Annual Report on Banking Ombudsman Scheme, 2008-09 - RBI - Reserve Bank of India
Annual Report on Banking Ombudsman Scheme, 2008-09
 Dr. K.C.Chakrabarty The issue of ‘Treating the bank customers fairly’ is gaining currency with the awakening of consumers on the issues of investor/consumer protection. Banking being a service industry it is all the more important that there is a well defined and functional mechanism to ensure fairness to the customer. That is all what the Banking Ombudsman Scheme (BO Scheme) is about and that is what RBI does- without significantly backtracking on the freedom given to banks' boards to fx their rates and fees. In view of the fact that the Courts are restrained through an amendment to Section 21 A of Banking Regulation Act, 1949 from intervening in the matter of interest rates- usurious or otherwise - fxed by the banks to their debtors, it is ordained on RBI to ensure that the rates and service charges are reasonable, not usurious in all spheres of lending. The RBI, over the years, has undertaken a large number of initiatives on ensuring fair treatment to customers. This has taken the form of both regulatory fats ( like reining in of recovery agents, introduction of comprehensive display board, banking facilities for the visually challenged, rationalization of service charges on collection of outstation cheques, free use of ATMs etc ) as also moral suasion and class action. A minimum standard of banking practices for banks to follow when dealing with individual customers was established on introduction of the Code of Bank's Commitment to Customers in July 2006. However, a number of challenges still need to be addressed to make customer services responsive to the 'small customer'. The actions taken by the RBI so far do not in any way dwarf the challenges that confronts us in regard to fair treatment of customers. There is a sharp asymmetry in information and expertise between the manufacturers and distributors of products and retail investors and the latter typically exhibit a relatively low level of financial sophistication. The act of 'packaging' investments / sale of products can increase this asymmetry, for instance, by adding complexity that makes key investments / service characteristics less transparent and introducing additional layers of cost which may not be readily apparent. The Banking Ombudsman Scheme introduced by RBI in 1995 attempts to bridge this information and expertise asymmetry between the banks and the end user of their products and services. Having given freedom to the bank boards to decide on many issues, RBI should not be compelled by omissions and commissions by commercial banks to issue directives to them. However, there are a few ground rules which every commercial bank should be compelled to follow: a. Minimum courtesy and behavioral standards - Extending minimum courtesy and proper behavior towards customers is one of the guiding principles and banks should follow a 'zero-tolerance' policy towards misbehavior. The Customer Service Committees at all levels need to adopt aggressive stance in this regard. b. Transparency - A minimum standard needs to be adopted towards fostering transparency by making MITC (Most Important Terms and Conditions) mandatory for all retail products. A sign off should be obtained from the customer on understanding of the MITC. While MITC for credit card products has already been introduced, RBI is in active dialogue with the Indian Banks Association regarding MITC for all lending and deposit products. Also, these MITCs should be in regional languages as far as possible. Secondly, there should be transparency in pricing products and services. Banks should come out with transparent pricing based on cost of deposits plus risk premia plus spread and the same should be conveyed to the customer at the point of sale. If there is a change in pricing during the tenure of the product, the same should only be on reaching mutually agreeable milestones. c. Non-discriminatory policy - Banks should establish a basic standard of non-discriminatory pricing. This is based on the premise that 'new' customers cannot get preferential treatment over the 'old' customers if in the same risk category. Non-discriminatory policy should be observed in pricing as well as establishing standards of services and implementation of services. d. Deliver what is promised - There will always be customer service related problems, but when problems are brought to a bank's notice, priority should be given to solving the problems. There is a need to set up internal benchmarks and escalation policies with regard to customer complaints. e. Allowing seamless 'switching'
- The consumer should be able to
change products or switch products
without incurring excessive penalty.
