances of the banks (19.7 per cent) over the previous year resulted in an overall decline in the international assets of the banks during the period. • For the quarter, the share of the nonbank sector in the international assets increased to 67.8 per cent from 62.9 per cent for the previous year. • At end-December 2009, almost all (98.4 per cent) assets denominated in Indian Rupee were towards non-bank sector. Consolidated Banking Statistics • The annual growth in consolidated international claims (in Rupees) of banks based on country of immediate risk, at end-December 2009, was 17.9 per cent compared to 24.6 per cent registered a year ago. • Consolidated international claims of Indian banks on immediate risk basis, at end-December 2009, continued to be of short-term nature (less than one year) and accounted for 61.2 per cent of total claims compared to 60.7 per cent a year ago. I. Introduction International Banking Statistics (IBS) is defined as banks’ on-balance sheet liabilities and assets vis-à-vis non-residents in any currency or unit of account along with such liabilities and assets vis-à-vis residents in foreign currencies or units of account. IBS
comprises Locational Banking Statistics (LBS) and Consolidated Banking Statistics (CBS). The LBS are designed to provide comprehensive and consistent quarterly data on international banking business conducted inside the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) reporting area. The purpose of CBS is to provide comprehensive and consistent quarterly data on banks’ financial claims on other countries on immediate borrower basis for providing a measure of country transfer risk and on an ultimate risk basis for assessing country risk exposures of national banking system. LBS provides the assets and liabilities by type of instrument/components, currency, sector, country of residence of counter-party/ transacting unit and nationality of reporting banks, while CBS provides data on international/foreign claims as per residual maturity and sector of borrower along with the exposures by country of immediate borrower and on the reallocation of claims (i.e., risk transfers) to the country of ultimate risk. The BIS reporting system of IBS was revised since March 2005, inter alia, covering the claims of domestic reporting
banks arising out of derivatives, guarantees and credit commitments, as well. Other than India, central banks from 43 other countries report aggregate LBS to BIS while central banks from 30 countries report aggregate CBS under the BIS reporting system of IBS. The data are published as a part of the BIS Quarterly Review. This article presents brief analysis of the LBS as well as CBS for India for the quarter ending December 2009. It also presents data on comparative position of CBS of India vis-àvis other countries based on data published by BIS1 II. Data Coverage and Methodology2 The analysis is based on the data as on December 31, 2009 reported by 88 banks. These banks are authorised to conduct business in foreign exchange through their branches, designated as authorised dealers. These banks include 58 Indian banks and 30 foreign banks (incorporated in 22 countries). Out of the 58 Indian banks, 27 are public sector banks (including IDBI Ltd.), 20 are private sector banks and 11 are cooperative banks. The banks received data from their branches, which in turn are consolidated at bank level and submitted to the Reserve Bank. The details such as asset or liability category, actual currency (24 major currencies and domestic currency), country of transacting unit, sector of the transacting unit, country of ultimate risk, sector of ultimate risk, etc., are reported. III. Comparison of External Debt Statistics and International Liabilities The international liabilities of banks covered in IBS (as per BIS definition) and external debt accounted for by banking sector in India are not strictly comparable, since certain items of liabilities, like, American Depository Receipts (ADRs), Global Depository Receipts (GDRs), equity of banks held by nonresidents, included in IBS, are not part of the external debt statistics. It may be construed that broadly international liabilities of banking sector in India (under IBS reporting) are the sum of external debt statistics (for banking sector in India), liabilities of banks in foreign currency towards residents (EEFC, RFC, Intrabank FC Deposits), equities of banks held by NRIs, non-debt credit flows on account of ADRs/ GDRs, capital supplied by head offices of foreign banks in India, Rupee and Asian Clearing Union (ACU) Dollar balance in vostro accounts. Table 1 presents a classification of the international liabilities as at the end of December 2009 covered under IBS, in US dollar terms, into items included and not included under external debt statistics.
Table 1: International Liabilities of Banks in India |
(US$ million) |
Categories/Items |
Amount Outstanding as at end |
December 2008 |
September 2009 |
December 2009 |
I. Items included under External Debt Statistics + |
62,904 |
65,309 |
68,447 |
1. Foreign Currency Non-Resident Bank [FCNR(B)] Schemes |
13,418 |
15,879 |
16,673 |
2. Non-Resident External (NRE) Rupee A/cs |
24,410 |
26,096 |
26,864 |
3. Foreign Currency Borrowings (includes Inter-bank borrowings and external commercial borrowings of banks) other than through ADRs, GDRs, Bonds, etc. |
18,105 |
13,913 |
15,552 |
4. Bonds |
1,651 |
1,361 |
909 |
5. Floating Rate Notes (FRNs) |
— |
— |
— |
6. Foreign Institutional Investors’ (FII) A/cs |
1,846 |
2,407 |
2,263 |
7. Other Own issues of Intl. Debt Securities |
0 |
105 |
104 |
8. Non-Resident Ordinary(NRO) Rupee Deposits |
3,475 |
5,548 |
6,081 |
II. Items not included under External Debt Statistics |
45 |
25 |
45 |
1. Embassy A/cs |
45 |
23 |
43 |
2. Escrow A/cs |
— |
3 |
2 |
III. Non-Debt Liabilities (not included in External Debt due
to definitional aspects) |
13,593 |
21,209 |
21,628 |
1. American Depository Receipts(ADRs) and Global
Depository Receipts (GDRs) |
2,935 |
6,452 |
6,115 |
2. Equities of banks held by NRIs |
5,351 |
9,300 |
9,748 |
3. Capital of foreign banks/branches in India and
certain other items in transition |
5,306 |
5,457 |
5,765 |
IV. FC Liabilities to Residents (not included in External
Debt due to definitional aspects) + |
3,789 |
4,932 |
5,179 |
1. Exchange Earners’ Foreign Currency (EEFC) A/cs |
3,102 |
3,981 |
3,815 |
2. Resident Foreign Currency (RFC) Deposits |
223 |
308 |
308 |
3. Inter-Bank Foreign Currency Deposits and
other Foreign Currency Deposits of Residents |
464 |
642 |
1,055 |
V. Other Items of International Liabilities (not included
in External Debt due to definitional aspects) |
370 |
811 |
397 |
1. Balances in vostro A/cs of non-resident banks and
exchange houses (including term deposits) |
401 |
811 |
835 |
VI. Total International Liabilities (I+II+III+IV+V) |
80,736 |
92,286 |
96,134 |
+ Data as reported under IBS do not cover all branches and are not comparable with data reported by all bank branches under a different set of data.
Notes: 1. All figures are inclusive of accrued interest.
2. The FEDAI revaluation rate for Rupee-US Dollar exchange as at end-Dec 2008, Sept 2009, and Dec 2009 were
`48.7100, `48.1050 and `46.5300 per US Dollar, respectively.
3. Data have been revised for previous quarters. |
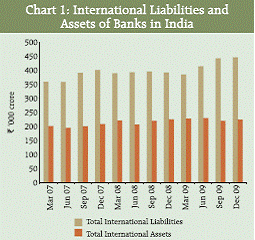
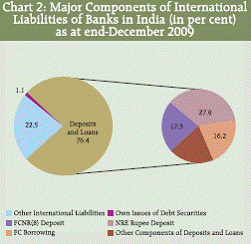
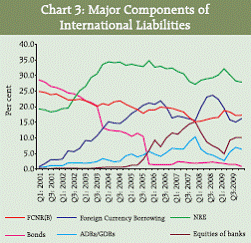
IV. Results IV.1 Locational Banking Statistics The LBS provides component/ instrument wise, country-wise (residence of transacting unit and the country of incorporation of reporting bank), sectorwise, major currency-wise classification of liabilities and assets of banks in India. Data presented in this section are based on data reported by branches of banks, which are conducting business in India, viz., the branches of Indian banks and branches of foreign banks in India. IV.1.A International Liabilities and Assets – Aggregate Level As at end-December 2009, the international assets declined by `872 crore (0.4 per cent) over the position a year ago while those increased over the previous quarter by `3,795 crore (0.8 per cent) (Statement I). The international liabilities recorded an increase of `54,047 crore (13.7 per cent) over the position a year ago and an increase of `3,369 (1.7 per cent) over the previous quarter. International liabilities of the commercial banks are higher than their international assets, as a part of the international liabilities of the commercial banks forms the sources of accretion to the foreign currency assets of the Reserve Bank of India. IV.1.B Components and Composition of International Liabilities For the quarter, the major component ‘Other International Liabilities’ comprising mainly of ADRs/GDRs and equities of banks held by non-residents along with other components, viz., non-resident deposits (FCNR(B), NRE and NRO deposits) under the major component ‘Deposits and Loans’ primarily caused the substantial rise (Statement I) in the international liabilities over the previous year. The investment in the ADRs/GDRs and equities of the banking sector by non-residents grew by 99.0 per cent and 74.0 per cent respectively. The share of the major component ‘Other International Liabilities’ in the total international liabilities increased to 22.5 per cent from 16.8 per cent a year ago (Chart 2 and 3) with a corresponding decline in the share of the major component ‘Deposits and Loans’ to 76.4 per cent from 81.1 per cent during the same period. The share of the foreign currency borrowings, which declined steadily during December 2008 to September 2009, increased as at end- December 2009.
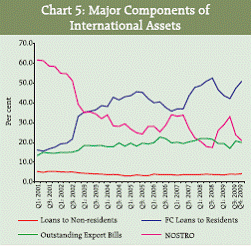
IV.1.C Components and Composition of International Assets At end-December 2009, the substantial decline in the nostro balances of the banks (19.7 per cent) over the previous year resulted in the overall decline in the international assets of the banks during the period (Statement I). The increase in the loans to the non-residents at 12.0 per cent and residents (foreign currency loans) at 8.6 per cent during the year kept the overall decline in the international assets at a low level of 0.4 per cent. The composition of the international assets in terms of the shares by the three major components (viz., ‘Loans and Deposits’, ‘Holdings of Debt Securities’ and ‘Other International Assets’) in the total international assets remained more or less same since December 2008 [Statement I]. The share of the ‘Nostro balances’ had an upward trend until June 2009 quarter, while it declined sharply from 33.0 per cent to 23.8 per cent for September 2009 and further to 21.0 per cent for the December 2009 quarter (Chart 4 and 5). The component ‘foreign currency loans to residents’ continued to be the dominating component of the international assets.
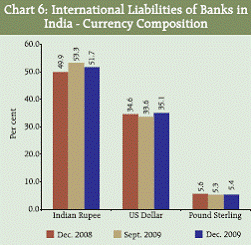
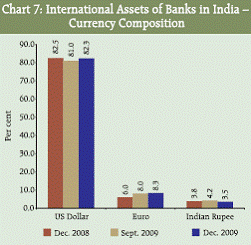
IV.1.D Composition of Liabilities and Assets by Sector and Currency As at end-December 2009, the share of the international liabilities towards the nonbank sector was higher at 75.9 per cent compared to 69.3 per cent a year ago Statement II). As regards the currency composition of the international liabilities, the Indian Rupee continued to be the dominating currency and at end-December 2009, the share of the currency in the international liabilities was higher than the corresponding share a year ago (Chart 6). The share of the liabilities denominated in each currency, except Euro and Japanese Yen, towards non-bank sector recorded an increase over the corresponding share a year ago. The share of non-bank sector in the international assets, at end-December 2009, increased to 67.8 per cent (Statement II) from 62.9 per cent a year ago. The corresponding share was at 65.1 per cent for the previous quarter. In terms of the currency composition of international assets for all sectors, the US Dollar continued to be the major currency with a share of 82.3 per cent, distantly followed by Euro (8.3 per cent). The international assets denominated in Indian Rupee had a share of 3.5 per cent in the total international assets (Chart 7, Statement II). Sector and currency-wise composition of total assets showed that as at end-December 2009, almost all (98.4 per cent) the assets denominated in Indian Rupee are towards non-bank sector. For the international assets denominated in Pound Sterling and US Dollar, the share of the non-bank sector substantially increased as compared to the corresponding share in the previous quarter, while in case of Euro, the share declined substantially during the period.
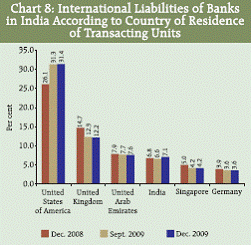
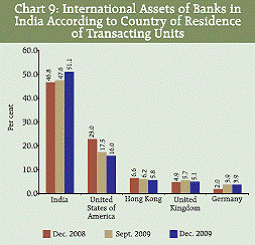
IV.1.E Composition by Country of Residence of Transaction Units Statement III presents the classification of liabilities and assets according to country of residence of transacting unit denominated in domestic as well as foreign currencies. At end-December 2009, the international liabilities towards transacting units (bank and non-bank sectors) from the US had the highest share of 31.4 per cent followed by the UK (12.2 per cent). The share towards transacting units in India was at 7.1 per cent. The country-wise breakup of major components of the international liabilities (Statement IV) revealed that at end-December 2009, the FCNR(B) deposits by the transacting units from the USA, the UK, the UAE and Singapore increased over the previous year while the borrowings from the transacting units from the USA, the UK, Singapore and France registered a decline during the period. For the quarter under reference, of the total international assets of banking sector, 67.1 per cent were concentrated in the two countries, viz., India (51.1 per cent) and the US (16.0 per cent) (Chart 9, Statement III). Among the major components of the international assets, the decline in the nostro balances at end-December 2009 (Statement V), over the previous quarter, was primarily towards the banks from the USA, the UK, France, Belgium and Japan.
Table 2 : International Liabilities and Assets of Banks in India (Branches of Indian and Foreign Banks in India) |
(in ` crore) |
| Items |
Amount Outstanding # as at end |
| |
December 2008 |
Septembe 2009 |
December 2009 |
International Liabilities |
`
Crore+ |
US$
million |
`
Crore+ |
US$
million |
`
Crore+ |
US$
million |
Liabilities to residents and non-residents
denominated in foreign currencies |
1,97,074 |
40,459 |
2,07,204 |
43,073 |
2,15,990 |
46,420 |
(50.1) |
(50.1) |
(46.7) |
(46.7) |
(48.3) |
(48.3) |
Liabilities to non-residents denominated in
Indian Rupees |
1,96,189 |
40,277 |
2,36,737 |
49,213 |
2,31,320 |
49,714 |
(49.9) |
(49.9) |
(53.3) |
(53.3) |
(51.7) |
(51.7) |
Total International Liabilities + |
3,93,263 |
80,736 |
4,43,941 |
92,286 |
4,47,310 |
96,134 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
International Assets |
Foreign Currency(FC) Assets
(includes FC loans to residents and non-residents, Outstanding Export Bills, FC lending to banks in India, FC deposits with banks in India, Overseas FC Assets, Remittable profits of foreign branches of Indian banks, etc.) |
2,17,958
|
44,746
|
2,12,604
|
44,196
|
2,17,695
|
46,786
|
(96.2) |
(96.2) |
(95.8) |
(95.8) |
(96.5) |
(96.5) |
Assets in Indian Rupees with Non-residents
(includes Rupee loans to non-residents
out of non-resident deposits) |
8,572
|
1,760
|
9,259
|
1,925
|
7,963
|
1,711
|
(3.8) |
(3.8) |
(4.2) |
(4.2) |
(3.5) |
(3.5) |
Total International Assets |
2,26,530 |
46,506 |
2,21,863 |
46,121 |
2,25,658 |
48,497 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
+ 1 crore= 10 million. The FEDAI revaluation rate for Rupee-US Dollar exchange as at end-Dec 2008, Sept 2009 and Dec 2009 were `48.7100, `48.1050 and `46.5300 per US Dollar, respectively .
# Data pertain to only reporting branches. As such, these data provide broad dimensions of international assets and liabilities.
Notes: 1. All figures are inclusive of accrued interest.
2. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total international assets.