Similarly, banks should not make it
unnecessarily difficult for consumers
to make claims or to complain when f. Appropriateness of 'sell' - Products and services need to be designed with the targeted customer segment in mind. The customers should be targeted appropriately, to minimise the risk that marketing might prompt customers who are unsuitable to buy such products. g. Unreasonable customer demand - When banks find that a customer is unreasonable, they should take a firm but polite stand that what he/she wanted could not be accepted for some particular reasons. The above seven tenets should form the guiding principles towards resolution of customer grievances. The ultimate aim of regulation is to move towards an outcome based approach where customer outcomes can be quantitatively measured and regulatory response formulated accordingly. While introducing a more cumbersome regulatory regime is not our objective, it may be needed to tie-up customer experience outcomes to regulatory capital. Looking forward, a customer service rating based approach with quantitative parameters ultimately linked to its capital can serve such a purpose. The Offices of the Banking Ombudsmen have been rendering excellent service over the years in redressing customer grievances in an impartial and efficient manner. During the year 2008-09 the Banking Ombudsmen received 69117 complaints as against 47887 complaints received in the previous year (an increase of 44% ) and disposed off 87% of the total complaints (89% in the previous year ). 10% of the pending complaints were more than 2 months old as on June 30, 2009, as against 15% during the previous year end. The offices of the Banking Ombudsmen received increasing number of complaints from rural and semi-urban areas during the year 2008-09. This is a testimony to the success of the awareness efforts undertaken by the Banking Ombudsmen as well as the RBI through personal/ village visits, media campaign etc. While the number of complaints from rural areas increased by 65%, complaints from the semi-urban areas increased by 48%,which can be well compared against the aggregate increase of 44% in the number of complaints during the year 2008-09. As Appellate Authority, I notice that there is a discerning trend in appeals made by the customer- he understands the issues and he makes a pointed appeal to rectify the service deficiency and it is a welcome trend. The BO Scheme revised on May 24, 2007, made a provision for appeals by either party. The increased number of appeals indicates that the customer understands the BO Scheme fairly. I am sure the office of the Banking Ombudsmen will continue to play a stellar role in mitigating the challenges - existing and anticipated. (Dr.K.C.Chakrabarty) November 16, 2009 Vision and Goals of the Banking Ombudsman Offices Vision Statement
Goals
Customer Service Initiatives by the Reserve Bank of India over the years The deregulation of interest rates and product pricing by banks in India was followed up by the RBI with certain institutional, regulatory and infrastructural changes. A summary of the important initiatives taken by the RBI for improvement in customer service rendered by banks is detailed below:-
PROFILE OF CUSTOMER COMPLAINTS RECEIVED AT BO OFFICES
The Banking Ombudsman Scheme 2006 1. The word ‘Ombudsman’ (‘ahm’ ‘bedz’ ‘man’) in general means a public official who is appointed to investigate the citizen’s complaints against the administration. He is to intervene for the ordinary citizen in his dealings with the complex machinery of the establishment. In India, any person whose grievance against a bank is not resolved to his satisfaction by that bank within a period of one month can approach the Banking Ombudsman (BO) if his complaint pertains to any of the matters specified in the Scheme. Banking Ombudsmen have been authorized to look into complaints concerning (a) deficiency in banking service (b) sanction of loans and advances in so far as they relate to non-observance of the RBI directives on interest rates, delay in sanction or non-observance of prescribed time schedule for disposal of loan applications or non-observance of any other directions or instructions of RBI as may be specified for this purpose from time to time, and (c) such other matters as may be specified by RBI. The Scheme envisages expeditious and satisfactory disposal of customer complaints in a time bound manner. The BOs on receipt of any complaint endeavors to promote, if necessary, a settlement of the complaint by agreement between the complainant and the bank named in the complaint through conciliation or mediation. For the purpose of promoting a settlement of the complaint, the Banking Ombudsman has been allowed to follow such procedures as he may consider appropriate and he is not bound by any legal rule of evidence. If a complaint is not settled by agreement within a period of one month from the date of receipt of the complaint or such further period as the Banking Ombudsman may consider necessary, he may pass an Award after affording the parties reasonable opportunity to present their case. He shall be guided by the evidence placed before him by the parties, the principles of banking law and practice, directions, instructions and guidelines issued by the RBI from time to time and such other factors, which in his opinion are necessary in the interest of justice. The Amendment vide notification dated February 3, 2009 As per the Notification dated February 3, 2009, the scope of the Banking Ombudsman Scheme 2006 was widened to include deficiencies arising out of internet banking. Under the amended Scheme, a customer would also be able to