3. Sum of the components may not tally with total due to rounding off.
4. Data have been revised for previous quarters. |
 |
 |
IV.1.F Composition by Country of Incorporation of Reporting Bank The classification of international liabilities of banks according to their country of incorporation is presented in Statement VI. Among the banks incorporated in countries other than India, at end-December 2009, the US had the highest share in international liabilities at 6.9 per cent while those from Hong Kong and the UK had shares of 6.7 per cent and 4.2 per cent, respectively. The banks incorporated in India accounted for the highest share at 75.5 per cent as against a share of 71.5 per cent a year ago. For the quarter, the share of the banks incorporated in India in the international assets (Statement VI) was higher at 74.5 per cent compared to 70.7 per cent a year ago. Among other countries, the share of the banks incorporated in the UK was highest at 9.9 per cent followed the share of the banks incorporated in the US at 7.2 per cent. IV.2 Consolidated Banking Statistics (CBS) The CBS provides country-wise (immediate country risk exposure), residual maturity-wise and sector-wise classification of international claims (on-balance-sheet) of banks on countries other than India. It also provides consolidated country risk exposure
on an ultimate risk basis and international claims arising out of derivatives, guarantees and credit commitments. There are four reports comprising the consolidated banking statistics on immediate risk basis. The first report is sum of the consolidated banking statistics for (i) domestic banks, (ii) inside (reporting) area foreign banks and (iii) outside (reporting) area foreign banks and the remaining three reports recount the above three components (i), (ii) and (iii), separately. The data presented in this section and Statement VII is based on data reported by all banks functioning in India as well as foreign branches of Indian banks i.e. based on the first combined report and no separate discussion is done on other three reports. IV.2.A Overall Exposure/Claims on Immediate Risk Basis Consolidated international claims of banks, based on immediate risk basis, on countries other than India at end-December 2009, recorded an increase of `6,066 crore (2.8 per cent) to ` 2,25,278 crore over the previous quarter and an increase of `34,160 crore (17.9 per cent) over the position a year ago (Statement VII). IV.2.B Composition by Country of Residence of Transacting Unit – Immediate Risk Consolidated international claims of banks, classified according to country of immediate risk, revealed that at end December 2009, reporting banks’ claims on the US accounted for the largest share (21.7 per cent), followed by the UK (15.9 per cent), Hong Kong (8.3 per cent) and Singapore (8.1 per cent) (Chart 10 and Table 3).
 |
Table 3: Consolidated International Claims of Indian Banks on Countries Other than India on
Immediate Country Risk Basis |
Country |
Amount Outstanding as at end |
December 2008 |
September 2009 |
December 2009 |
`
Crore+ |
US$ million |
`
Crore+ |
US$ million |
`
Crore+ |
US$ million |
Total Consolidated International Claims (excluding claims on India) |
1,91,118 |
39,236 |
2,19,212 |
45,569 |
2,25,278 |
48,416 |
| of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
United States of America # |
43,986 |
9,030
|
48,446
|
10,071
|
48,874
|
10,504
|
(23.0) |
(23.0) |
(22.1) |
(22.1) |
(21.7) |
(21.7) |
United Kingdom@ |
25,246 |
5,183
|
31,622
|
6,574
|
35,919
|
7,720
|
(13.2) |
(13.2) |
(14.4) |
(14.4) |
(15.9) |
(15.9) |
Singapore |
14,454 |
2,967
|
17,546
|
3,647
|
18,350
|
3,944
|
(7.6) |
(7.6) |
(8.0) |
(8.0) |
(8.1) |
(8.1) |
Hong Kong |
14,779
|
3,034
|
19,032
|
3,956
|
18,785
|
4,037
|
(7.7) |
(7.7) |
(8.7) |
(8.7) |
(8.3) |
(8.3) |
United Arab Emirates |
9,660
|
1,983
|
10,605
|
2,205
|
12,645
|
2,718
|
(5.1) |
(5.1) |
(4.8) |
(4.8) |
(5.6) |
(5.6) |
Germany |
9,565
|
1,964
|
11,862
|
2,466
|
11,976
|
2,574
|
(5.0) |
(5.0) |
(5.4) |
(5.4) |
(5.3) |
(5.3) |
+ 1 crore= 10 million. The FEDAI revaluation rate for Rupee-US Dollar exchange as at end-Dec 2008, Sept 2009 and Dec 2009 were ` 48.7100, ` 48.1050 and ` 46.5300 per US Dollar, respectively.
@ Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey. # Includes Midway Island and Wake Islands.
Note: 1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to the total international claims.
2. Data have been revised for previous quarters. |
IV.2.C Composition by Sector – Immediate Risk Basis Sectoral classification of consolidated international claims of banks on other countries, on immediate country risk basis is presented in Statement VII. At end- December 2009, the share of the banking sector in the international claims was marginally higher at 40.5 per cent compared to 39.3 per cent a year ago. A corresponding marginal decline was observed in the share towards the non-bank private sector. Among the countries having shares more than 5 per cent in the total consolidated international claims, the sectoral composition of the consolidated international claims of banks against the USA and Germany depicted a shift towards the banking sector since December 2008, while the sectoral composition for other countries, viz., the UK,Singapore, Hong Kong and the UAE, the composition remained more or less same. IV.2.D Composition by Residual Maturity – Immediate Risk Basis As evidenced by the data as at end- December 2009, the reporting banks continued to prefer short-term lending/ investments over the long-term portfolio. The share of the long-term claims to the total international claims declined marginally to 36.5 per cent against 37.7 per cent a year ago. The details of consolidated international claims of banks according to residual maturity and country of immediate risk are provided in Statement VII. IV.2.E Exposure/Claims on Ultimate Risk Basis Consolidated foreign claims of domestic banks (international claims of Indian banks plus local claims in local currency of foreign offices of Indian banks) on ultimate risk basis, as at end-December 2009, has seen a rise to `1,87,478 crore (3.8 per cent) from `1,80,585 crore a year ago (Table 4). Consolidated foreign claims of Indian banks, for the quarter, against the UK and Hong Kong increased to 15.4 per cent and 7.3 per cent from 9.7 per cent and 4.5 per cent, respectively, as observed a year ago. The shares against other countries, viz., the USA, Singapore and Canada declined during the period. The consolidated claims/exposure of Indian banks, on countries other than India, arising out of derivatives, as at end-December 2009, declined to `16,820 crore from `19,001 crore a year ago. The claims, arising out of guarantees, as at end-December 2009 registered a decline to `42,994 crore from `45,920 crore over the level a year ago. For the reference quarter, the consolidated claims of India, on countries other than India, arising out of credit commitments has witnessed a decline over the position a year
ago, as well as over the previous quarter.
Table 4: Consolidated Foreign Claims and Contingent Claims/Exposures arising from Derivatives,Guarantees and Credit Commitments of Domestic Banks on Ultimate Risk Basis |
(` crore) |
Total Foreign Claims |
Contingent Claims/Exposures Arising from Guarantees |
Country of
Ultimate Risk |
Consolidated Claims |
Country of
Ultimate Risk |
Consolidated Claims |
Dec. 2008 |
Sept. 2009 |
Dec. 2009 |
Dec. 2008 |
Sept. 2009 |
Dec. 2009 |
Total |
1,80,585 |
1,88,205 |
1,87,478 |
Total |
45,920 |
42,127 |
42,994 |
of which: |
|
|
|
of which: |
|
|
|
United States of
America # |
37,941 |
38,911 |
38,002 |
United States of
America # |
8,884 |
6,964 |
8,280 |
(21.0) |
(20.7) |
(20.3) |
(19.3) |
(16.5) |
(19.3) |
United Kingdom @ |
17,537 |
25,190 |
28,939 |
China |
5,156 |
5,652 |
5,833 |
(9.7) |
(13.4) |
(15.4) |
(11.2) |
(13.4) |
(13.6) |
Singapore |
14,725 |
13,351 |
10,435 |
United Arab
Emirates |
3,270 |
3,337 |
3,557 |
(8.2) |
(7.1) |
(5.6) |
(7.1) |
(7.9) |
(8.3) |
Canada |
11,239 |
11,558 |
9,869 |
Singapore |
1,702 |
4,104 |
5,062 |
(6.2) |
(6.1) |
(5.3) |
(3.7) |
(9.7) |
(11.8) |
Hong Kong |
8,098 |
13,217 |
13,601 |
United Kingdom @ |
3,619 |
2,469 |
2,621 |
(4.5) |
(7.0) |
(7.3) |
(7.9) |
(5.9) |
(6.1) |
Contingent Claims/Exposures Arising from Derivatives |
Contingent Claims/Exposures Arising from Credit Commitments |
Country of
Ultimate Risk |
Consolidated Claim |
Country of
Ultimate Risk |
Consolidated Claim |
Dec. 2008 |
Sept. 2009 |
Dec. 2009 |
Dec. 2008 |
Sept. 2009 |
Dec. 2009 |
Total |
19,001 |
15,696 |
16,820 |
Total |
6,737 |
5,126 |
4,155 |
of which: |
|
|
|
of which: |
|
|
|
United Kingdom @ |
4,887 |
3,363 |
3,676 |
Bangladesh |
870 |
1,470 |
1,438 |
(25.7) |
(21.4) |
(21.9) |
(12.9) |
(28.7) |
(34.6) |
United States of
America # |
3,491 |
2,237 |
2,454 |
United States of
America # |
4,113 |
1,419 |
1,058 |
(18.4) |
(14.3) |
(14.6) |
(61.1) |
(27.7) |
(25.5) |
France |
2,284 |
3,121 |
2,630 |
Singapore |
458 |
532 |
422 |
(12.0) |
(19.9) |
(15.6) |
(6.8) |
(27.7) |
(10.2) |
Germany |
1,135 |
646 |
3,086 |
Switzerland |
7 |
304 |
229 |
(6.0) |
(4.1) |
(18.3) |
(0.1) |
(5.9) |
(5.5) |
Singapore |
815 |
662 |
808 |
Sri Lanka |
— |
116 |
200 |
(4.3) |
(4.2) |
(4.8) |
— |
(2.3) |
(4.8) |
@ Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey, # Includes Midway Island and Wake Islands.
Note: Figures in brackets represent percentages to total. |
IV.2.F Comparison of CBS of the Countries Reporting Data to BIS vis-à-vis CBS of India A comparative position of CBS of India and the CBS of BIS reporting countries as at end-December 2009 and end-December 2008 has been presented in various tables (Table 5, 6, 7 and 8) covering three aspects, viz., (i) consolidated international/foreign claims of banks in the BIS reporting countries on all other countries, (ii) consolidated international/foreign claims of banks in the BIS reporting countries on India and (iii) international/foreign claims of Indian banks on countries other than India. The data published by the BIS relate to the consolidated total international/foreign claims of all BIS reporting countries on other countries. Further, the claims of India denote claims of Indian banks’ branches/offices, operating in India and abroad, on countries other than India.
Table 5: International Claims of BIS Reporting Banks vis-à-vis Indian Banks – by Maturity and Sector |
Maturity/sector |
Claims of BIS Reporting Countries on all Other Countries |
Claims of BIS Reporting Countries on India |
Claims of Indian Banks on Countries other than India # |
Dec. 2008 |
Dec. 2009 |
Dec. 2008 |
Dec. 2009 |
Dec. 2008 |
Dec. 2009 |
(a) Total Foreign Claims (b+c) |
30,291.6 |
30,457.1 |
207.0
|
229.9 |
43.6 |
53.1 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(b) Local Claims in Local Currencies |
10,177.5 |
10,535.2 |
73.9 |
80.6 |
4.4 |
4.7 |
(33.6) |
(34.6) |
(35.7) |
(35.1) |
(10.0) |
(8.9) |
(c) Total International Claims |
20,114.1 |
19,921.9 |
133.1
|
149.3
|
39.2
|
48.4 |
(66.4) |
(65.4) |
(64.3) |
(64.9) |
(90.0) |
(91.1) |
of which: |
Maturity |
Short-Term * |
10,023.5 |
9,727.7 |
69.2 |
82.0 |
23.8 |
29.6 |
(49.8) |
(48.8) |
(52.0) |
(55.0) |
(60.7) |
(61.2) |
Long-Term ** |
6,963.4 |
7,120.3 |
48.5 |
46.4 |
14.8 |
17.7 |
(34.6) |
(35.7) |
(36.4) |
(31.1) |
(37.7) |
(36.5) |
Sector$ |
Bank |
8,948.7 |
8,369.6 |
44.6 |
48.0 |
15.4 |
19.6 |
(44.5) |
(42.0) |
(33.5) |
(32.1) |
(39.3) |
(40.5) |
Non-Bank Public |
2,231.2 |
2,704.2 |
6.8 |
5.6 |
0.2 |
0.2 |
(11.1) |
(13.6) |
(5.1) |
(3.7) |
(0.4) |
(0.3) |
Non-Bank Private |
8,684.6 |
8,618.9
|
77.9 |
91.1 |
23.7
|
28.7
|
(43.2) |
(43.3) |
(58.5) |
(61.1) |
(60.3) |
(59.2) |
# : Claims of Indian banks’ branches/offices operating in India and abroad, on countries other than India; these data are taken from the data supplied to the BIS.
* : Claims with a residual maturity of up to and including one year.
** : Claims with a maturity of over one year (excluding unallocated maturity)
$ : Excluding unallocated sector.
Note : Figures in brackets represent percentages to total international claims.
Source : BIS International Consolidated Banking Statistics (www.bis.org) |
Table 6: International Claims of BIS Reporting Banks on all Other Countries – by Country of Incorporation |
(US$ billion) |
Country of Incorporation |
International Claims on all Other Countries |
December 2008 |
December 2009 |
Total International Claims |
15,675.2 |
15,658.5 |
of which : |
|
|
Germany |
2,979.5 |
2,729.6 |
(19.0) |
(17.4) |
Japan |
1,906.2 |
2,044.1 |
(12.2) |
(13.1) |
France |
1,970.1 |
1,948.0 |
(12.6) |
(12.4) |
United States |
871.0 |
1,678.4 |
(5.6) |
(10.7) |
United Kingdom |
1,751.2 |
1,705.6 |
(11.2) |
(10.9) |
Switzerland |
1,073.3 |
933.3 |
(6.8) |
(6.0) |
Netherlands |
934.2 |
828.3 |
(6.0) |
(5.3) |
India # |
37.3 |
48.4 |
(0.2) |
(0.3) |
# Claims of Indian banks’ branches/offices operating in India and abroad, on countries other than India; these data are taken from the data supplied to the BIS.
Note : Figures in brackets represent percentages to total international claims.
Source: BIS International Consolidated Banking Statistics (www.bis.org) |
Table 7: Consolidated Foreign Claims of BIS Reporting Banks on India & Other Countries and
Indian Banks’ Claims on Other Countries: Ultimate Risk Basis |
(US$ billion) |
Claims |
Claims of BIS Reporting
Countries’ Banks on all
Countries including India## |
Claims of BIS Reporting Countries’ Banks on India |
Claims of Indian Banks on Countries Other than India # |
Dec. 2008 |
Dec. 2009 |
Dec. 2008 |
Dec. 2009 |
Dec. 2008 |
Dec. 2009 |
(a) Total Foreign Claims |
24,960.4 |
25,100.0 |
183.3 |
206.0 |
37.1 |
40.3 |
of which: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Sector |
Banks |
6,424.2 |
5,823.7 |
39.5 |
41.2 |
17.3 |
18.2 |
(25.7) |
(23.2) |
(21.6) |
(20.0) |
(46.6) |
(45.3) |
Non-Bank Public |
3,992.3 |
4,684.5 |
16.3 |
28.0 |
0.7 |
0.7 |
(16.0) |
(18.7) |
(8.9) |
(13.6) |
(2.0) |
(1.8) |
Non-Bank Private |
14,296.8 |
14,381.5 |
127.3 |
136.5 |
19.3 |
21.3 |
(57.3) |
(57.3) |
(69.4) |
(66.3) |
(52.0) |
(52.9) |
(b) Other Exposures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Derivatives |
7,153.6 |
3,999.2 |
25.8 |
12.8 |
3.9 |
3.6 |
Guarantees |
6,628.4 |
8,022.2 |
22.9 |
23.7 |
9.4 |
9.2 |
Credit Commitments |
3,990.4 |
3,746.3 |
16.0 |
19.8 |
1.4 |
0.9 |
# Claims of Indian banks’ branches/offices operating in India and abroad, on countries other than India; these data are taken from the data supplied to the BIS.
## Out of thirty countries submitting CBS on immediate risk basis, 24 countries submitted CBS on ultimate risk basis to the BIS.
Note: Figures in brackets represent percentages to total foreign claims.
Source: BIS International Consolidated Banking Statistics (www.bis.org) |
Table 8: International Claims of BIS Reporting Banks on India – by Country of Incorporation |
(US$ billion) |
Country of Incorporation |
International Claims on India |
December 2008 |
December 2009 |
Total International Claims |
108.7 |
118.6 |
of which: |
|
|
United States of America |
18.2 |
30.9 |
(16.7) |
(26.0) |
United Kingdom |
18.9 |
20.6 |
(17.4) |
(17.4) |
Japan |
11.0 |
12.7 |
(10.1) |
(10.7) |
Germany |
15.8 |
11.7 |
(14.5) |
(9.8) |
France |
7.5 |
10.6 |
(6.9) |
(9.0) |
Netherlands |
10.8 |
8.5 |
(10.0) |
(7.1) |
Switzerland |
4.5 |
5.5 |
(4.1) |
(4.7) |
Chinese Taipei |
4.1 |
4.3 |
(3.8) |
(3.6) |
Note: 1. The data on international claims on India of banks incorporated in Canada and Ireland are masked by the BIS.
2. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total international claims.
Source: BIS International Consolidated Banking Statistics (www.bis.org) |
Statement I : International Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified According to Type of Instrument
(Based on LBS Statements) |
(` crore) |
Liability/Asset Category |
International Liabilities |
Amount Outstanding as at end of |
Q4 : 2008 |
Q1: 2009 |
Q2 : 2009 |
Q3 : 2009 |
Q4 : 2009 |
1. Deposits and Loans |
3,18,994 |
3,23,205 |
3,21,689 |
3,34,858 |
3,41,962 |
(81.1) |
(83.6) |
(77.3) |
(75.4) |
(76.4) |
(a) Foreign Currency Non-resident Bank
[FCNR(B)] scheme |
65,357 |
72,783 |
76,341 |
76,388 |
77,580 |
(16.6) |
(18.8) |
(18.3) |
(17.2) |
(17.3) |
(b) Resident Foreign Currency (RFC) A/Cs |
1,084 |
947 |
1,036 |
1,484 |
1,435 |
(0.3) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.3) |
(0.3) |
(c) Exchange Earners Foreign
Currency (EEFC) A/Cs |
15,112 |
15,914 |
15,677 |
19,150 |
17,752 |
(3.8) |
(4.1) |
(3.8) |
(4.3) |
(4.0) |
(d) Other foreign currency deposits (including
Inter-bank Foreign Currency deposits) |
2,261 |
1,648 |
2,424 |
3,089 |
4,911 |
(0.6) |
(0.4) |
(0.6) |
(0.7) |
(1.1) |
(e) Foreign Currency Borrowing (Inter-bank
borrowing in India and from abroad,
external commercial borrowings of banks) |
88,189 |
75,398 |
65,934 |
66,927 |
72,363 |
(22.4) |
(19.5) |
(15.8) |
(15.1) |
(16.2) |
(f) Vostro balances and balances in
exchange houses and in term deposits |
1,954 |
2,012 |
2,112 |
3,899 |
3,886 |
(0.5) |
(0.5) |
(0.5) |
(0.9) |
(0.9) |
(g) Non-Resident External
Rupee (NRE) Accounts |
1,18,899 |
1,24,488 |
1,25,513 |
1,25,536 |
1,25,000 |
(30.2) |
(32.2) |
(30.2) |
(28.3) |
(27.9) |
(h) Non-Resident Ordinary (NRO)
Rupee Accounts |
16,929 |
20,686 |
22,707 |
26,687 |
28,296 |
(4.3) |
(5.4) |
(5.5) |
(6.0) |
(6.3) |
(i) Embassy accounts |
218 |
116 |
110 |
109 |
199 |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(j) Foreign Institutional Investors’
(FII) Accounts |
8,991 |
9,211 |
9,822 |
11,577 |
10,531 |
(2.3) |
(2.4) |
(2.4) |
(2.6) |
(2.4) |
(k) Escrow A/cs |
1 |
1 |
14 |
13 |
11 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
2. Own Issues of International Securities |
8,058 |
6,864 |
6,446 |
7,055 |
4,713 |
(2.0) |
(1.8) |
(1.5) |
(1.6) |
(1.1) |
(a) Bonds |
8,040 |
6,849 |
6,436 |
6,549 |
4,228 |
(2.0) |
(1.8) |
(1.5) |
(1.5) |
(0.9) |
(b) Floating Rate Notes (FRNs) |
19 |
14 |
11 |
— |
— |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
— |
— |
(c) Other Own Issues of International
Debt Securities |
0 |
0 |
— |
506 |
485 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
— |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
3. Other International Liabilities |
66,210 |
56,540 |
87,913 |
1,02,028 |
1,00,634 |
(16.8) |
(14.6) |
(21.1) |
(23.0) |
(22.5) |
(a) ADRs/GDRs |
14,298 |
10,357 |
23,038 |
31,038 |
28,453 |
(3.6) |
(2.7) |
(5.5) |
(7.0) |
(6.4) |
(b) Equities of banks held by non-residents |
26,066 |
18,932 |
38,555 |
44,736 |
45,356 |
(6.6) |
(4.9) |
(9.3) |
(10.1) |
(10.1) |
(c) Capital/remittable profits of foreign banks
in India and other unclassified
international liabilities |
25,846 |
27,251 |
26,321 |
26,253 |
26,825 |
(6.6) |
(7.0) |
(6.3) |
(5.9) |
(6.0) |
Total International Liabilities + |
3,93,263 |
3,86,608 |
4,16,048 |
4,43,941 |
4,47,310 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
Statement I: International Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified According to Type of Instrument
(Based on LBS Statements) (Concld.) |
(` crore) |
Liability/Asset Category |
International Assets |
Amount Outstanding as at end of |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
1. Loans and Deposits |
2,17,310 |
2,19,547 |
2,22,220 |
2,12,481 |
2,16,690 |
(95.9) |
(95.7) |
(96.1) |
(95.8) |
(96.0) |
(a) Loans to Non-residents (includes Rupee
loans and Foreign Currency (FC)
loans out of non-resident deposits) |
8,387 |
8,341 |
9,132 |
8,613 |
9,395 |
(3.7) |
(3.6) |
(4.0) |
(3.9) |
(4.2) |
(b) FC Loans to Residents (incl. loans out
of FCNR(B) deposits, PCFCs, FC lending
to & FC Deposits with banks in India, etc., |
1,05,582 |
99,973 |
97,337 |
1,04,950 |
1,14,619 |
(46.6) |
(43.6) |
(42.1) |
(47.3) |
(50.8) |
(c) Outstanding Export Bills drawn on
non-residents by residents |
44,041 |
44,564 |
39,391 |
45,861 |
45,087 |
(19.4) |
(19.4) |
(17.0) |
(20.7) |
(20.0) |
(d) Foreign Currency/TTs, etc., in hand |
159 |
172 |
161 |
148 |
117 |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(e) Nostro balances including balances in
Term Deposits with non-resident banks
(includes FCNR funds held abroad) |
|
|
|
|
|
59,140 |
66,496 |
76,199 |
52,909 |
47,472 |
(26.1) |
(29.0) |
(33.0) |
(23.8) |
(21.0) |
2. Holdings of Debt Securities |
84 |
76 |
70 |
59 |
59 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(a) Investment in Foreign Government
Securities (including Treasury Bills) |
61 |
54 |
48 |
38 |
38 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(b) Investment in Other Debt Securities |
23 |
22 |
22 |
21 |
20 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
3. Other International Assets |
9,137 |
9,733 |
8,863 |
9,323 |
8,909 |
(4.0) |
(4.2) |
(3.8) |
(4.2) |
(3.9) |
(a) Investments in Equities Abroad |
1,585 |
1,556 |
1,544 |
1,669 |
1,194 |
(0.7) |
(0.7) |
(0.7) |
(0.8) |
(0.5) |
(b) Capital supplied to and receivable profits from foreign branches of Indian banks and other unclassified intl. assets |
7,552 |
8,177 |
7,319 |
7,653 |
7,715 |
(3.3) |
(3.6) |
(3.2) |
(3.4) |
(3.4) |
Total International Assets + |
2,26,530 |
2,29,356 |
2,31,153 |
2,21,863 |
2,25,658 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
+ In view of the incomplete data coverage from all the branches, the data reported under the LBS are not strictly
comparable with those capturing data from all the branches.
‘-’ nil/negligible.
Notes: 1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total international liabilities/assets.
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off.
3. Data have been revised for previous quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended March, June, September and December, respectively. |
Statement II: Currency and Sector-wise Breakup of International Liabilities/Assets of Banks
(Based on LBS Statements) |
(` crore) |
Currency |
International Liabilities |
All Sector |
Non-Bank Sector |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Swiss Franc |
594 |
792 |
814 |
786 |
459 |
59 |
34 |
34 |
114 |
117 |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
Euro |
16,802 |
16,695 |
17,097 |
19,250 |
21,180 |
11,944 |
12,774 |
12,756 |
13,662 |
13,536 |
(4.3) |
(4.3) |
(4.1) |
(4.3) |
(4.7) |
(4.4) |
(4.6) |
(4.0) |
(4.0) |
(4.0) |
Pound Sterling |
21,831 |
22,584 |
25,531 |
23,628 |
23,964 |
17,681 |
18,819 |
21,883 |
19,873 |
20,429 |
(5.6) |
(5.8) |
(6.1) |
(5.3) |
(5.4) |
(6.5) |
(6.8) |
(6.9) |
(5.9) |
(6.0) |
Indian Rupee |
1,96,188 |
2,00,437 |
2,23,491 |
2,36,737 |
2,31,319 |
1,67,458 |
1,70,943 |
1,92,544 |
2,03,887 |
2,03,795 |
(49.9) |
(51.8) |
(53.7) |
(53.3) |
(51.7) |
(61.4) |
(61.6) |
(61.1) |
(60.3) |
(60.0) |
Japanese Yen |
17,451 |
12,541 |
9,060 |
8,592 |
7,869 |
1,178 |
651 |
229 |
70
|
272 |
(4.4) |
(3.2) |
(2.2) |
(1.9) |
(1.8) |
(0.4) |
(0.2) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
Other Foreign Currencies |
4,341 |
5,451 |
6,328 |
5,904 |
5,673 |
983 |
1,337 |
1,693 |
1,413 |
1,788 |
(1.1) |
(1.4) |
(1.5) |
(1.3) |
(1.3) |
(0.4) |
(0.5) |
(0.5) |
(0.4) |
(0.5) |
US Dollar |
1,36,056 |
1,28,109 |
1,33,727 |
1,49,045 |
1,56,846 |
73,307 |
73,005 |
85,952 |
99,254 |
99,609 |
(34.6) |
(33.1) |
(32.1) |
(33.6) |
(35.1) |
(26.9) |
(26.3) |
(27.3) |
(29.3) |
(29.3) |
Total |
3,93,263 |
3,86,608 |
4,16,048 |
4,43,941 |
4,47,310 |
2,72,609 |
2,77,562 |
3,15,090 |
3,38,271 |
3,39,549 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
International Assets |
Swiss Franc |
1,555 |
1,212 |
758 |
527 |
431 |
1,043 |
889 |
282 |
299 |
270 |
(0.7) |
(0.5) |
(0.3) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.7) |
(0.6) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
Euro |
13,650 |
13,999 |
18,553 |
17,703 |
18,690 |
8,776 |
6,634 |
5,857 |
6,675 |
7,219 |
(6.0) |
(6.1) |
(8.0) |
(8.0) |
(8.3) |
(6.2) |
(4.8) |
(4.6) |
(4.6) |
(4.7) |
Pound Sterling |
5,690 |
5,712 |
5,578 |
5,828 |
5,814 |
1,147 |
1,349 |
1,794 |
1,937 |
1,685 |
(2.5) |
(2.5) |
(2.4) |
(2.6) |
(2.6) |
(0.8) |
(1.0) |
(1.4) |
(1.3) |
(1.1) |
Indian Rupee |
8,572 |
7,680 |
8,577 |
9,259 |
7,963 |
8,529 |
7,606 |
8,495 |
9,140 |
7,839 |
(3.8) |
(3.3) |
(3.7) |
(4.2) |
(3.5) |
(6.0) |
(5.5) |
(6.6) |
(6.3) |
(5.1) |
Japanese Yen |
3,049 |
4,156 |
3,974 |
3,650 |
2,023 |
1,753 |
2,999 |
2,358 |
2,860 |
1,037 |
(1.3) |
(1.8) |
(1.7) |
(1.6) |
(0.9) |
(1.2) |
(2.2) |
(1.8) |
(2.0) |
(0.7) |
Other Foreign Currencies |
7,167 |
6,737 |
6,719 |
5,209 |
4,936 |
839 |
1,110 |
1,230 |
1,083 |
812 |
(3.2) |
(2.9) |
(2.9) |
(2.3) |
(2.2) |
(0.6) |
(0.8) |
(1.0) |
(0.7) |
(0.5) |
US Dollar |
1,86,848 |
1,89,860 |
1,86,994 |
1,79,688 |
1,85,801 |
1,20,292 |
1,17,424 |
1,08,523 |
1,22,469 |
1,34,216 |
(82.5) |
(82.8) |
(80.9) |
(81.0) |
(82.3) |
(84.5) |
(85.1) |
(84.4) |
(84.8) |
(87.7) |
Total |
2,26,530 |
2,29,356 |
2,31,153 |
2,21,863 |
2,25,658 |
1,42,378 |
1,38,011 |
1,28,538 |
1,44,463 |
1,53,078 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
‘-’ nil/negligible.
Note: 1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total in the respective group (column).
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off.
3. Data have been revised for previous quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended March, June, September and December, respectively. |
Statement III : International Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified According to Country of
Residence of Transacting Units (Based on LBS Statements) — Amount Outstanding as at end Quarter |
(` crore) |
Country |
International Liabilities |
All Currencies |
Foreign Currencies |
|
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Total |
3,93,263 |
3,86,608 |
4,16,048 |
4,43,941 |
4,47,310 |
1,97,074 |
1,86,171 |
1,92,557 |
2,07,204 |
2,15,990 |
of which |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
Bahrain |
8,059 |
9,260 |
9,157 |
8,535 |
7,876 |
5,874 |
6,446 |
6,324 |
6,320 |
5,510 |
(2.0) |
(2.4) |
(2.2) |
(1.9) |
(1.8) |
(3.0) |
(3.5) |
(3.3) |
(3.1) |
(2.6) |
Canada |
4,079 |
4,847 |
5,727 |
6,142 |
6,013 |
1,598 |
1,493 |
2,055 |
2,445 |
2,272 |
(1.0) |
(1.3) |
(1.4) |
(1.4) |
(1.3) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(1.1) |
(1.2) |
(1.1) |
China |
5,076 |
5,697 |
5,562 |
5,973 |
6,205 |
4,874 |
5,533 |
5,376 |
5,799 |
5,951 |
(1.3) |
(1.5) |
(1.3) |
(1.3) |
(1.4) |
(2.5) |
(3.0) |
(2.8) |
(2.8) |
(2.8) |
France |
6,452 |
6,116 |
6,771 |
8,445 |
9,233 |
4,007 |
2,609 |
2,368 |
3,351 |
3,843 |
(1.6) |
(1.6) |
(1.6) |
(1.9) |
(2.1) |
(2.0) |
(1.4) |
(1.2) |
(1.6) |
(1.8) |
Germany
(includes ECB) |
15,221 |
16,819 |
16,865 |
15,967 |
16,011 |
10,622 |
11,665 |
11,963 |
12,417 |
12,470 |
(3.9) |
(4.4) |
(4.1) |
(3.6) |
(3.6) |
(5.4) |
(6.3) |
(6.2) |
(6.0) |
(5.8) |
Hong Kong |
14,153 |
11,682 |
11,316 |
11,778 |
13,455 |
7,933 |
5,245 |
4,590 |
5,340 |
7,780 |
(3.6) |
(3.0) |
(2.7) |
(2.7) |
(3.0) |
(4.0) |
(2.8) |
(2.4) |
(2.6) |
(3.6) |
India |
26,711 |
24,725 |
24,583 |
29,246 |
31,644 |
26,711 |
24,725 |
24,583 |
29,246 |
31,644 |
(6.8) |
(6.4) |
(5.9) |
(6.6) |
(7.1) |
(13.6) |
(13.3) |
(12.8) |
(14.1) |
(14.7) |
Kuwait |
6,348 |
7,213 |
7,224 |
7,981 |
7,496 |
1,745 |
1,868 |
1,489 |
2,066 |
1,855 |
(1.6) |
(1.9) |
(1.7) |
(1.8) |
(1.7) |
(0.9) |
(1.0) |
(0.8) |
(1.0) |
(0.9) |
Mauritius |
11,565 |
9,970 |
15,256 |
16,671 |
14,878 |
1,745 |
2,143 |
283 |
417 |
290 |
(2.9) |
(2.6) |
(3.7) |
(3.8) |
(3.3) |
(0.9) |
(1.2) |
(0.1) |
(0.2) |
(0.1) |
No Specific
Country (Country
unknown) |
15,329 |
12,626 |
16,621 |
16,003 |
16,261 |
1,629 |
1,550 |
1,820 |
2,100 |
1,611 |
(3.9) |
(3.3) |
(4.0) |
(3.6) |
(3.6) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(0.9) |
(1.0) |
(0.7) |
Saudi Arabia |
11,930 |
11,853 |
13,080 |
10,740 |
10,873 |
1,660 |
1,694 |
1,596 |
1,641 |
1,587 |
(3.0) |
(3.1) |
(3.1) |
(2.4) |
(2.4) |
(0.8) |
(0.9) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(0.7) |
Singapore |
19,789 |
19,753 |
18,745 |
18,540 |
18,711 |
13,865 |
13,932 |
12,480 |
11,934 |
11,939 |
(5.0) |
(5.1) |
(4.5) |
(4.2) |
(4.2) |
(7.0) |
(7.5) |
(6.5) |
(5.8) |
(5.5) |
United Arab
Emirates |
31,018 |
29,417 |
31,818 |
34,219 |
34,174 |
5,503 |
6,406 |
7,022 |
7,124 |
7,025 |
(7.9) |
(7.6) |
(7.6) |
(7.7) |
(7.6) |
(2.8) |
(3.4) |
(3.6) |
(3.4) |
(3.3) |
United Kingdom@ |
57,665 |
50,419 |
51,894 |
54,601 |
54,648 |
36,350 |
33,409 |
33,392 |
36,388 |
35,582 |
(14.7) |
(13.0) |
(12.5) |
(12.3) |
(12.2) |
(18.4) |
(17.9) |
(17.3) |
(17.6) |
(16.5) |
United States # |
1,02,571 |
1,09,933 |
1,23,434 |
1,38,981 |
1,40,619 |
48,174 |
45,955 |
56,818 |
58,531 |
64,355 |
(26.1) |
(28.4) |
(29.7) |
(31.3) |
(31.4) |
(24.4) |
(24.7) |
(29.5) |
(28.2) |
(29.8) |
Statement III : International Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified According to Country of
Residence of Transacting Units (Based on LBS Statements) — Amount Outstanding as at end Quarter (Concld.) |
(` crore) |
Country |
International Assets |
All Currencies |
Foreign Currencies |
|
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Total
of which |
2,26,530 |
2,29,356 |
2,31,153 |
2,21,863 |
2,25,658 |
2,17,958 |
2,21,676 |
2,22,577 |
2,12,604 |
2,17,695 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
Belgium |
1,871 |
2,013 |
2,976 |
2,560 |
1,701 |
1,864 |
2,005 |
2,930 |
2,452 |
1,668 |
(0.8) |
(0.9) |
(1.3) |
(1.2) |
(0.8) |
(0.9) |
(0.9) |
(1.3) |
(1.2) |
(0.8) |
Canada |
1,432 |
1,974 |
1,813 |
1,809 |
1,689 |
1,256 |
1,806 |
1,676 |
1,630 |
1,515 |
(0.6) |
(0.9) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(0.7) |
(0.6) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(0.7) |
China |
1,444 |
1,476 |
1,650 |
2,236 |
1,966 |
1,433 |
1,463 |
1,636 |
2,218 |
1,946 |
(0.6) |
(0.6) |
(0.7) |
(1.0) |
(0.9) |
(0.7) |
(0.7) |
(0.7) |
(1.0) |
(0.9) |
France |
1,640 |
3,168 |
4,432 |
2,570 |
2,531 |
1,627 |
3,119 |
4,378 |
2,517 |
2,517 |
(0.7) |
(1.4) |
(1.9) |
(1.2) |
(1.1) |
(0.7) |
(1.4) |
(2.0) |
(1.2) |
(1.2) |
Germany
(Includes ECB) |
4,517 |
5,779 |
8,274 |
8,588 |
8,904 |
4,442 |
5,675 |
8,176 |
8,466 |
8,783 |
(2.0) |
(2.5) |
(3.6) |
(3.9) |
(3.9) |
(2.0) |
(2.6) |
(3.7) |
(4.0) |
(4.0) |
Hong Kong |
14,915 |
16,176 |
15,223 |
13,801 |
13,172 |
14,841 |
16,107 |
15,010 |
13,581 |
13,027 |
(6.6) |
(7.1) |
(6.6) |
(6.2) |
(5.8) |
(6.8) |
(7.3) |
(6.7) |
(6.4) |
(6.0) |
India |
1,06,062 |
1,00,480 |
97,894 |
1,05,498 |
1,15,216 |
1,06,062 |
1,00,480 |
97,894 |
1,05,498 |
1,15,216 |
(46.8) |
(43.8) |
(42.4) |
(47.6) |
(51.1) |
(48.7) |
(45.3) |
(44.0) |
(49.6) |
(52.9) |
Italy |
1,234 |
1,397 |
1,092 |
1,225 |
1,271 |
1,224 |
1,389 |
1,081 |
1,218 |
1,262 |
(0.5) |
(0.6) |
(0.5) |
(0.6) |
(0.6) |
(0.6) |
(0.6) |
(0.5) |
(0.6) |
(0.6) |
Japan |
1,862 |
2,793 |
2,961 |
1,977 |
1,284 |
1,834 |
2,766 |
2,930 |
1,948 |
1,257 |
(0.8) |
(1.2) |
(1.3) |
(0.9) |
(0.6) |
(0.8) |
(1.2) |
(1.3) |
(0.9) |
(0.6) |
Netherlands |
651 |
1,111 |
1,472 |
1,559 |
1,297 |
644 |
1,104 |
1,452 |
1,537 |
1,283 |
(0.3) |
(0.5) |
(0.6) |
(0.7) |
(0.6) |
(0.3) |
(0.5) |
(0.7) |
(0.7) |
(0.6) |
No Specific
Country (Country
unknown) |
1,127 |
962 |
1,566 |
1,702 |
1,651 |
433 |
316 |
728 |
501 |
526 |
(0.5) |
(0.4) |
(0.7) |
(0.8) |
(0.7) |
(0.2) |
(0.1) |
(0.3) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
Singapore |
4,179 |
3,800 |
4,567 |
4,266 |
4,029 |
3,861 |
3,517 |
4,263 |
3,979 |
3,771 |
(1.8) |
(1.7) |
(2.0) |
(1.9) |
(1.8) |
(1.8) |
(1.6) |
(1.9) |
(1.9) |
(1.7) |
United Arab
Emirates |
5,024 |
5,225 |
5,827 |
6,113 |
6,324 |
4,219 |
4,440 |
4,714 |
4,683 |
5,158 |
(2.2) |
(2.3) |
(2.5) |
(2.8) |
(2.8) |
(1.9) |
(2.0) |
(2.1) |
(2.2) |
(2.4) |
United Kingdom@ |
11,190 |
14,430 |
15,821 |
12,542 |
11,563 |
10,536 |
13,806 |
15,170 |
11,780 |
10,892 |
(4.9) |
(6.3) |
(6.8) |
(5.7) |
(5.1) |
(4.8) |
(6.2) |
(6.8) |
(5.5) |
(5.0) |
United States # |
52,053 |
52,685 |
48,258 |
38,843 |
36,157 |
48,521 |
48,781 |
44,531 |
35,591 |
33,075 |
(23.0) |
(23.0) |
(20.9) |
(17.5) |
(16.0) |
(22.3) |
(22.0) |
(20.0) |
(16.7) |
(15.2) |
@ Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey. # Includes Midway Island and Wake Islands.