lodge a complaint against the bank for its non-adherence to the provisions of the Fair Practices Code for lenders or the Code of Bank's Commitment to Customers issued by the Banking Codes and Standards Board of India (BCSBI). Further, non-observance of the RBI guidelines on engagement of recovery agents by banks has also been brought specifically under the purview of the Scheme. The amended Scheme, however, does not include certain banking transactions, such as, failure to honour bank guarantee or letter of credit, etc. since complaints on these areas of banking services are insignificant in number. The extant provisions allow the Banking Ombudsman to award compensation for the actual loss suffered by the complainant as a direct consequence of the act of omission or commission of the bank or Rupees ten lakh whichever is lower. As per the amended Scheme, the Banking Ombudsman can also award compensation not exceeding Rupees one lakh to the complainant in the case of complaints arising out of credit card operations, taking into account the loss of the complainant's time, expenses incurred by him as also harassment and mental anguish suffered. Any customer who has a grievance against a bank can complain to the Banking Ombudsman in whose jurisdiction the branch of the bank complained against is located. Some banks have centralised certain transactions, like housing loans, credit cards, etc. If there are complaints regarding such transactions, complaints would have to be made to the Banking Ombudsman in the State in which the bank customer receives the bill/ monthly statement. In addition, the RBI has simplified the format for lodging complaint to the Banking Ombudsman. Though the complainant need not lodge his complaint in a specific format, the Scheme now provides for an easy-to-fill format for lodging complaints, in case complainants prefer to use it. The jurisdictions of the Banking Ombudsman at Kanpur, New Delhi, Chandigarh, Chennai and Thiruvananthapuram have been rationalized to include/exclude certain areas taking into account the geographical proximity of those areas to the Office of the Banking Ombudsman. For wider dissemination, the RBI has asked all banks to place a copy of the Banking Ombudsman Scheme on their website. Causes of Complaints Any person, whose grievance against a bank is not resolved to his/her satisfaction by that bank within a period of one month, can approach the Banking Ombudsman if his complaint pertains to any of the matters alleging deficiency in banking including internet banking as specified in the Scheme. The matters include (a) non-payment or inordinate delay in the payment or collection of cheques, drafts, bills etc.;(b) non-acceptance, without sufficient cause, of small denomination notes tendered for any purpose, and for charging of commission in respect thereof; (c) non-acceptance, without sufficient cause, of coins tendered and for charging of commission in respect thereof; (d) non-payment or delay in payment of inward remittances ; (e) failure to issue or delay in issue of drafts, pay orders or bankers’ cheques; (f) non-adherence to prescribed working hours; (g) failure to provide or delay in providing a banking facility (other than loans and advances) promised in writing by a bank or its direct selling agents; (h) delays, non-credit of proceeds to parties' accounts, non-payment of deposit or non-observance of the RBI directives, if any, applicable to rate of interest on deposits in any savings, current or other account maintained with a bank ; (i) complaints from Non-Resident Indians having accounts in India in relation to their remittances from abroad, deposits and other bank-related matters; (j) refusal to open deposit accounts without any valid reason for refusal; (k) levying of charges without adequate prior notice to the customer; (l) non-adherence by the bank or its subsidiaries to the instructions of RBI on ATM/Debit card operations or credit card operations; (m) non-disbursement or delay in disbursement of pension (to the extent the grievance can be attributed to the action on the part of the bank concerned, but not with regard to its employees); (n) refusal to accept or delay in accepting payment towards taxes, as required by Reserve Bank/Government; (o) refusal to issue or delay in issuing, or failure to service or delay in servicing or redemption of Government securities; (p) forced closure of deposit accounts without due notice or without sufficient reason; (q) refusal to close or delay in closing the accounts; (r) non-adherence to the fair practices code as adopted by the bank and (s) non-adherence to the provisions of the Code of Bank's Commitment to Customers issued by Banking Codes and Standard Board of India and as adopted by the bank (t) non-observance of RBI guidelines on engagement of recovery agents by banks; and (u) any other matter relating to the violation of the directives issued by the RBI in relation to banking or other services. In respect of loans and advances, complaints relating to (a) non-observance of RBI Directives on interest rates; (b) delays in sanction, disbursement or non-observance of prescribed time schedule for disposal of loan applications; (c) non-acceptance of application for loans without furnishing valid reasons to the applicant; (d) non-adherence to the provisions of fair practices code for lenders as adopted by the bank or Code of Bank's Commitment to Customers, as the case may be (e) non-observance of RBI guidelines on engagement of recovery agents by banks; and (f) non-observance of any other direction or instruction of the RBI as may be specified by the RBI for this purpose from time to time.