Note: 1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total in the respective group (column).
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off .
3. “No Specific Country” means the country information has not been provided by the reporting bank branches.
4. Data have been revised for previous quarters
5. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended March, June, September and December, respectively. |
Statement IV : Country-wise Breakup of Major Components of International Liabilities of Banks
(Based on LBS Statements) |
(` crore) |
Country |
Major
Components |
Q4: 2008 |
Q1: 2009 |
Q2: 2009 |
Q3: 2009 |
Q4: 2009 |
Australia |
FCNR(B) |
289 |
(0.4) |
552 |
(0.8) |
596 |
(0.8) |
417 |
(0.5) |
439 |
(0.6) |
Borrowings |
144 |
(0.2) |
443 |
(0.6) |
507 |
(0.8) |
212 |
(0.3) |
90 |
(0.1) |
NRE Deposits |
710 |
(0.6) |
781 |
(0.6) |
799 |
(0.6) |
775 |
(0.6) |
827 |
(0.7) |
Total |
1,637 |
(0.4) |
2,294 |
(0.6) |
2,637 |
(0.6) |
2,430 |
(0.5) |
2,537 |
(0.6) |
Bahrain |
FCNR(B) |
5,579 |
(8.5) |
6,273 |
(8.6) |
6,147 |
(8.1) |
6,139 |
(8.0) |
5,434 |
(7.0) |
Borrowings |
220 |
(0.2) |
100 |
(0.1) |
117 |
(0.2) |
116 |
(0.2) |
19 |
(0.0) |
NRE Deposits |
1,721 |
(1.4) |
2,241 |
(1.8) |
2,359 |
(1.9) |
1,800 |
(1.4) |
1,899 |
(1.5) |
Total |
8,059 |
(2.0) |
9,260 |
(2.4) |
9,157 |
(2.2) |
8,535 |
(1.9) |
7,876 |
(1.8) |
Belgium |
FCNR(B) |
89 |
(0.1) |
105 |
(0.1) |
71 |
(0.1) |
80 |
(0.1) |
691 |
(0.9) |
Borrowings |
3,036 |
(3.4) |
1,179 |
(1.6) |
1,201 |
(1.8) |
1,182 |
(1.8) |
456 |
(0.6) |
NRE Deposits |
168 |
(0.1) |
246 |
(0.2) |
246 |
(0.2) |
217 |
(0.2) |
207 |
(0.2) |
Total |
3,588 |
(0.9) |
1,822 |
(0.5) |
1,846 |
(0.4) |
1,820 |
(0.4) |
1,671 |
(0.4) |
Canada |
FCNR(B) |
974 |
(1.5) |
950 |
(1.3) |
897 |
(1.2) |
1,109 |
(1.5) |
1,208 |
(1.6) |
Borrowings |
441 |
(0.5) |
306 |
(0.4) |
463 |
(0.7) |
615 |
(0.9) |
440 |
(0.6) |
NRE Deposits |
1,171 |
(1.0) |
1,753 |
(1.4) |
1,851 |
(1.5) |
1,680 |
(1.3) |
1,696 |
(1.4) |
Total |
4,079 |
(1.0) |
4,847 |
(1.3) |
5,727 |
(1.4) |
6,142 |
(1.4) |
6,013 |
(1.3) |
China |
FCNR(B) |
4,874 |
(7.5) |
5,506 |
(7.6) |
5,359 |
(7.0) |
5,374 |
(7.0) |
5,625 |
(7.3) |
Borrowings |
— |
— |
25 |
(0.0) |
— |
— |
298 |
(0.4) |
223 |
(0.3) |
NRE Deposits |
113 |
(0.1) |
120 |
(0.1) |
129 |
(0.1) |
112 |
(0.1) |
157 |
(0.1) |
Total |
5,076 |
(1.3) |
5,697 |
(1.5) |
5,562 |
(1.3) |
5,973 |
(1.3) |
6,205 |
(1.4) |
France |
FCNR(B) |
203 |
(0.3) |
265 |
(0.4) |
238 |
(0.3) |
277 |
(0.4) |
285 |
(0.4) |
Borrowings |
3,340 |
(3.8) |
2,078 |
(2.8) |
1,803 |
(2.7) |
2,203 |
(3.3) |
2,653 |
(3.7) |
NRE Deposits |
344 |
(0.3) |
416 |
(0.3) |
385 |
(0.3) |
439 |
(0.3) |
597 |
(0.5) |
Total |
6,452 |
(1.6) |
6,116 |
(1.6) |
6,771 |
(1.6) |
8,445 |
(1.9) |
9,233 |
(2.1) |
Germany
(Includes ECB) |
FCNR(B) |
7,000 |
(10.7) |
7,651 |
(10.5) |
7,428 |
(9.7) |
7,463 |
(9.8) |
6,379 |
(8.2) |
Borrowings |
3,283 |
(3.7) |
3,675 |
(4.9) |
3,958 |
(6.0) |
4,094 |
(6.1) |
5,229 |
(7.2) |
NRE Deposits |
1,055 |
(0.9) |
1,865 |
(1.5) |
1,873 |
(1.5) |
880 |
(0.7) |
906 |
(0.7) |
Total |
15,221 |
(3.9) |
16,819 |
(4.4) |
16,865 |
(4.1) |
15,967 |
(3.6) |
16,011 |
(3.6) |
Hong Kong |
FCNR(B) |
904 |
(1.4) |
886 |
(1.2) |
1,271 |
(1.7) |
1,055 |
(1.4) |
907 |
(1.2) |
Borrowings |
3,817 |
(4.3) |
2,683 |
(3.6) |
1,358 |
(2.1) |
2,113 |
(3.2) |
2,370 |
(3.3) |
NRE Deposits |
1,203 |
(1.0) |
1,315 |
(1.1) |
1,395 |
(1.1) |
939 |
(0.7) |
3,380 |
(2.7) |
Total |
14,153 |
(3.6) |
11,682 |
(3.0) |
11,316 |
(2.7) |
11,778 |
(2.7) |
13,455 |
(3.0) |
India |
FCNR(B) |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
Borrowings |
8,944 |
(10.1) |
7,486 |
(9.9) |
7,134 |
(10.8) |
7,805 |
(11.7) |
9,332 |
(12.9) |
NRE Deposits |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
Total |
26,711 |
(6.8) |
24,725 |
(6.4) |
24,583 |
(5.9) |
29,246 |
(6.6) |
31,644 |
(7.1) |
Japan |
FCNR(B) |
370 |
(0.6) |
259 |
(0.4) |
498 |
(0.7) |
450 |
(0.6) |
498 |
(0.6) |
Borrowings |
1,521 |
(1.7) |
1,419 |
(1.9) |
1,371 |
(2.1) |
1,407 |
(2.1) |
1,449 |
(2.0) |
NRE Deposits |
587 |
(0.5) |
671 |
(0.5) |
751 |
(0.6) |
625 |
(0.5) |
675 |
(0.5) |
Total |
4,481 |
(1.1) |
4,361 |
(1.1) |
5,112 |
(1.2) |
5,077 |
(1.1) |
5,618 |
(1.3) |
Kenya |
FCNR(B) |
916 |
(1.4) |
848 |
(1.2) |
819 |
(1.1) |
712 |
(0.9) |
703 |
(0.9) |
Borrowings |
43 |
(0.0) |
56 |
(0.1) |
53 |
(0.1) |
53 |
(0.1) |
98 |
(0.1) |
NRE Deposits |
950 |
(0.8) |
1,167 |
(0.9) |
1,136 |
(0.9) |
1,104 |
(0.9) |
1,140 |
(0.9) |
Total |
1,999 |
(0.5) |
2,387 |
(0.6) |
2,329 |
(0.6) |
2,159 |
(0.5) |
2,229 |
(0.5) |
Kuwait |
FCNR(B) |
1,692 |
(2.6) |
1,712 |
(2.4) |
1,448 |
(1.9) |
2,008 |
(2.6) |
1,222 |
(1.6) |
Borrowings |
2 |
(0.0) |
109 |
(0.1) |
— |
(0.0) |
5 |
(0.0) |
2 |
(0.0) |
NRE Deposits |
4,101 |
(3.4) |
4,588 |
(3.7) |
5,177 |
(4.1) |
4,990 |
(4.0) |
4,980 |
(4.0) |
Total |
6,348 |
(1.6) |
7,213 |
(1.9) |
7,224 |
(1.7) |
7,981 |
(1.8) |
7,496 |
(1.7) |
Luxembourg |
FCNR(B) |
5 |
(0.0) |
21 |
(0.0) |
21 |
(0.0) |
7 |
(0.0) |
7 |
(0.0) |
Borrowings |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
NRE Deposits |
4 |
(0.0) |
4 |
(0.0) |
4 |
(0.0) |
5 |
(0.0) |
6 |
(0.0) |
Total |
1,138 |
(0.3) |
1,528 |
(0.4) |
2,871 |
(0.7) |
2,810 |
(0.6) |
1,720 |
(0.4) |
Mauritius |
FCNR(B) |
15 |
(0.0) |
35 |
(0.0) |
32 |
(0.0) |
31 |
(0.0) |
32 |
(0.0) |
Borrowings |
1,624 |
(1.8) |
2,028 |
(2.7) |
129 |
(0.2) |
108 |
(0.2) |
153 |
(0.2) |
NRE Deposits |
31 |
(0.0) |
237 |
(0.2) |
169 |
(0.1) |
63 |
(0.1) |
58 |
(0.0) |
Total |
11,565 |
(2.9) |
9,970 |
(2.6) |
15,256 |
(3.7) |
16,671 |
(3.8) |
14,878 |
(3.3) |
Statement IV: Country-wise Breakup of Major Components of International Liabilities of Banks
(Based on LBS Statements) (Concld.) |
(` crore) |
Country |
Major
Components |
Q4: 2008 |
Q1: 2009 |
Q2: 2009 |
Q3: 2009 |
Q4: 2009 |
Netherlands |
FCNR(B) |
175 |
(0.3) |
175 |
(0.2) |
185 |
(0.2) |
186 |
(0.2) |
198 |
(0.3) |
Borrowings |
4,496 |
(5.1) |
2,319 |
(3.1) |
117 |
(0.2) |
1,388 |
(2.1) |
954 |
(1.3) |
NRE Deposits |
164 |
(0.1) |
269 |
(0.2) |
234 |
(0.2) |
364 |
(0.3) |
304 |
(0.2) |
Total |
9,989 |
(2.5) |
6,851 |
(1.8) |
3,925 |
(0.9) |
5,186 |
(1.2) |
5,271 |
(1.2) |
No Specific Country
(Country unknown) |
FCNR(B) |
1,291 |
(2.0) |
1,230 |
(1.7) |
1,252 |
(1.6) |
1,226 |
(1.6) |
843 |
(1.1) |
Borrowings |
— |
— |
— |
— |
3 |
(0.0) |
2 |
(0.0) |
2 |
(0.0) |
NRE Deposits |
5,519 |
(4.6) |
6,005 |
(4.8) |
6,139 |
(4.9) |
4,340 |
(3.5) |
3,782 |
(3.0) |
Total |
15,329 |
(3.9) |
12,626 |
(3.3) |
16,621 |
(4.0) |
16,003 |
(3.6) |
16,261 |
(3.6) |
Oman |
FCNR(B) |
638 |
(1.0) |
658 |
(0.9) |
630 |
(0.8) |
611 |
(0.8) |
578 |
(0.7) |
Borrowings |
15 |
(0.0) |
26 |
(0.0) |
19 |
(0.0) |
31 |
(0.0) |
20 |
(0.0) |
NRE Deposits |
3,999 |
(3.4) |
3,783 |
(3.0) |
3,896 |
(3.1) |
3,676 |
(2.9) |
3,386 |
(2.7) |
Total |
5,059 |
(1.3) |
4,927 |
(1.3) |
5,174 |
(1.2) |
4,935 |
(1.1) |
4,657 |
(1.0) |
Qatar |
FCNR(B) |
377 |
(0.6) |
362 |
(0.5) |
406 |
(0.5) |
425 |
(0.6) |
396 |
(0.5) |
Borrowings |
— |
(0.0) |
— |
(0.0) |
— |
(0.0) |
2 |
(0.0) |
2 |
(0.0) |
NRE Deposits |
2,267 |
(1.9) |
2,572 |
(2.1) |
2,839 |
(2.3) |
2,674 |
(2.1) |
2,511 |
(2.0) |
Total |
2,979 |
(0.8) |
3,588 |
(0.9) |
3,902 |
(0.9) |
3,688 |
(0.8) |
3,464 |
(0.8) |
Saudi Arabia |
FCNR(B) |
1,638 |
(2.5) |
1,573 |
(2.2) |
1,474 |
(1.9) |
1,531 |
(2.0) |
1,385 |
(1.8) |
Borrowings |
3 |
(0.0) |
103 |
(0.1) |
108 |
(0.2) |
94 |
(0.1) |
194 |
(0.3) |
NRE Deposits |
9,555 |
(8.0) |
9,376 |
(7.5) |
10,165 |
(8.1) |
8,138 |
(6.5) |
8,124 |
(6.5) |
Total |
11,930 |
(3.0) |
11,853 |
(3.1) |
13,080 |
(3.1) |
10,740 |
(2.4) |
10,873 |
(2.4) |
Singapore |
FCNR(B) |
626 |
(1.0) |
739 |
(1.0) |
1,217 |
(1.6) |
2,338 |
(3.1) |
2,229 |
(2.9) |
Borrowings |
11,821 |
(13.4) |
12,085 |
(16.0) |
10,326 |
(15.7) |
8,487 |
(12.7) |
9,252 |
(12.8) |
NRE Deposits |
2,199 |
(1.8) |
2,398 |
(1.9) |
2,548 |
(2.0) |
2,324 |
(1.9) |
2,350 |
(1.9) |
Total |
19,789 |
(5.0) |
19,753 |
(5.1) |
18,745 |
(4.5) |
18,540 |
(4.2) |
18,711 |
(4.2) |
Switzerland
(Includes BIS) |
FCNR(B) |
145 |
(0.2) |
350 |
(0.5) |
121 |
(0.2) |
127 |
(0.2) |
144 |
(0.2) |
Borrowings |
523 |
(0.6) |
724 |
(1.0) |
779 |
(1.2) |
672 |
(1.0) |
339 |
(0.5) |
NRE Deposits |
396 |
(0.3) |
420 |
(0.3) |
493 |
(0.4) |
372 |
(0.3) |
364 |
(0.3) |
Total |
1,570 |
(0.4) |
2,230 |
(0.6) |
2,032 |
(0.5) |
2,620 |
(0.6) |
2,202 |
(0.5) |
United Arab
Emirates |
FCNR(B) |
5,358 |
(8.2) |
5,853 |
(8.0) |
6,772 |
(8.9) |
6,621 |
(8.7) |
6,692 |
(8.6) |
Borrowings |
2 |
(0.0) |
397 |
(0.5) |
96 |
(0.1) |
208 |
(0.3) |
108 |
(0.1) |
NRE Deposits |
22,007 |
(18.5) |
18,799 |
(15.1) |
19,943 |
(15.9) |
20,486 |
(16.3) |
20,111 |
(16.1) |
Total |
31,018 |
(7.9) |
29,417 |
(7.6) |
31,818 |
(7.6) |
34,219 |
(7.7) |
34,174 |
(7.6) |
United Kingdom @ |
FCNR(B) |
14,766 |
(22.6) |
16,396 |
(22.5) |
18,000 |
(23.6) |
17,884 |
(23.4) |
17,267 |
(22.3) |
Borrowings |
19,663 |
(22.3) |
15,739 |
(20.9) |
13,462 |
(20.4) |
15,399 |
(23.0) |
15,226 |
(21.0) |
NRE Deposits |
12,920 |
(10.9) |
8,691 |
(7.0) |
9,066 |
(7.2) |
8,087 |
(6.4) |
8,850 |
(7.1) |
Total |
57,665 |
(14.7) |
50,419 |
(13.0) |
51,894 |
(12.5) |
54,601 |
(12.3) |
54,648 |
(12.2) |
United States # |
FCNR(B) |
10,733 |
(16.4) |
14,494 |
(19.9) |
15,026 |
(19.7) |
14,041 |
(18.4) |
17,419 |
(22.5) |
Borrowings |
21,742 |
(24.7) |
18,587 |
(24.7) |
19,310 |
(29.3) |
16,843 |
(25.2) |
21,009 |
(29.0) |
NRE Deposits |
38,221 |
(32.1) |
45,797 |
(36.8) |
43,052 |
(34.3) |
50,939 |
(40.6) |
47,576 |
(38.1) |
Total |
1,02,571 |
(26.1) |
1,09,933 |
(28.4) |
1,23,434 |
(29.7) |
1,38,981 |
(31.3) |
1,40,619 |
(31.4) |
Total |
FCNR(B) |
65,357 |
(100.0) |
72,783 |
(100.0) |
76,341 |
(100.0) |
76,388 |
(100.0) |
77,580 |
(100.0) |
Borrowings |
88,189 |
(100.0) |
75,398 |
(100.0) |
65,934 |
(100.0) |
66,927 |
(100.0) |
72,363 |
(100.0) |
NRE Deposits |
1,18,899 |
(100.0) |
1,24,488 |
(100.0) |
1,25,513 |
(100.0) |
1,25,536 |
(100.0) |
1,25,000 |
(100.0) |
Total |
3,93,263 |
(100.0) |
3,86,608 |
(100.0) |
4,16,048 |
(100.0) |
4,43,941 |
(100.0) |
4,47,310 |
(100.0) |
@ Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey. # includes Midway Island and Wake Islands. ‘–’ : nil/negligible.
Notes: 1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total.
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off .
3. Data have been revised for previous quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended March, June, September and December, respectively. |
Statement V : Country-wise Breakup of Major Components of International Assets of Banks
(Based on LBS Statements) |
(` crore) |
Country |
Major
Components |
Q4: 2008 |
Q1: 2009 |
Q2: 2009 |
Q3: 2009 |
Q4: 2009 |
Australia |
Export Bill |
203 |
(0.5) |
203 |
(0.5) |
343 |
(0.9) |
445 |
(1.0) |
432 |
(1.0) |
Nostro |
504 |
(0.9) |
684 |
(1.0) |
594 |
(0.8) |
349 |
(0.7) |
254 |
(0.5) |
Total |
768 |
(0.3) |
947 |
(0.4) |
1,007 |
(0.4) |
867 |
(0.4) |
753 |
(0.3) |
Bahrain |
Export Bill |
55 |
(0.1) |
191 |
(0.4) |
158 |
(0.4) |
226 |
(0.5) |
169 |
(0.4) |
Nostro |
668 |
(1.1) |
923 |
(1.4) |
876 |
(1.1) |
403 |
(0.8) |
264 |
(0.6) |
Total |
1,123 |
(0.5) |
1,508 |
(0.7) |
1,414 |
(0.6) |
1,003 |
(0.5) |
1,009 |
(0.4) |
Belgium |
Export Bill |
1,268 |
(2.9) |
1,228 |
(2.8) |
922 |
(2.3) |
941 |
(2.1) |
838 |
(1.9) |
Nostro |
332 |
(0.6) |
518 |
(0.8) |
1,804 |
(2.4) |
1,092 |
(2.1) |
452 |
(1.0) |
Total |
1,871 |
(0.8) |
2,013 |
(0.9) |
2,976 |
(1.3) |
2,560 |
(1.2) |
1,701 |
(0.8) |
Canada |
Export Bill |
382 |
(0.9) |
315 |
(0.7) |
293 |
(0.7) |
379 |
(0.8) |
377 |
(0.8) |
Nostro |
537 |
(0.9) |
514 |
(0.8) |
402 |
(0.5) |
266 |
(0.5) |
269 |
(0.6) |
Total |
1,432 |
(0.6) |
1,974 |
(0.9) |
1,813 |
(0.8) |
1,809 |
(0.8) |
1,689 |
(0.7) |
China |
Export Bill |
761 |
(1.7) |
749 |
(1.7) |
826 |
(2.1) |
1,555 |
(3.4) |
1,048 |
(2.3) |
Nostro |
— |
(0.0) |
— |
(0.0) |
— |
(0.0) |
— |
(0.0) |
2 |
(0.0) |
Total |
1,444 |
(0.6) |
1,476 |
(0.6) |
1,650 |
(0.7) |
2,236 |
(1.0) |
1,966 |
(0.9) |
France |
Export Bill |
1,010 |
(2.3) |
874 |
(2.0) |
719 |
(1.8) |
789 |
(1.7) |
950 |
(2.1) |
Nostro |
472 |
(0.8) |
2,128 |
(3.2) |
3,486 |
(4.6) |
1,621 |
(3.1) |
1,429 |
(3.0) |
Total |
1,640 |
(0.7) |
3,168 |
(1.4) |
4,432 |
(1.9) |
2,570 |
(1.2) |
2,531 |
(1.1) |
Germany
(Includes ECB) |
Export Bill |
1,269 |
(2.9) |
1,360 |
(3.1) |
993 |
(2.5) |
1,429 |
(3.1) |
1,668 |
(3.7) |
Nostro |
2,614 |
(4.4) |
3,757 |
(5.6) |
6,662 |
(8.7) |
6,565 |
(12.4) |
6,661 |
(14.0) |
Total |
4,517 |
(2.0) |
5,779 |
(2.5) |
8,274 |
(3.6) |
8,588 |
(3.9) |
8,904 |
(3.9) |
Hong Kong |
Export Bill |
3,478 |
(7.9) |
4,392 |
(9.9) |
4,762 |
(12.1) |
4,817 |
(10.5) |
4,105 |
(9.1) |
Nostro |
10,262 |
(17.4) |
10,545 |
(15.9) |
9,128 |
(12.0) |
7,844 |
(14.8) |
7,423 |
(15.6) |
Total |
14,915 |
(6.6) |
16,176 |
(7.1) |
15,223 |
(6.6) |
13,801 |
(6.2) |
13,172 |
(5.8) |
India |
Export Bill |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
Nostro |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
— |
Total |
1,06,062 |
(46.8) |
1,00,480 |
(43.8) |
97,894 |
(42.4) |
1,05,498 |
(47.6) |
1,15,216 |
(51.1) |
Italy |
Export Bill |
1,128 |
(2.6) |
1,291 |
(2.9) |
943 |
(2.4) |
1,097 |
(2.4) |
1,146 |
(2.5) |
Nostro |
68 |
(0.1) |
69 |
(0.1) |
110 |
(0.1) |
94 |
(0.2) |
90 |
(0.2) |
Total |
1,234 |
(0.5) |
1,397 |
(0.6) |
1,092 |
(0.5) |
1,225 |
(0.6) |
1,271 |
(0.6) |
Japan |
Export Bill |
443 |
(1.0) |
1,547 |
(3.5) |
1,191 |
(3.0) |
1,059 |
(2.3) |
474 |
(1.1) |
Nostro |
1,087 |
(1.8) |
941 |
(1.4) |
1,439 |
(1.9) |
614 |
(1.2) |
512 |
(1.1) |
Total |
1,862 |
(0.8) |
2,793 |
(1.2) |
2,961 |
(1.3) |
1,977 |
(0.9) |
1,284 |
(0.6) |
Netherlands |
Export Bill |
581 |
(1.3) |
573 |
(1.3) |
355 |
(0.9) |
633 |
(1.4) |
516 |
(1.1) |
Nostro |
52 |
(0.1) |
524 |
(0.8) |
1,063 |
(1.4) |
908 |
(1.7) |
725 |
(1.5) |
Total |
651 |
(0.3) |
1,111 |
(0.5) |
1,472 |
(0.6) |
1,559 |
(0.7) |
1,297 |
(0.6) |
Statement V : Country-wise Breakup of Major Components of International Assets of Banks
(Based on LBS Statements) (Concld.) |
(` crore) |
Country |
Major
Components |
Q4: 2008 |
Q1: 2009 |
Q2: 2009 |
Q3: 2009 |
Q4: 2009 |
No Specific
Country (Country
unknown) |
Export Bill |
330 |
(0.7) |
315 |
(0.7) |
263 |
(0.7) |
422 |
(0.9) |
408 |
(0.9) |
Nostro |
— |
— |
— |
— |
199 |
(0.3) |
— |
— |
— |
(0.0) |
Total |
1,127 |
(0.5) |
962 |
(0.4) |
1,566 |
(0.7) |
1,702 |
(0.8) |
1,651 |
(0.7) |
Singapore |
Export Bill |
1,118 |
(2.5) |
1,080 |
(2.4) |
1,092 |
(2.8) |
1,529 |
(3.3) |
1,529 |
(3.4) |
Nostro |
1,672 |
(2.8) |
1,682 |
(2.5) |
2,392 |
(3.1) |
1,255 |
(2.4) |
1,319 |
(2.8) |
Total |
4,179 |
(1.8) |
3,800 |
(1.7) |
4,567 |
(2.0) |
4,266 |
(1.9) |
4,029 |
(1.8) |
United Arab
Emirates |
Export Bill |
3,412 |
(7.7) |
3,403 |
(7.6) |
4,040 |
(10.3) |
4,356 |
(9.5) |
3,942 |
(8.7) |
Nostro |
109 |
(0.2) |
410 |
(0.6) |
423 |
(0.6) |
469 |
(0.9) |
943 |
(2.0) |
Total |
5,024 |
(2.2) |
5,225 |
(2.3) |
5,827 |
(2.5) |
6,113 |
(2.8) |
6,324 |
(2.8) |
United Kingdom@ |
Export Bill |
2,002 |
(4.5) |
2,171 |
(4.9) |
2,128 |
(5.4) |
2,509 |
(5.5) |
2,455 |
(5.4) |
Nostro |
6,938 |
(11.7) |
9,469 |
(14.2) |
11,643 |
(15.3) |
8,153 |
(15.4) |
7,480 |
(15.8) |
Total |
11,190 |
(4.9) |
14,430 |
(6.3) |
15,821 |
(6.8) |
12,542 |
(5.7) |
11,563 |
(5.1) |
United States # |
Export Bill |
16,637 |
(37.8) |
16,395 |
(36.8) |
12,219 |
(31.0) |
13,868 |
(30.2) |
14,405 |
(31.9) |
Nostro |
31,691 |
(53.6) |
32,360 |
(48.7) |
32,333 |
(42.4) |
21,637 |
(40.9) |
17,996 |
(37.9) |
Total |
52,053 |
(23.0) |
52,685 |
(23.0) |
48,258 |
(20.9) |
38,843 |
(17.5) |
36,157 |
(16.0) |
Total |
Export Bill |
44,041 |
(100.0) |
44,564 |
(100.0) |
39,391 |
(100.0) |
45,861 |
(100.0) |
45,087 |
(100.0) |
Nostro |
59,140 |
(100.0) |
66,496 |
(100.0) |
76,199 |
(100.0) |
52,909 |
(100.0) |
47,472 |
(100.0) |
Total |
2,26,530 |
(100.0) |
2,29,356 |
(100.0) |
2,31,153 |
(100.0) |
2,21,863 |
(100.0) |
2,25,658 |
(100.0) |
@ excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey. # includes Midway Island and Wake Islands. ‘—’ nil/negligible.
Notes: 1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total.
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off .