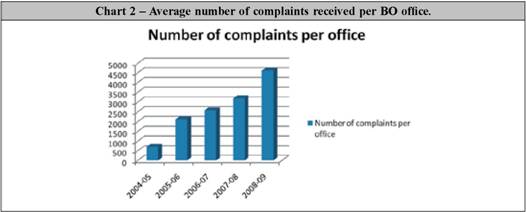
3.1 The Banking Ombudsman Offices receive complaints pertaining to deficiency in service provided by banks. The number of complaints received has increased substantially over the years and this trend is maintained during the year 2008-09 also by recording an increase of 44% over the previous year. The number of complaints received has recorded substantial increase since 2006 as new grounds of complaints such as credit card issues, failure in providing the promised facilities, non-adherence to fair practices code and levying of excessive charges without prior notice, etc were included in the Scheme. Further, internet banking related complaints were added as a new ground for complaint as per amendment of the Scheme dated February 3, 2009. Increased awareness among the public about the BOS and online accessibility to BO office through internet also contributed to the increase in receipt of complaints.
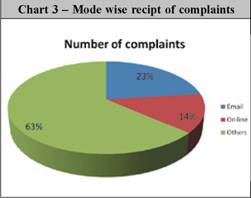
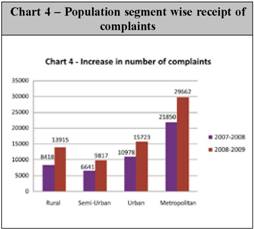
Mode-wise receipt of complaints 3.2 Complainants can log on to the RBI web site at “www.rbi.org.in” and complain about deficiency in bank’s services by using the online complaint form. The email ids of the Banking Ombudsmen are also available in the public domain and complainants can send emails to them. For those who have no access to internet, complaints can be sent by post. Complaints received are acknowledged and tracked till they are closed in the books of the Office of the Banking Ombudsman. During the year 2007-08 and 2008-09, the complaints received by different modes are as under: Though 63% of complaints received during 2008-09 are through letters, post-cards etc, the receipt in the electronic mode has been slowly picking up. Email complaints increased from 15% to 23% of the total complaints between 2007-08 and 2008-09. The Complaint Tracking Software in place in the Banking Ombudsman Office gives acknowledgement automatically and complaint number is given as soon as it is taken into the book of the Banking Ombudsman. The Complaint Tracking Software is updated from time to time to meet the changing requirements related to complaints. Population-segment wise Receipt 3.3 The offices of the Banking Ombudsmen received increasing number of complaints from rural and semi-urban areas during the year 2008-09. This is a testimony to the success of the awareness efforts undertaken by the Banking Ombudsmen as well as the RBI through personal/village visits, media campaign etc. While the number of complaints from rural areas increased by 65% during the year 2008-09, complaints from the semi-urban areas increased by 48%. These figures can be well compared against the total increase in the number of complaints by 44%. The region wise position of complaints is given below: Complainant group-wise Receipt 3.4 The majority of complaints are from individuals as seen from the break up given below. There is no substantial change regarding the source of complaints as compared to previous years. Since the Scheme is primarily meant for common individual customers, the focus continues to remain on the non-institutional category. Banking Ombudsman-wise receipt 3.5 The 15 Offices of the Banking Ombudsman receive and consider complaints from customers relating to the deficiencies in banking services in respect to their territorial jurisdiction. The revised territorial jurisdiction is given in Annex-1. During 2008-09, higher number of complaints were received by the BO Offices in New Delhi(15%), Chennai (15%), Mumbai (14%)and Kanpur (11%) followed by Hyderabad(6%) and Ahmedabad (6%). Percentage wise, Chennai office witnessed the highest increase in the number of complaints (128%).