3. Data have been revised for previous quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended March, June, September and December, respectively. |
Statement VI : International Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified According to Country of Incorporation of Banks (Based on LBS Statements) — Amount Outstanding as at end Quarter |
(` crore) |
Country |
International Liabilities |
Total: All Sectors |
Position vis-a-vis Banks |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Bahrain |
301 |
341 |
286 |
302 |
339 |
59 |
59 |
59 |
59 |
62 |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Bangladesh |
52 |
74 |
88 |
83 |
54 |
49 |
71 |
87 |
81 |
53 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
Belgium |
1,023 |
887 |
720 |
639 |
595 |
968 |
816 |
666 |
581 |
543 |
(0.3) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.8) |
(0.7) |
(0.7) |
(0.5) |
(0.5) |
Canada |
3,835 |
3,485 |
3,488 |
3,465 |
3,401 |
3,609 |
3,350 |
3,345 |
3,316 |
3,273 |
(1.0) |
(0.9) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(3.0) |
(3.1) |
(3.3) |
(3.1) |
(3.0) |
France |
4,821 |
5,653 |
5,122 |
5,678 |
7,080 |
3,831 |
4,419 |
3,937 |
4,809 |
6,243 |
(1.2) |
(1.5) |
(1.2) |
(1.3) |
(1.6) |
(3.2) |
(4.1) |
(3.9) |
(4.6) |
(5.8) |
Germany
(Includes ECB) |
9,461 |
9,963 |
9,206 |
7,763 |
7,027 |
3,541 |
3,341 |
2,922 |
2,339 |
2,267 |
(2.4) |
(2.6) |
(2.2) |
(1.7) |
(1.6) |
(2.9) |
(3.1) |
(2.9) |
(2.2) |
(2.1) |
Hong Kong |
26,822 |
26,357 |
25,110 |
28,861 |
29,841 |
10,920 |
9,106 |
6,250 |
7,962 |
8,503 |
(6.8) |
(6.8) |
(6.0) |
(6.5) |
(6.7) |
(9.1) |
(8.4) |
(6.2) |
(7.5) |
(7.9) |
India |
2,81,267 |
2,74,230 |
3,08,573 |
3,34,885 |
3,37,928 |
57,534 |
49,977 |
52,303 |
54,508 |
55,981 |
(71.5) |
(70.9) |
(74.2) |
(75.4) |
(75.5) |
(47.7) |
(45.8) |
(51.8) |
(51.6) |
(51.9) |
Japan |
1,368 |
1,417 |
1,206 |
1,209 |
1,379 |
1,311 |
1,340 |
1,174 |
1,146 |
1,304 |
(0.3) |
(0.4) |
(0.3) |
(0.3) |
(0.3) |
(1.1) |
(1.2) |
(1.2) |
(1.1) |
(1.2) |
Mauritius |
83 |
104 |
104 |
108 |
107 |
71 |
74 |
74 |
78 |
78 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Netherlands |
10,691 |
7,082 |
4,422 |
4,511 |
3,500 |
8,499 |
5,432 |
2,388 |
2,007 |
1,415 |
(2.7) |
(1.8) |
(1.1) |
(1.0) |
(0.8) |
(7.0) |
(5.0) |
(2.4) |
(1.9) |
(1.3) |
Oman |
201 |
218 |
207 |
187 |
211 |
20 |
42 |
37 |
48 |
38 |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
Russia |
— |
— |
131 |
108 |
181 |
— |
— |
111 |
108 |
111 |
— |
— |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
— |
— |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Singapore |
3,989 |
3,650 |
3,598 |
3,287 |
4,277 |
3,976 |
3,638 |
3,585 |
3,287 |
4,277 |
(1.0) |
(0.9) |
(0.9) |
(0.7) |
(1.0) |
(3.3) |
(3.3) |
(3.6) |
(3.1) |
(4.0) |
South Africa |
— |
— |
138 |
164 |
164 |
— |
— |
138 |
164 |
164 |
— |
— |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
— |
— |
(0.1) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
South Korea |
202 |
228 |
190 |
191 |
188 |
195 |
203 |
169 |
169 |
169 |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
Sri Lanka |
101 |
83 |
78 |
84 |
106 |
46 |
55 |
51 |
50 |
62 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
Switzerland
(Includes BIS) |
— |
259 |
253 |
723 |
723 |
— |
259 |
253 |
723 |
721 |
— |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
— |
(0.2) |
(0.3) |
(0.7) |
(0.7) |
Taiwan, China |
110 |
110 |
112 |
110 |
112 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
112 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Thailand |
139 |
141 |
142 |
141 |
140 |
36 |
36 |
36 |
36 |
36 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
United Arab
Emirates |
412 |
399 |
411 |
429 |
432 |
88 |
82 |
83 |
84 |
82 |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
United Kingdom@ |
20,986 |
20,718 |
19,833 |
19,312 |
18,875 |
12,050 |
11,510 |
10,272 |
9,869 |
8,892 |
(5.3) |
(5.4) |
(4.8) |
(4.4) |
(4.2) |
(10.0) |
(10.6) |
(10.2) |
(9.3) |
(8.3) |
United States # |
27,327 |
31,134 |
32,558 |
31,701 |
30,649 |
13,667 |
15,052 |
12,835 |
14,136 |
13,375 |
(6.9) |
(8.1) |
(7.8) |
(7.1) |
(6.9) |
(11.3) |
(13.8) |
(12.7) |
(13.4) |
(12.4) |
Total |
3,93,263 |
3,86,608 |
4,16,048 |
4,43,941 |
4,47,310 |
1,20,653 |
1,09,046 |
1,00,958 |
1,05,670 |
1,07,761 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
Statement VI : International Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified According to Country of Incorporation of Banks (Based on LBS Statements) — Amount Outstanding as at end Quarter |
(` crore) |
Country |
International Liabilities |
Total: All Sectors |
Position vis-a-vis Banks |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Bahrain |
301 |
341 |
286 |
302 |
339 |
59 |
59 |
59 |
59 |
62 |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Bangladesh |
52 |
74 |
88 |
83 |
54 |
49 |
71 |
87 |
81 |
53 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
Belgium |
1,023 |
887 |
720 |
639 |
595 |
968 |
816 |
666 |
581 |
543 |
(0.3) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.8) |
(0.7) |
(0.7) |
(0.5) |
(0.5) |
Canada |
3,835 |
3,485 |
3,488 |
3,465 |
3,401 |
3,609 |
3,350 |
3,345 |
3,316 |
3,273 |
(1.0) |
(0.9) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(0.8) |
(3.0) |
(3.1) |
(3.3) |
(3.1) |
(3.0) |
France |
4,821 |
5,653 |
5,122 |
5,678 |
7,080 |
3,831 |
4,419 |
3,937 |
4,809 |
6,243 |
(1.2) |
(1.5) |
(1.2) |
(1.3) |
(1.6) |
(3.2) |
(4.1) |
(3.9) |
(4.6) |
(5.8) |
Germany
(Includes ECB) |
9,461 |
9,963 |
9,206 |
7,763 |
7,027 |
3,541 |
3,341 |
2,922 |
2,339 |
2,267 |
(2.4) |
(2.6) |
(2.2) |
(1.7) |
(1.6) |
(2.9) |
(3.1) |
(2.9) |
(2.2) |
(2.1) |
Hong Kong |
26,822 |
26,357 |
25,110 |
28,861 |
29,841 |
10,920 |
9,106 |
6,250 |
7,962 |
8,503 |
(6.8) |
(6.8) |
(6.0) |
(6.5) |
(6.7) |
(9.1) |
(8.4) |
(6.2) |
(7.5) |
(7.9) |
India |
2,81,267 |
2,74,230 |
3,08,573 |
3,34,885 |
3,37,928 |
57,534 |
49,977 |
52,303 |
54,508 |
55,981 |
(71.5) |
(70.9) |
(74.2) |
(75.4) |
(75.5) |
(47.7) |
(45.8) |
(51.8) |
(51.6) |
(51.9) |
Japan |
1,368 |
1,417 |
1,206 |
1,209 |
1,379 |
1,311 |
1,340 |
1,174 |
1,146 |
1,304 |
(0.3) |
(0.4) |
(0.3) |
(0.3) |
(0.3) |
(1.1) |
(1.2) |
(1.2) |
(1.1) |
(1.2) |
Mauritius |
83 |
104 |
104 |
108 |
107 |
71 |
74 |
74 |
78 |
78 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Netherlands |
10,691 |
7,082 |
4,422 |
4,511 |
3,500 |
8,499 |
5,432 |
2,388 |
2,007 |
1,415 |
(2.7) |
(1.8) |
(1.1) |
(1.0) |
(0.8) |
(7.0) |
(5.0) |
(2.4) |
(1.9) |
(1.3) |
Oman |
201 |
218 |
207 |
187 |
211 |
20 |
42 |
37 |
48 |
38 |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
Russia |
— |
— |
131 |
108 |
181 |
— |
— |
111 |
108 |
111 |
— |
— |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
— |
— |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Singapore |
3,989 |
3,650 |
3,598 |
3,287 |
4,277 |
3,976 |
3,638 |
3,585 |
3,287 |
4,277 |
(1.0) |
(0.9) |
(0.9) |
(0.7) |
(1.0) |
(3.3) |
(3.3) |
(3.6) |
(3.1) |
(4.0) |
South Africa |
— |
— |
138 |
164 |
164 |
— |
— |
138 |
164 |
164 |
— |
— |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
— |
— |
(0.1) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
South Korea |
202 |
228 |
190 |
191 |
188 |
195 |
203 |
169 |
169 |
169 |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
Sri Lanka |
101 |
83 |
78 |
84 |
106 |
46 |
55 |
51 |
50 |
62 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
Switzerland
(Includes BIS) |
— |
259 |
253 |
723 |
723 |
— |
259 |
253 |
723 |
721 |
— |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
— |
(0.2) |
(0.3) |
(0.7) |
(0.7) |
Taiwan, China |
110 |
110 |
112 |
110 |
112 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
110 |
112 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Thailand |
139 |
141 |
142 |
141 |
140 |
36 |
36 |
36 |
36 |
36 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
United Arab
Emirates |
412 |
399 |
411 |
429 |
432 |
88 |
82 |
83 |
84 |
82 |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
United Kingdom@ |
20,986 |
20,718 |
19,833 |
19,312 |
18,875 |
12,050 |
11,510 |
10,272 |
9,869 |
8,892 |
(5.3) |
(5.4) |
(4.8) |
(4.4) |
(4.2) |
(10.0) |
(10.6) |
(10.2) |
(9.3) |
(8.3) |
United States # |
27,327 |
31,134 |
32,558 |
31,701 |
30,649 |
13,667 |
15,052 |
12,835 |
14,136 |
13,375 |
(6.9) |
(8.1) |
(7.8) |
(7.1) |
(6.9) |
(11.3) |
(13.8) |
(12.7) |
(13.4) |
(12.4) |
Total |
3,93,263 |
3,86,608 |
4,16,048 |
4,43,941 |
4,47,310 |
1,20,653 |
1,09,046 |
1,00,958 |
1,05,670 |
1,07,761 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
Statement VI : International Liabilities/Assets of Banks Classified According to Country of Incorporation of Banks (Based on LBS Statements) — Amount Outstanding as at end Quarter (Concld.) |
(` crore) |
Country |
International Assets |
Total: All Sectors |
Position vis-a-vis Banks |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Q4:2008 |
Q1:2009 |
Q2:2009 |
Q3:2009 |
Q4:2009 |
Bahrain |
327 |
379 |
361 |
382 |
344 |
23 |
70 |
49 |
53 |
15 |
(0.1) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
Bangladesh |
10 |
35 |
20 |
24 |
10 |
8 |
28 |
15 |
20 |
8 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
Belgium |
810 |
666 |
514 |
477 |
403 |
186 |
167 |
36 |
46 |
67 |
(0.4) |
(0.3) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Canada |
1,391 |
1,159 |
848 |
838 |
619 |
32 |
52 |
68 |
26 |
23 |
(0.6) |
(0.5) |
(0.4) |
(0.4) |
(0.3) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
France |
948 |
2,366 |
2,693 |
2,530 |
1,251 |
228 |
1,626 |
2,085 |
2,104 |
324 |
(0.4) |
(1.0) |
(1.2) |
(1.1) |
(0.6) |
(0.3) |
(1.8) |
(2.0) |
(2.7) |
(0.4) |
Germany
(Includes ECB) |
1,472 |
1,570 |
1,008 |
1,154 |
1,559 |
332 |
295 |
451 |
216 |
634 |
(0.6) |
(0.7) |
(0.4) |
(0.5) |
(0.7) |
(0.4) |
(0.3) |
(0.4) |
(0.3) |
(0.9) |
Hong Kong |
11,196 |
12,863 |
7,848 |
6,817 |
4,670 |
5,735 |
7,123 |
3,343 |
1,779 |
435 |
(4.9) |
(5.6) |
(3.4) |
(3.1) |
(2.1) |
(6.8) |
(7.8) |
(3.3) |
(2.3) |
(0.6) |
India |
1,60,197 |
1,62,004 |
1,66,149 |
1,59,301 |
1,68,056 |
60,357 |
63,963 |
73,231 |
51,590 |
52,540 |
(70.7) |
(70.6) |
(71.9) |
(71.8) |
(74.5) |
(71.7) |
(70.0) |
(71.4) |
(66.7) |
(72.4) |
Japan |
1,573 |
1,113 |
809 |
634 |
967 |
358 |
438 |
476 |
503 |
776 |
(0.7) |
(0.5) |
(0.3) |
(0.3) |
(0.4) |
(0.4) |
(0.5) |
(0.5) |
(0.6) |
(1.1) |
Mauritius |
10 |
9 |
27 |
27 |
18 |
1 |
6 |
24 |
24 |
15 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
Netherlands |
6,935 |
5,881 |
5,552 |
4,458 |
3,670 |
116 |
134 |
1,258 |
38 |
218 |
(3.1) |
(2.6) |
(2.4) |
(2.0) |
(1.6) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(1.2) |
(0.0) |
(0.3) |
Oman |
29 |
27 |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
2 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
Russia |
— |
— |
21 |
74 |
71 |
— |
— |
21 |
74 |
71 |
— |
— |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
— |
— |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
Singapore |
4,893 |
5,919 |
5,848 |
5,283 |
5,330 |
2,974 |
3,626 |
3,590 |
3,181 |
3,223 |
(2.2) |
(2.6) |
(2.5) |
(2.4) |
(2.4) |
(3.5) |
(4.0) |
(3.5) |
(4.1) |
(4.4) |
South Korea |
68 |
160 |
179 |
167 |
51 |
58 |
123 |
163 |
155 |
44 |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
(0.2) |
(0.2) |
(0.1) |
Sri Lanka |
69 |
68 |
57 |
63 |
64 |
7 |
4 |
3 |
10 |
11 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
Switzerland
(Includes BIS) |
— |
0 |
5 |
5 |
7 |
— |
0 |
0 |
0 |
2 |
— |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
— |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
Taiwan, China |
2 |
17 |
7 |
10 |
3 |
1 |
14 |
3 |
0 |
0 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
Thailand |
11 |
12 |
11 |
10 |
9 |
11 |
12 |
11 |
10 |
9 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
United Arab
Emirates |
49 |
34 |
40 |
67 |
79 |
28 |
21 |
23 |
51 |
59 |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.0) |
(0.1) |
(0.1) |
United Kingdom@ |
21,638 |
21,824 |
24,147 |
21,807 |
22,257 |
7,828 |
7,709 |
8,790 |
7,457 |
7,479 |
(9.6) |
(9.5) |
(10.4) |
(9.8) |
(9.9) |
(9.3) |
(8.4) |
(8.6) |
(9.6) |
(10.3) |
United States # |
14,904 |
13,247 |
15,008 |
17,732 |
16,215 |
5,862 |
5,934 |
8,976 |
10,058 |
6,618 |
(6.6) |
(5.8) |
(6.5) |
(8.0) |
(7.2) |
(7.0) |
(6.5) |
(8.7) |
(13.0) |
(9.1) |
Total |
2,26,530 |
2,29,356 |
2,31,153 |
2,21,863 |
2,25,658 |
84,152 |
91,345 |
1,02,615 |
77,400 |
72,575 |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
(100.0) |
@ excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey. # includes Midway Island and Wake Islands. ‘–’ nil/negligible.
Note: 1. Figures in brackets represent percentages to total in the respective group (column).
2. Totals may not tally due to rounding off.
3. Data have been revised for previous quarters.
4. Q1, Q2, Q3 and Q4 denote quarters ended March, June, September and December, respectively. |
Statement VII : Residual Maturity and Sector-wise Classification of Consolidated International Claims of Banks (Based on CBS Statements) — Amount Outstanding as at end of Period on Immediate Country Risk Basis |
(` crore) |
Country of Transacting Units |
Period |
Total International
Claims |
Residual Maturity |
Sector |
Short-
Term |
Long-
Term |
Un-
allocated |
Bank |
Non-Bank
Public |
Non-Bank
Private |
Total International Claims |
Dec-2008 |
191,118 |
1,16,029 |
72,088 |
3,000 |
75,135 |
732 |
1,15,251 |
Mar-2009 |
2,24,665 |
1,40,290 |
79,828 |
4,548 |
1,02,223 |
656 |
1,21,786 |
Jun-2009 |
2,31,556 |
1,44,319 |
82,699 |
4,537 |
1,10,573 |
804 |
1,20,179 |
Sep-2009 |
2,19,212 |
1,33,688 |
80,578 |
4,947 |
89,957 |
726 |
1,28,529 |
Dec-2009 |
2,25,278 |
1,37,778 |
82,228 |
5,272 |
91,188 |
713 |
1,33,377 |
Australia |
Dec-2008 |
1,999 |
531 |
1,469 |
— |
1,470 |
— |
529 |
Mar-2009 |
1,917 |
764 |
1,154 |
— |
1,384 |
1 |
532 |
Jun-2009 |
2,281 |
1,039 |
1,242 |
— |
1,437 |
3 |
842 |
Sep-2009 |
2,020 |
857 |
1,163 |
— |
1,126 |
7 |
887 |
Dec-2009 |
2,190 |
986 |
1,204 |
— |
1,138 |
— |
1,051 |
Bahamas |
Dec-2008 |
726 |
717 |
9 |
— |
49 |
— |
677 |
Mar-2009 |
999 |
835 |
164 |
— |
195 |
— |
804 |
Jun-2009 |
1,124 |
1,003 |
121 |
— |
440 |
— |
684 |
Sep-2009 |
915 |
792 |
122 |
— |
182 |
— |
733 |
Dec-2009 |
979 |
861 |
117 |
— |
248 |
— |
731 |
Bahrain |
Dec-2008 |
3,302 |
1,557 |
1,745 |
— |
2,995 |
— |
307 |
Mar-2009 |
3,561 |
1,969 |
1,592 |
— |
3,021 |
— |
539 |
Jun-2009 |
4,603 |
2,059 |
2,521 |
22 |
4,150 |
— |
453 |
Sep-2009 |
4,894 |
1,985 |
2,576 |
333 |
4,340 |
— |
554 |
Dec-2009 |
4,923 |
2,036 |
2,571 |
317 |
4,295 |
— |
628 |
Belgium |
Dec-2008 |
3,433 |
3,013 |
419 |
— |
463 |
— |
2,970 |
Mar-2009 |
3,835 |
3,208 |
627 |
— |
1,137 |
— |
2,697 |
Jun-2009 |
4,014 |
3,331 |
684 |
— |
1,902 |
— |
2,112 |
Sep-2009 |
4,218 |
3,431 |
787 |
— |
1,710 |
— |
2,508 |
Dec-2009 |
4,740 |
4,077 |
663 |
— |
2,395 |
— |
2,345 |
Canada |
Dec-2008 |
5,636 |
1,443 |
3,205 |
989 |
3,124 |
1 |
2,511 |
Mar-2009 |
6,348 |
1,547 |
3,325 |
1,476 |
3,823 |
2 |
2,523 |
Jun-2009 |
6,316 |
1,363 |
3,256 |
1,697 |
3,870 |
1 |
2,445 |
Sep-2009 |
6,400 |
887 |
3,267 |
2,246 |
3,944 |
2 |
2,454 |
Dec-2009 |
6,211 |
694 |
3,279 |
2,238 |
3,747 |
1 |
2,462 |
Cayman Islands |
Dec-2008 |
1,660 |
1,083 |
577 |
— |
90 |
— |
1,570 |
Mar-2009 |
2,230 |
1,164 |
1,066 |
— |
161 |
— |
2,070 |
Jun-2009 |
2,792 |
1,384 |
1,408 |
— |
262 |
— |
2,529 |
Sep-2009 |
2,421 |
1,359 |
1,062 |
— |
— |
— |
2,421 |
Dec-2009 |
2,611 |
1,472 |
1,138 |
— |
146 |
— |
2,465 |
China |
Dec-2008 |
1,419 |
1,275 |
144 |
— |
— |
— |
1,419 |
Mar-2009 |
1,418 |
1,278 |
140 |
— |
1 |
— |
1,417 |
Jun-2009 |
1,460 |
1,338 |
122 |
— |
1 |
— |
1,459 |
Sep-2009 |
2,030 |
1,895 |
135 |
— |
1 |
— |
2,028 |
Dec-2009 |
1,543 |
1,463 |
80 |
— |
4 |
— |
1,539 |
Cyprus |
Dec-2008 |
2,565 |
1,038 |
1,527 |
— |
1,027 |
— |
1,539 |
Mar-2009 |
2,513 |
1,104 |
1,409 |
— |
985 |
— |
1,528 |
Jun-2009 |
2,615 |
1,323 |
1,292 |
— |
960 |
— |
1,655 |
Sep-2009 |
1,884 |
624 |
1,260 |
— |
149 |
— |
1,735 |
Dec-2009 |
1,814 |
518 |
1,296 |
— |
140 |
— |
1,674 |
Denmark |
Dec-2008 |
1,305 |
866 |
439 |
— |
1,112 |
— |
193 |
Mar-2009 |
1,461 |
1,014 |
447 |
— |
1,271 |
— |
190 |
Jun-2009 |
1,333 |
893 |
441 |
— |
1,164 |
— |
169 |
Sep-2009 |
865 |
484 |
381 |
— |
720 |
— |
145 |
Dec-2009 |
801 |
512 |
289 |
— |
628 |
— |
173 |
Statement VII : Residual Maturity and Sector-wise Classification of Consolidated International
Claims of Banks (Based on CBS Statements) — Amount Outstanding as at end of Period on Immediate Country Risk Basis (Contd.) |
(` crore) |
Country of Transacting
Units |
Period |
Total
International
Claims |
Residual Maturity |
Sector |
Short-
Term |
Long-
Term |
Un-
allocated |
Bank |
Non-Bank
Public |
Non-Bank
Private |
Egypt |
Dec-2008 |
94 |
94 |
1 |
— |
— |
— |
94 |
Mar-2009 |
590 |
194 |
397 |
— |
— |
— |
590 |
Jun-2009 |
716 |
223 |
494 |
— |
— |
— |
716 |
Sep-2009 |
816 |
299 |
517 |
— |
— |
— |
816 |
Dec-2009 |
1,166 |
360 |
805 |
— |
2 |
— |
1,163 |
France |
Dec-2008 |
4,126 |
2,675 |
1,451 |
— |
2,742 |
— |
1,383 |
Mar-2009 |
4,393 |
2,949 |
1,444 |
— |
3,134 |
— |
1,259 |
Jun-2009 |
5,427 |
4,164 |
1,263 |
— |
4,298 |
— |
1,130 |
Sep-2009 |
4,009 |
2,862 |
1,147 |
— |
2,377 |
— |
1,631 |
Dec-2009 |
3,810 |
2,737 |
1,073 |
— |
2,147 |
— |
1,662 |
Germany (includes ECB) |
Dec-2008 |
9,565 |
7,838 |
1,727 |
— |
4,756 |
80 |
4,730 |
Mar-2009 |
9,869 |
8,380 |
1,488 |
— |
5,295 |
107 |
4,467 |
Jun-2009 |
12,089 |
10,334 |
1,755 |
— |
7,815 |
110 |
4,164 |
Sep-2009 |
11,862 |
10,168 |
1,695 |
— |
8,030 |
32 |
3,800 |
Dec-2009 |
11,976 |
10,378 |
1,598 |
— |
8,169 |
24 |
3,783 |
Hong Kong |
Dec-2008 |
14,779 |
13,364 |
1,414 |
— |
9,605 |
— |
5,174 |
Mar-2009 |
19,031 |
17,018 |
2,013 |
— |
13,857 |
— |
5,174 |
Jun-2009 |
19,784 |
17,581 |
2,203 |
— |
13,751 |
19 |
6,014 |
Sep-2009 |
19,032 |
17,800 |
1,232 |
— |
13,480 |
— |
5,552 |
Dec-2009 |
18,785 |
17,591 |
1,194 |
— |
13,258 |
— |
5,527 |
Indonesia |
Dec-2008 |
1,416 |
887 |
529 |
— |
22 |
— |
1,393 |
Mar-2009 |
1,645 |
914 |
730 |
— |
119 |
— |
1,525 |
Jun-2009 |
1,371 |
630 |
741 |
— |
172 |
— |
1,198 |
Sep-2009 |
1,443 |
714 |
729 |
— |
33 |
— |
1,410 |
Dec-2009 |
1,297 |
998 |
300 |
— |
51 |
— |
1,246 |
Ireland |
Dec-2008 |
1,253 |
491 |
762 |
— |
775 |
— |
478 |
Mar-2009 |
1,135 |
340 |
795 |
— |
730 |
— |
405 |
Jun-2009 |
1,875 |
826 |
1,049 |
— |
1,619 |
— |
256 |
Sep-2009 |
1,836 |
769 |
1,067 |
— |
1,388 |
— |
448 |
Dec-2009 |
1,815 |
690 |
1,125 |
— |
1,294 |
— |
521 |
Israel |
Dec-2008 |
873 |
858 |
15 |
— |
— |
— |
873 |
Mar-2009 |
875 |
823 |
52 |
— |
— |
— |
875 |
Jun-2009 |
840 |
791 |
49 |
— |
— |
— |
840 |
Sep-2009 |
782 |
729 |
54 |
— |
— |
— |
782 |
Dec-2009 |
703 |
655 |
49 |
— |
14 |
— |
690 |
Italy |
Dec-2008 |
2,240 |
1,294 |
946 |
— |
1,140 |
— |
1,100 |
Mar-2009 |
2,857 |
1,961 |
896 |
— |
1,599 |
— |
1,258 |
Jun-2009 |
2,438 |
1,577 |
861 |
— |
1,489 |
— |
949 |
Sep-2009 |
2,158 |
1,224 |
934 |
— |
1,058 |
— |
1,100 |
Dec-2009 |
2,014 |
1,101 |
913 |
— |
865 |
— |
1,148 |
Japan |
Dec-2008 |
2,139 |
1,720 |
419 |
— |
1,702 |
— |
437 |
Mar-2009 |
2,233 |
1,629 |
604 |
— |
1,573 |
1 |
660 |
Jun-2009 |
2,302 |
1,795 |
507 |
— |
1,473 |
— |
829 |
Sep-2009 |
2,778 |
2,199 |
579 |
— |
1,337 |
— |
1,441 |
Dec-2009 |
2,399 |
1,876 |
523 |
— |
1,337 |
— |
1,062 |
Jersey |
Dec-2008 |
230 |
171 |
60 |
— |
230 |
— |
— |
Mar-2009 |
913 |
153 |
760 |
— |
153 |
— |
760 |
Jun-2009 |
1,213 |
239 |
973 |
— |
272 |
— |
940 |
Sep-2009 |
1,769 |
836 |
932 |
— |
278 |
— |
1,491 |
Dec-2009 |
1,537 |
443 |
1,094 |
— |
443 |
— |
1,094 |
Statement VII : Residual Maturity and Sector-wise Classification of Consolidated International
Claims of Banks (Based on CBS Statements) — Amount Outstanding as at end of Period on Immediate Country Risk Basis (Contd.) |
(` crore) |
Country of Transacting
Units |
Period |
Total
International
Claims |
Residual Maturity |
Sector |
Short-
Term |
Long-
Term |
Un-
allocated |
Bank |
Non-Bank
Public |
Non-Bank
Private |
Luxembourg |
Dec-2008 |
4,383 |
2,891 |
1,492 |
— |
1,340 |
— |
3,043 |
Mar-2009 |
4,391 |
2,380 |
2,011 |
— |
1,153 |
— |
3,238 |
Jun-2009 |
3,828 |
2,124 |
1,704 |
— |
1,003 |
— |
2,824 |
Sep-2009 |
2,880 |
1,823 |
1,057 |
— |
853 |
— |
2,028 |
Dec-2009 |
2,415 |
1,553 |
863 |
— |
699 |
— |
1,716 |
Malpes |
Dec-2008 |
1,476 |
1,476 |
1 |
— |
— |
— |
1,476 |
Mar-2009 |
3,990 |
3,989 |
1 |
— |
— |
— |
3,990 |
Jun-2009 |
2,114 |
2,113 |
1 |
— |
— |
— |
2,114 |
Sep-2009 |
1,884 |
1,883 |
1 |
— |
— |
— |
1,884 |
Dec-2009 |
1,849 |
1,849 |
1 |
— |
— |
— |
1,849 |
Malta |
Dec-2008 |
6 |
6 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
6 |
Mar-2009 |
814 |
452 |
362 |
— |
— |
— |
814 |
Jun-2009 |
769 |
426 |
343 |
— |
— |
— |
769 |
Sep-2009 |
694 |
434 |
260 |
— |
— |
— |
694 |
Dec-2009 |
746 |
746 |
— |
— |
— |
— |
746 |
Mauritius |
Dec-2008 |
1,022 |
192 |
831 |
— |
278 |
— |
745 |
Mar-2009 |
2,079 |
401 |
1,676 |
2 |
339 |
— |
1,740 |
Jun-2009 |
2,499 |
655 |
1,842 |
2 |
495 |
— |
2,004 |
Sep-2009 |
3,255 |
1,184 |
2,071 |
— |
367 |
— |
2,888 |
Dec-2009 |
3,326 |
820 |
2,504 |
2 |
107 |
— |
3,219 |
Netherlands |
Dec-2008 |
5,073 |
1,518 |
3,555 |
— |
989 |
32 |
4,053 |
Mar-2009 |
6,092 |
1,845 |
4,247 |
— |
1,133 |
— |
4,959 |
Jun-2009 |
6,586 |
2,062 |
4,525 |
— |
1,542 |
— |
5,044 |
Sep-2009 |
6,263 |
1,876 |
4,387 |
— |
1,522 |
— |
4,741 |
Dec-2009 |
6,640 |
2,214 |
4,426 |
— |
1,235 |
— |
5,404 |
No Specific Country
(Country Unknown) |
Dec-2008 |
1,430 |
481 |
949 |
— |
447 |
— |
983 |
Mar-2009 |
1,543 |
535 |
1,008 |
— |
487 |
— |
1,056 |
Jun-2009 |
1,053 |
518 |
535 |
— |
199 |
— |
854 |
Sep-2009 |
1,009 |
529 |
480 |
— |
— |
— |
1,009 |
Dec-2009 |
959 |
495 |
464 |
— |
— |
— |
959 |
Norway |
Dec-2008 |
908 |
83 |
825 |
— |
267 |
— |
641 |
Mar-2009 |
957 |
120 |
837 |
— |
300 |
— |
657 |
Jun-2009 |
905 |
103 |
802 |
— |
287 |
— |
618 |
Sep-2009 |
830 |
67 |
763 |
— |
235 |
— |
595 |
Dec-2009 |
901 |
284 |
617 |
— |
161 |
— |
740 |
Russia |
Dec-2008 |
6,170 |
3,763 |
2,285 |
122 |
3,428 |
— |
2,742 |
Mar-2009 |
5,340 |
3,031 |
2,182 |
127 |
2,780 |
— |
2,560 |
Jun-2009 |
5,189 |
3,003 |
2,067 |
120 |
2,598 |
— |
2,591 |
Sep-2009 |
4,925 |
2,520 |
2,284 |
120 |
2,367 |
— |
2,557 |
Dec-2009 |
4,793 |
2,535 |
2,142 |
116 |
2,345 |
— |
2,448 |
Saudi Arabia |
Dec-2008 |
904 |
491 |
414 |
— |
136 |
— |
768 |
Mar-2009 |
790 |
439 |
350 |
— |
91 |
— |
698 |
Jun-2009 |
719 |
441 |
278 |
— |
187 |
— |
532 |
Sep-2009 |
564 |
374 |
190 |
— |
14 |
— |
550 |
Dec-2009 |
611 |
355 |
256 |
— |
9 |
— |
602 |
Singapore |
Dec-2008 |
14,454 |
6,861 |
7,261 |
332 |
4,656 |
— |
9,799 |
Mar-2009 |
15,762 |
7,620 |
7,837 |
306 |
4,408 |
— |
11,354 |
Jun-2009 |
16,919 |
8,232 |
8,687 |
— |
5,735 |
— |
11,184 |
Sep-2009 |
17,546 |
8,944 |
8,601 |
— |
5,616 |
— |
11,930 |
Dec-2009 |
18,350 |
9,710 |
8,640 |
— |
5,591 |
— |
12,758 |
Statement VII: Residual Maturity and Sector-wise Classification of Consolidated International
Claims of Banks (Based on CBS Statements) — Amount Outstanding as at
end of Period on Immediate Country Risk Basis (Concld.) |
(` crore) |
Country of Transacting
Units |
Period |
Total
International
Claims |
Residual Maturity |
Sector |
Short-
Term |
Long-
Term |
Un-
allocated |
Bank |
Non-Bank
Public |
Non-Bank
Private |
Spain (incl. Balearic Is, Canary Is. and Ceuta & Melilla) |
Dec-2008 |
821 |
714 |
107 |
— |
— |
— |
821 |
Mar-2009 |
1,358 |
1,306 |
52 |
— |
670 |
— |
689 |
Jun-2009 |
1,564 |
1,512 |
52 |
— |
982 |
— |
582 |
Sep-2009 |
695 |
588 |
108 |
— |
49 |
— |
647 |
Dec-2009 |
831 |
753 |
79 |
— |
139 |
— |
692 |
Sri Lanka |
Dec-2008 |
2,281 |
1,916 |
318 |
47 |
596 |
328 |
1,357 |
Mar-2009 |
2,305 |
1,859 |
350 |
96 |
499 |
396 |
1,410 |
Jun-2009 |
1,428 |
1,087 |
201 |
140 |
45 |
432 |
951 |
Sep-2009 |
1,454 |
1,038 |
234 |
182 |
67 |
419 |
969 |
Dec-2009 |
1,299 |
870 |
250 |
179 |
48 |
410 |
841 |
Switzerland (includes BIS) |
Dec-2008 |
1,597 |
812 |
785 |
— |
850 |
— |
746 |
Mar-2009 |
1,672 |
827 |
845 |
— |
819 |
— |
853 |
Jun-2009 |
1,451 |
630 |
821 |
— |
607 |
— |
844 |
Sep-2009 |
1,630 |
843 |
787 |
— |
594 |
— |
1,035 |
Dec-2009 |
1,280 |
654 |
626 |
— |
316 |
— |
964 |
United Arab Emirates |
Dec-2008 |
9,660 |
5,296 |
4,364 |
— |
984 |
— |
8,675 |
Mar-2009 |
11,309 |
6,447 |
4,862 |
— |
2,319 |
— |
8,989 |
Jun-2009 |
11,567 |
6,115 |
5,452 |
— |
2,176 |
— |
9,391 |
Sep-2009 |
10,605 |
5,423 |
5,181 |
— |
1,420 |
— |
9,184 |
Dec-2009 |
12,645 |
6,617 |
6,028 |
— |
1,317 |
— |
11,327 |
United Kingdom@ |
Dec-2008 |
25,246 |
11,481 |
12,255 |
1,510 |
12,518 |
6 |
12,722 |
Mar-2009 |
29,753 |
14,713 |
12,529 |
2,511 |
16,291 |
38 |
13,423 |
Jun-2009 |
32,648 |
16,503 |
13,599 |
2,546 |
18,232 |
18 |
14,397 |
Sep-2009 |
31,622 |
14,681 |
14,893 |
2,047 |
13,784 |
28 |
17,810 |
Dec-2009 |
35,919 |
17,151 |
16,365 |
2,403 |
16,857 |
29 |
19,033 |
United States # |
Dec-2008 |
43,986 |
28,502 |
15,484 |
— |
13,159 |
268 |
30,560 |
Mar-2009 |
55,734 |
37,993 |
17,711 |
31 |
27,629 |
94 |
28,011 |
Jun-2009 |
55,931 |
38,148 |
17,773 |
10 |
27,619 |
213 |
28,099 |
Sep-2009 |
48,446 |
31,740 |
16,689 |
17 |
20,020 |
238 |
28,188 |
Dec-2009 |
48,874 |
32,062 |
16,795 |
17 |
19,633 |
241 |
29,000 |
@ Excluding Guernsey, Isle of Man and Jersey. # Includes Midway Island and Wake Islands.