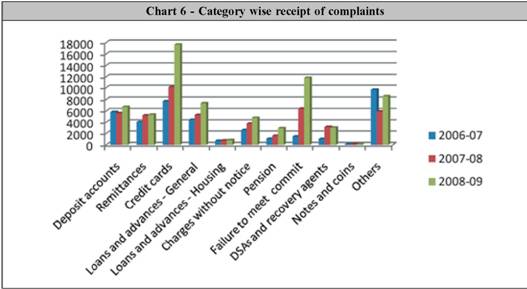
Enhancing Internal Grievance Redressal machinery of banks Bankers are required to place a complaint form in their home page on their website. With a view to enhance the effectiveness of the internal grievance redressal mechanism, banks were advised to place a review of complaints before their Boards / Customer Service Committees along with an analysis of the complaints received with effect from February 2007. The analysis should (i) Identify customer service areas in which the complaints are frequently received, (ii) Identify frequent sources of complaint, (iii) Identify systemic deficiencies and (iv) Make recommendations for initiating appropriate action to make the grievance redressal mechanism more effective. Details of complaints received and disposed off, awards passed and unimplemented awards of the Banking Ombudsman are required to be disclosed along with financial results. Banks were also advised in May 2008 to (i) Ensure that the complaint registers are kept at prominent place in their branches which would make it possible for the customers to enter their complaints, (ii) Have a system of acknowledging the complaints, where the complaints are received through letters / forms, (iii) Fix a time frame for resolving the complaints received at different levels, (iv) Ensure that redressal of complaints emanating from rural areas and those relating to financial assistance to Priority Sector and Government's Poverty Alleviation Programmes also form part of the above process, (v) Prominently display at the branches, the names of the officials who can be contacted for redressal of complaints, together with their direct telephone number, fax number, complete address (other than Post Box No.) and e-mail address etc. for proper and timely contact by the customers and for enhancing the effectiveness of the redressal machinery. 3.6 Bank Group wise receipt of complaints The complaints received by BO Offices against different bank groups are indicated below: Complaints vis-a vis business size 3.6 Instead of considering complaints in isolation, the number of complaints is seen with reference to the bank’s business size and the number of accounts and is analyzed as such. It is seen that the private sector banks and the foreign banks continue to have a larger share in the number of complaints vis a vis the total number of deposits and loan accounts. This may be due to the fact that these banks cater to customers who are more aware of their rights. The break-up of bank wise (scheduled commercial banks) complaints received in the year 2008-09 is given in Annex 4. 4.1 The grounds of complaints have been enumerated in Clause 8 of the Banking Ombudsman Scheme 2006. The following Table gives the broad category wise complaints received during the last three years:- 4.2 Complaints relating to credit cards (comprising 26% of the total complaints in 2008-09) continue to show an uptrend. The number of complaints pertaining to credit cards increased by 74% during 2008-09. While the user base of credit cards has definitely increased during 2008-09 (from 137.17 million to 170.03 million, i.e. by 24%), it does obviate the need for better service and transparency at the point of sales by banks. The types of complaints pertaining to credit cards continue to be those related to issuance of unsolicited credit cards and unsolicited insurance policies and recovery of premium charges, charging of annual fee in spite of being offered as 'free' cards and issuance of loans over phone, disputes over wrong billing, settlement offers conveyed telephonically, non-settlement of insurance claims after the demise of the card holder, abusive calls, excessive charges etc. A general source of these complaints continues to be difficulty in accessing the credit card issuers and the poor response from the call centers. This, in sum, is the issue of non-transparency and mis-selling. 4.3 Complaints relating to failure on commitments made (non-adherence to fair practices code as adopted by the bank, failure to provide or delay in providing banking facilities other than loans and advances etc) ranked second among the complaints received at the offices of the Banking Ombudsman (17% of the total complaints - an increase of 85% over the previous year). This points to the lack of sensitivity, transparency and need for improved MITC at the point of sales. As these complaints mostly relate to basic banking facilities, banks need to address these issues on priority basis without any demur. 4.4 ‘Other' complaints comprised 12% of the total complaints and increased by 45% during the year. These include mainly non-adherence to prescribed working hours, refusal to accept or delay in accepting payments towards taxes as required by RBI/ Government of India, refusal to accept/delay in issuing or failure to service or delay in servicing or redemption of Government securities, refusal to close or delay in closing of accounts. 5.1 A brief profile of the complaints disposed of by BO Offices during the year is given below:
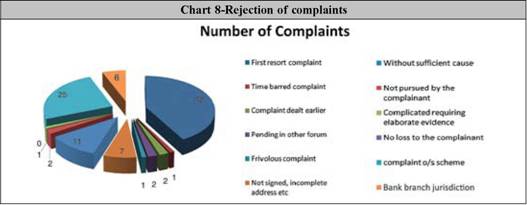
5.2 Banking Ombudsman Offices disposed of 87% (65576) of the 75009 complaints received during the year 2008-09, as against disposal of 89% of the complaints received during previous year. Broadly, around 35% (22461) of the complaints dealt with (65576) have been closed by mutual settlement or by issue of awards while 65% (43115) of the complaints have been disposed of citing reasons like : First resort complaints(27.73%), Complaints Pending in other forum(1%), Subject matter outside the BO Scheme(16.50%), Complicated complaint requiring elaborate evidence(1%), Complaint without sufficient cause(7.30%), Bank branches outside the BO jurisdiction (4.20%), etc as shown in Table 11. Non maintainable complaints were rejected at the initial scrutiny stage itself while other complaints were rejected only after due processing. In both the cases, however, copy of the complaint is endorsed to the bank concerned for redressal. Banks were generally prompt in redressing the cases forwarded to them. In several cases, banks have kept BO informed of the action taken thereon, by endorsing a copy of their resolution letter issued to the complainant. 5.3 Mode of disposal of complaints Mode of disposal of complaints (other than rejected complaints) during the years 2004 - 05 to 2008-09 is as under:- As many as 22,388 complaints were settled by mutual agreement during the year as compared to mutual settlement of 29,295 complaints during the previous year. BO offices issued 73 awards during the year. Lesser number of awards issued by the BOs may be attributed to the bank’s attempt to resolve the complaints before issue of awards, since receipt of awards is considered as un-desirable. 5.4 Conciliation meetings Conciliation meetings which enable two parties to meet “face to face” has played an important role in the process of resolution of complaints. Although, Banking Ombudsman does not force parties to come to settlement, such meetings facilitate them to come to their own solution rather than have a solution imposed on them by way of an award. During the year, as many as 22,388 complaints were settled by the BO offices after holding conciliation meetings and other persuasive efforts. Thus, the objective of the BO Scheme (expeditious and inexpensive resolution of customer complaints without having to examine elaborate documentary evidences) could be satisfactorily achieved to a large extent by promoting settlement by mutual consent. 5.5 Rejected complaints
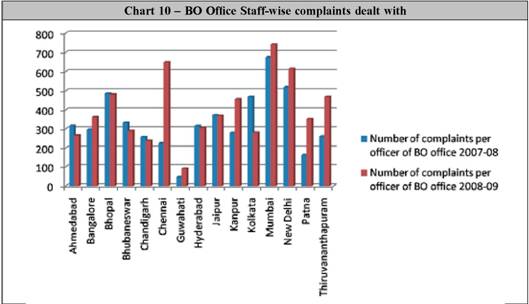
Although as much as 43,115 complaints were shown as rejected during the year, it may be mentioned that, as stated in paragraph 5.2, in most of these cases, the Scheme could provide relief to the complainant to a large extent by way of reversal of bank charges, overdue interest, over limit charges, partial settlement/ write off of overdue, etc during the process of resolution. 5.6 First resort complaints (42%) First resort complaints accounted for the highest percentage of complaints rejected (42% in 2008-09 as against 40% in 2007-08). High percentage of first resort complaints indicates greater faith of the complainants in the institution of the BO Scheme rather than in their banks or the inept handling of customer’s complaints by front line staff in the banks. While this highlights the marked increase in the customer awareness about the BO Scheme, it also points to the requirement of educating the public to lodge their complaints first with the bank concerned, and to approach the BO later, if they are not satisfied with the response from the bank. While rejecting such complaints, one copy of the complaint is endorsed to the bank concerned. The banks were generally prompt in redressing such complaints forwarded to them. Thus, although no data is available as to the exact number of such complaints redressed, it is our experience that very few first resort complaints rejected by BOs were received back. It could be that the reference to BO has helped the complainants to get their grievances redressed from the banks concerned. 5.7 Complaints outside the BO Scheme (25%) The second-highest cause of rejection, viz. complaints outside the Scheme comprising 25% of rejected complaints, indicates that the customer awareness campaigns need to be more fine-tuned and focused. These complaints were also rejected after initial scrutiny. However, copies of these complaints, as in the case of first resort complaints, were endorsed to the banks concerned .In several cases, banks have kept BO informed of the redressal measures taken on these complaints. Some of these complaints were sent to other RBI departments like Department of Banking Supervision, Department of Banking Operations and Development, Department of Non Banking Supervision, Rural Planning and Credit Department, etc or other organizations like Securities and Exchange Board of India, Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority for redressal. 5.8 Complaints made without sufficient cause (11%) Complaints made without sufficient cause represent those complaints where the banks concerned may have acted as per the covenants of the products and service contracts. Here also the complaints will be processed as usual and a decision taken to reject the complaint as it was made without sufficient cause. 5.9 Rejection due to other reasons Rejection of such complaints will be done only after giving proper opportunities to both the parties and due examination of bank’s submissions. Meetings will be arranged, wherever necessary, and if the complaint cannot be resolved fully under the BO Scheme provisions, it will be rejected giving reasons like complicated complaint requiring elaborate evidence, no loss to the complainant, beyond the pecuniary jurisdiction of BO Scheme, etc. 5.10 Pending complaints at BO Offices As regards pendency, 13% of the complaints were carried forward to the next year as against 11% in the previous year. During the year 2008-09, 10% of the pending complaints were pending for more than 2 months and 7% of them were pending for more than 3 months (15% and 15% respectively in the previous year). This indicates a slight improvement in position. The complaints not accompanied by documentary evidence, unusually long time given to the concerned banks to respond to queries etc mostly contributed to the delay in disposing of the complaints. Disposal of Complaints staff wise 6. During the year under review, most of the SLBC staff have been repatriated back to their banks in a phased manner. To handle the increased number of complaints and as replacement for the SLBC staff, the Offices of Banking Ombudsman were given additional staff. The staff wise position of complaints handled is given in the following table :