‘—’ Nil/Negligible.
Notes: 1. Totals may not tally due to rounding off.
2. Residual Maturity ‘Unallocated’ comprises maturity not applicable (e.g., for equities) and maturity information not available
3. ‘No Specific Country’ means the country information has not been provided by the reporting bank branches.
4. Data have been revised for previous quarters. |
Annex : BIS Reporting System and Methodology of Compilation of IBS 1. BIS Reporting System of International Banking Statistics The BIS reporting system of IBS has two sets of statistics, viz., (i) ‘Locational Banking Statistics (LBS)’ and (ii) ‘Consolidated Banking Statistics (CBS)’ both quarterly reviews. The LBS are designed to provide comprehensive and consistent quarterly data on international banking business conducted in the BIS reporting area. The purpose of the CBS is to provide comprehensive and consistent quarterly data on banks’ financial claims on other countries, both on an immediate borrower basis for providing a measure of country transfer risk, and on an ultimate risk basis for assessing country risk exposures of national banking system. The international banking business is defined as banks’ on balance-sheet liabilities and assets vis-à-vis non-residents in any currency or unit of account plus similar liabilities and assets vis-à-vis residents in foreign currencies or units of account. 2. BIS Reporting Area for International Banking Statistics 2.1 Reporting Area for Locational Banking Statistics : The aim of the LBS is to provide accurate, comprehensive and up-to-date information on international banking activity. To achieve this goal, data should ideally be collected from banks in each and every country. However, the hub like nature of international banking means that it is sufficient to gather data from only a limited number of key international banking centres. In this way at least one side of most international banking relationships will be captured. This procedure keeps the system manageable and produces accurate and up-todate data. Additional countries are, therefore, asked to contribute to the LBS when their crossborder
banking business becomes substantial. The countries currently making up the reporting area are listed in Box 1. 2.2 Reporting Area for Consolidated Banking Statistics : The CBS are a hybrid scheme combining features of a worldwide-consolidated reporting system with elements of a territorial, i.e.,
balance of payments, based reporting system. For this reason, it is not possible to speak of a ‘reporting area’ that is well-defined in terms of the location of the banking offices conducting the business in question. The worldwide consolidation of balance sheet
positions means that the activities of a great number of banking offices located outside the reporting countries are also covered. The expression ‘reporting area’ is used for reasons of convenience to indicate the countries that submit data to the BIS (see Box 1). 3. Distinction/Relation Between IBS of India vis-à-vis External Debt of India In India, with the growing liberalisation of the external sector, close monitoring of the cross-border flow of funds assume critical importance. Commercial and co-operative banks in India (including foreign banks having offices in India) provide information on their domestic and international operations to the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) to meet the specific regulatory and policy requirements. Currently, efforts have been made to meet the data standards of BIS by devising a new reporting system for International Banking Statistics (IBS) of India. The IBS is not the same as the external debt statistics, which are separately collected and disseminated (see the Box 2).
Box-1 : Countries Reporting IBS data to the BIS Year in bracket indicates first year of data submission to the BIS) |
I. Reporting countries providing Locational Banking Statistics to the BIS: |
Australia (1997) |
Cyprus (2008) |
Italy (1977) |
Portugal (1997) |
Austria (1977) |
Denmark (1977) |
Japan (1977) |
Singapore (1983) |
Bahamas 1 (1983) |
Finland (1983) |
Jersey (2001) |
South Africa (2009) |
Bahrain (1983) |
France (1977) |
Luxembourg (1977) |
South Korea (2005) |
Belgium (1977) |
Germany (1977) |
Macau SAR (2006) |
Spain (1983) |
Bermuda (2002) |
Greece (2003) |
Malaysia (2008) |
Sweden (1977) |
Brazil (2002) |
Guernsey (2001) |
Mexico (2003) |
Switzerland (1977) |
Canada (1977) |
Hong Kong SAR (1983) |
Netherlands (1977) |
Turkey (2000) |
Cayman Island (1983) |
India (2001) |
Netherlands Antilles (1983) |
United Kingdom (1977) |
Chile (2002) |
Ireland (1977) |
Norway (1983) |
United States (1977) |
Chinese Taipei (2000) |
Isle of Man (2001) |
Panama (2002) |
|
1: Semi-annual reporting |
II. Reporting countries providing Consolidated Banking Statistics to the BIS: |
Australia (2003) |
Finland (1985) |
Japan (1983) |
Spain (1985) |
Austria (1983) |
France (1983) |
Luxembourg 1 (1983) |
Sweden (1983) |
Belgium (1983) |
Germany (1983) |
Mexico 1 (2003) |
Switzerland (1983) |
Brazil 1 (2002) |
Greece (2003) |
Netherlands (1983) |
Turkey (2000) |
Canada (1983) |
Hong Kong SAR 1 (1997) |
Norway (1994) |
United Kingdom (1983) |
Chile (2002) |
India (2001) |
Panama 1 (2002) |
United States (1983) |
Chinese Taipei (2000) |
Ireland (1983) |
Portugal (1999) |
|
Denmark 1 (1983) |
Italy (1983) |
Singapore (2000) |
|
1: Provides only consolidated banking statistics on an immediate borrower basis
Source: BIS: International Banking Statistics December 2009. |
4. Methodoly of Compilation of LBS and CBS The LBS provide for the collection of data on the positions of all banking offices located within the reporting area. Such offices report exclusively on their own (unconsolidated) business, which thus includes international transactions with any of their own affiliates (branches, subsidiaries, joint ventures) located either inside or outside the reporting area. The basic organising principle underlying the reporting system is the residence of the banking office. This conforms to balance of payments and external debt methodology. In addition, data on ownership or nationality basis are also calculated by regrouping according to country of origin. Thus, the LBS cover both international liabilities and assets of offices of domestic and foreign banks operating within the reporting country. The LBS data are classified by currency (domestic and foreign currencies), sector (banks and nonbanks) and country of residence of counterparty, and by nationality of reporting banks. Box 2 : External Debt Statistics vis-à-vis International Banking Statistics of India In India, while the international banking statistics have been developed recently, there has been a closely related reporting system of external debt statistics. Besides, there are other periodic returns through which banks are reporting external assets and liabilities to the Reserve Bank of India. The existing systems are not as comprehensive as the IBS system for reporting international liabilities and assets of banks in India. The external debt statistics and international banking statistics are different in many respects. First, external debt statistics relate to external debt of the country as a whole comprising banking and other sectors whereas international banking statistics relate to international liabilities as well as international assets in respect of only banks. Second, liabilities of banks in foreign currencies towards residents (like, Exchange Earners’ Foreign Currency (EEFC) A/cs, Resident Foreign Currency (RFC) A/Cs, Intra-bank foreign currency deposits/borrowing, etc.) are included in International Banking Statistics, whereas the same are not included under external debt statistics. Third, equities of banks held by NRIs, Rupee and ACU Dollar balances in Vostro A/ Cs+ , non-debt credit flows on account of ADRs/ GDRs and capital supplied by head offices of foreign banks in India form part of International Banking Statistics. Fourth, outstanding amounts on account of nonresident non-repatriable Rupee deposits (either principal and/or interest are not repatriable) are not included in external debt whereas the same are included in International Banking Statistics as per the definition stated under ‘BIS Reporting System of International Banking Statistics’. The CBS focus on the assets side of banks’ balance sheet. The data mainly cover financial claims reported by domestic banks’ offices, including the exposures of their foreign affiliates, and are collected on worldwide basis with inter-office transactions being netted out. Unlike the locational banking statistics, the consolidated banking statistics call for maturity details of assets, and they also entail a somewhat finer sectoral breakdown (banks, non-bank public sector and non-bank private sector). The additional information can be used to supplement locational banking data while compiling and evaluating external debt statistics from creditor side, although, unlike the locational statistics, the reporting system underlying the consolidated statistics does not conform to balance of payments and external debt methodology. Thus, in the CBS, banks with head office in the reporting country (e.g., India) provide data on total international assets for all their offices in the reporting country and abroad excluding inter-office transactions, i.e., data are reported on consolidated basis. Affiliates/branches of foreign banks operating in the reporting country (e.g., India) also report their claims on countries other than the reporting country (e.g., India) including transactions with their offices outside the reporting country. In the CBS, the reporting banks are classified under three categories, viz., ‘Domestic Banks’ having head offices in India,‘Inside Area Foreign Banks’ having head offices in another BIS Reporting country and ‘Outside Area Foreign Banks’ having head offices outside BIS–Reporting countries. The following aspects are taken into consideration for reporting/segregating the international claims for the three categories of banks: (i) Head offices of banks in the reporting countries (i.e., domestic banks) are required to provide consolidated reports on financial claims of their offices worldwide both on an ultimate risk and an immediate borrower basis; worldwide consolidated reporting entails that, for example, an Indian bank, with a foreign branch in the US, should report – (a) the claims of its domestic branches on all nonresidents, (b) the claims of its foreign branch in the US on all non-residents (but other than entities in India), and (c) the
claims, of its foreign branch in the US, on residents/entities in the US in currencies other than US dollar. Claims between the Indian head office and its foreign branch in the US should be netted out. Besides, the foreign branches are also required to report their local assets and local liabilities in local currency. (ii) Banking offices in reporting countries whose head office is located in another reporting country (i.e., inside area foreign banks, such as, Mumbai office of a US bank where US is a BIS reporting country) are required to provide non-consolidated data on claims on entities in their respective home country only (e.g., the branch or subsidiary of a US bank in India should report its claims on the US only to avoid the double-counting of its claims on other countries which are reported through its head office to the BIS) and on an immediate borrower basis only. These data should, therefore, include any positions the banks have vis-à-vis their own affiliates or head offices in their home country. (iii) Banking offices in reporting countries whose head office is outside the reporting countries (i.e., outside area foreign banks, such as, Mumbai office of a Thai bank where Thailand is not a BIS reporting country) are required to provide non-consolidated data on financial claims on non-residents, including their home country, on an immediate borrower basis only. The three major sub-components of international assets and liabilities are: (i) loans and deposits, (ii) holding of debt securities and own issues of debt securities, and (iii) other assets and liabilities. The ‘other assets and liabilities’ mainly comprise, on the asset side, equity shares (including mutual and investment fund units and holdings of shares in a bank’s own name but on behalf of third parties), participations, and working capital supplied by head offices to their branches abroad and, on the liability side, working capital received by local branches from their head offices abroad. The BIS revised its guidelines for consolidated banking statistics (CBS) by modifying its reporting format and increasing the coverage of products by including financial instruments such as derivatives, guarantees, etc. The revised system has been implemented from the reporting quarter March 2005 which covers, besides existing items, the claims of domestic reporting banks on ultimate risk basis arising from derivatives, guarantees and credit commitments. 5. Terms Used in International Banking Statistics Cross Border positions : It refers to the transactions (assets/liabilities) with non-residents in any currency. International Position : Banks’ on balance sheet assets and liabilities vis-à-vis non-residents in any currency plus similar assets and liabilities vis-à-vis residents in foreign currencies. Foreign Claims : It can be disaggregated into cross-border claims and local claims of foreign branches of domestic banks. Alternately, it can also be disaggregated into international claims and local claims denominated in local currencies. International Claims : They are defined as cross-border claims plus local claims in foreign currencies. Cross-border Claims : They are the claims on the borrowers resident outside the country in which the office of bank booking the claim is located. Local Claims : It is the claim booked by foreign offices of domestic banks on the resident of the country in which foreign office is located. 6. Explanation of the Methodology : (a) Compilation of LBS/CBS and Different Terms Used in IBS with the Help of an Example
Reporting of IBS Data |
Reporting Bank |
Assets/
Liabilities |
Currency+ |
Assets with/Liabilities towards |
| |
IN |
LK |
US |
XX |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
Domestic (Indian) Banks'
Branches in India (IN) |
Asset |
Local |
A |
–– |
15 |
25 |
10* |
Non-Local |
B |
15 |
5 |
30 |
10 |
Liability |
Local Non- |
C |
– |
15 |
20 |
10* |
Local |
D |
12 |
15 |
10 |
5 |
Domestic (Indian) Banks'
Branches in the US |
Asset |
Local Non- |
E |
25 |
10 |
30 |
5 |
Local |
F |
20 |
30 |
35 |
10 |
Liability |
Local Non- |
G |
– |
– |
35 |
– |
Local |
H |
– |
– |
– |
– |
US-based Banks' Branches in India (IN) (Inside Area Bank) |
Asset |
Local |
I |
–– |
20 |
25 |
15 |
Non-Local |
J |
10 |
15 |
30 |
5 |
Liability |
Local |
K |
–– |
20 |
35 |
10 |
Non-Local |
L |
25 |
20 |
40 |
5 |
Sri Lanka-based Banks'
Branches in India (IN)
(Outside Area Bank) |
Asset |
Local |
M |
–– |
20 |
15 |
10 |
Non-Local |
N |
10 |
30 |
20 |
15 |
Liability |
Local |
O |
–– |
12 |
25 |
10 |
Non-Local |
P |
20 |
15 |
35 |
10 |
IN - India LK - Sri Lanka, US - United States, XX - Not a Specific Country.
+ : Local/non-local currency is according to the country of operation of the reporting branches.
* : Asset/Liabilities with/towards own office operating in the country 'XX'.
'—' : Not required under IBS reporting. |
Compilation of LBS/CBS |
Locational Banking Statistics (LBS) |
Country |
International Assets |
International Liabilities |
IN |
B1+J1+N1 |
35 |
D1+L1+P1 |
57 |
LK |
A2+B2+I2+J2+M2+N2 |
105 |
C2+D2+K2+L2+O2+P2 |
97 |
US |
A3+B3+I3+J3+M3+N3 |
145 |
C3+D3+K3+L3+O3+P3 |
165 |
XX |
A4+B4+I4+J4+M4+N4 |
65 |
C4+D4+K4+L4+O4+P4 |
50 |
Consolidated Banking Statistics (CBS) |
Reporting Banks
according to Country
of Incorporation |
Cross-Border
Claims (in all
curriencies) |
Non-local |
Local |
International
Claims |
Foreign
Claims |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4[='1'+'2'] |
5[='3'+'4'] |
Domestic (Indian) Banks |
X |
140 |
35 |
30 |
175 |
205 |
Inside Area Banks |
Y |
55 |
– |
– |
55 |
55 |
| Outside Area Banks |
Z |
110 |
– |
– |
110 |
110 |
Note: The claims on home country (i.e., India) is excluded in CBS.
X1=140 (=A2+A3+A4+B2+B3+E2+E4+F2+F4) X2=35 (=F3) X3=30 (=E3)
Y1= 55 (=I3+J3) Z1=110 (=M2+M3+M4+N2+N3+N4)
'—' : Not required under CBS reporting. |
(b) Compilation of Risk Transfer : The procedure for calculating Outward Risk/ Inward Risk/Net Risk transfer is given in the following Table.
Country of
Operation of
Reporting
Banks |
Country of
Immediate Risk
(Country of
Customer/
Borrower) |
Country of
Ultimate Risk
(Guarantors’
Country) |
Balance |
|
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
|
IN |
IN |
IN |
10 |
A |
IN |
IN |
GB |
30 |
B |
US |
GB |
IN |
50 |
C |
US |
GB |
GB |
25 |
D |
IN |
GB |
US |
45 |
E |
JP |
US |
GB |
15 |
F |
Risk Transefer |
Country |
IN |
GB |
US |
Outward Risk (O)* |
– |
C4+E4 |
F4 |
95 |
15 |
Inward Risk (I)# |
– |
B4+F4 |
E4 |
45 |
45 |
Net risk (I - O) |
– |
-50 |
30 |
IN - India, US - United States, GB - United Kindom, JP - Japan.
‘–’ : Not required under IBS reporting.
* : Exposure against the country which is guaranteed by another country.
# : Exposure against the guaranteeing country which is availed by another country. |
* Prepared in the Banking Statistics Division of the Department of Statistics and Information Management. The previous article on the subject as at end of September 2009 was published in August 2010 issue of the Bulletin. 1 A brief outline of the BIS reporting system of IBS comprising LBS and CBS, purpose of IBS, BIS reporting area for IBS, the distinction / relation between IBS vis-àvis external debt of India has been provided in the Annex. 2 The methodology of compilation of LBS/CBS and explanation to various terms used in IBS has been provided in the Annex to this article. + These are accounts of non-resident branches of banks with banks in India in ACU Dollar or Indian Rupee. |