7. The total expenditure in operationalizing the Banking Ombudsman Scheme was shared by the banks, in the proportion of their working funds, up to December 2005. From January 1, 2006, the expenditure is fully borne by RBI in terms of the revised Banking Ombudsman Scheme, 2006. The cost of the Scheme includes the revenue expenditure and capital expenditure incurred in running the Banking Ombudsman offices. The revenue expenditure includes the establishment items like salary and allowances of the staff attached to Banking Ombudsman offices and non-establishment items such as rent, taxes, insurance, law charges, postage and telegram charges, printing and stationery expenses, publicity expenses, depreciation and other miscellaneous items. The capital expenditure items include the furniture, electrical installations, computers/ related equipments, telecommunication equipments and motor vehicle. While the aggregate cost of running the fifteen Banking Ombudsman Offices has increased by 22% during the year under review, with the increase in the number of complaints dealt with, the cost per complaint dealt has declined by 15%. The details are given as below. Appeal against the decisions of the Banking Ombudsmen 8.1 The Banking Ombudsman Scheme 2006 permits banks and complainants to appeal against the decisions of the Banking Ombudsman. The Appellate Authority is the Deputy Governor in charge of the Banking Ombudsman Scheme and secretariat is provided by the Customer Service Department. The number of Appeals preferred by banks and complainants during the year 2007-08 and 2008-09 are as under: 8.2. The number of appeals received at Central office level by the Appellate authority (AA) is increasing steadily since the appealing facility was widened to cover all decisions of BO and that appeals can be submitted by both the complainant and banks since May 2007. AA has handled 301 appeals during the year as against 191 during the previous year, recording an increase of 57%. 251 out of 301 appeals were received from public and 18 appeals were received from banks. The AA has disposed 180 complaints during the current year as compared to 159 appeals disposed during the previous year.
Some Important Developments during the year 2008-09 9.1 Meeting of the Committee on Subordinate Legislation, Rajya Sabha on functioning of the Banking Ombudsman Scheme in the private sector banks and foreign banks Deputy Governor represented the Bank during the deliberations of the Committee on Subordinate Legislation on functioning of the Banking Ombudsman Scheme in the private sector banks and foreign banks. The Committee was headed by Dr Najma Heptulla, MP and the banks called for discussion were HDFC, Citibank, Standard Chartered Bank, Deutsche Bank and HSBC Ltd. 9.2 Standing Committee on Finance The Standing Committee on Finance under the Chairmanship of Shri Ananth Kumar, Member of Parliament convened a meeting at Pune on July 26, 2008 to discuss the matters regarding Customer Service in public sector banks. Bank of Baroda and Central Bank of India were invited for the discussions. 9.3 Up gradation of Complaint Tracking Software (CTS) The upgraded version of CTS package went live from July 1, 2009. The upgraded CTS package has provision to enter the complaints, acknowledge the complaints, edit the complaints to update it, upload/ down load supporting files in respect of a complaint by the banks, view complaint details, view status of complaints, etc. It is capable of generating reports like complaint received reports, complaint disposed reports, award issued reports, complaint pending reports, bank wise/ subject wise reports, non-maintainable complaints report, monthly /quarterly statements, etc. 9.4 Advertisement under series 'Jago Grahak Jago" An advertisement campaign on the Banking Ombudsman Scheme has been released by the Bank in collaboration with Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food & Public Distribution, Government of India as a joint campaign under the 'Jago Grahak Jago' series. A massive advertising & visual publicity campaign on the Banking Ombudsman scheme had been carried out in both print and electronic media. This publicity will help in elevating awareness about the BO Scheme among the common people. In addition, banks were instructed to display details of the BO Scheme in all bank branches for the benefit of their customers. 9.5 PGRC portal Department of Administrative Reforms and Public Grievances (DARPG), Government of India, with technical support from National Informatics Center (NIC) has developed a Public Portal viz. Centralized Public Grievances Redressal and Monitoring System (CPGRAMS) for prompt and effective redressal of grievances of citizens. The System is to record and receive the grievances online and redress them indicating action at different levels. The Government of India is monitoring the System. All the Public Sector banks, Offices of the Banking Ombudsman, RBI, SIDBI, IDBI Bank, NABARD etc., have been listed by Government of India as subordinate Offices and given username and password to access the DARPG portal to enable them to dispose of the grievances against banks online. The Government of India intends to discontinue with the disposal of grievances in paper form in a phased manner. 9.6 Committee on Financial Education and Investor Protection headed by Chairman of PFRDA (Pension Fund Regulatory & Development Authority) A Committee has been constituted by GOI under the chairmanship of Shri D. Swarup, Chairman, PFRDA for deliberation on the issues of financial education and investor protection in the Indian financial market. RBI was represented by Shri G. Gopalakrishna, Executive Director as a member of the Committee. The first meeting was held on March 30, 2009 and subsequent meetings were held at periodic intervals. The Committee has submitted the report to GOI. 9.7 International Network of Financial Services Deputy Governor, Dr. K C Chakrabarty, has been nominated as a member of International Network of Financial Education and also member of International Network of Financial Services. All BOs have been registered with the network of Financial Services Ombudsman Schemes and receive regular bulletins where latest news is incorporated and important decisions are conveyed. This forms an important aspect of knowledge sharing and helps the Banking Ombudsmen in disposal of cases.  9.8 Class Action Certain omissions and commissions by banks in their dealing with the customers in matters of lending, other services including liabilities tend to be detrimental to the interests of the customers at times. When such instances are noticed by/ brought to the notice of the Regulator, corrective action in the form of general directions to all banks is taken so that the customers in general including the complainants are protected against such omissions and commissions. This is a proactive measure as against a reactive one in that the redressal is afforded not just to the complainant but to all those similarly placed without waiting for further formal complaints. RBI has initiated class action against a foreign bank regarding mode of calculation of interest rates on deposit accounts. A PSU bank was advised to recalculate interest rate on all the housing loans as per terms of the agreements entered into with all the borrowers without their application for relief. Yet another PSU bank was asked to recredit insurance premium which was debited to SB account holders without their concurrence under group insurance scheme. The Customer Service Department of the Bank, on the basis of news items appearing in newspapers or any other media takes proactive action by taking up the matter with concerned bank for corrective action even if no specific complaints are received. 9.9 Outreach activities carried out by BOs for creating awareness of BOS 2006 The growing popularity of the Banking Ombudsman Scheme, 2006 stems from its hassle- free accessibility as well as the credibility of its processes and outcomes. Nevertheless, there are vast chunks of bank customer base, which are not aware of the Banking Ombudsman Scheme or how to access its redressal mechanism. Therefore, awareness and sensitization of banks and their customers necessarily remain at the core of any meaningful initiative to empower the bank customer. Towards this end, a number of focused initiatives were pursued during the year across the entire country.
Exemplary Cases dealt with by BO offices where customers were right Case 1 The complainant had availed a housing loan of Rs 3,40,000/- from the bank at a fixed rate of interest of 8% per annum at quarterly rests on highest monthly reducing balance. The complainant alleged that the bank had subsequently increased the rate of interest to 12.75% contrary to terms of sanction of the loan. The bank submitted that the customer was sanctioned loan at fixed interest rate, but as per their extant instructions and internal circular, the interest rates are to be reset at the end of every two years on the basis of interest rates prevailing at that time. Accordingly, the fixed interest rates were changed from 8% to 12.75%. During the course of the proceedings before the Banking Ombudsman, the bank re-worked the applicable interest at the contracted rate of interest and refunded the excess amount of Rs 17,936/-, by credit to the complainant’s account. However, the bank contended that going forward, the reset interest rate would be applicable. The complainant was also given an exit option, which was not acceptable to him. If the interest rates are subject to periodical rests, it is only fair and reasonable that the same is explicitly stated in the loan agreement and sanction letter in an unambiguous and transparent manner. Further, in choosing to provide a fixed rate loan to the customer, the bank has consciously decided to carry the interest rate risk associated with the product. The loan also carried a higher interest rate compared to floating rate product as a premium towards the interest rate risk. BO passed an Award advising the bank to strictly abide by the terms and conditions of the original arrangement and not give effect to their proposal to increase interest rate on the loan, unless explicitly consented to by the complainant in writing. The bank was also advised to pay an amount of Rs 1,000 to the complainant towards the cost of pursuing this remedy to his grievance. The bank has implemented the Award. Case 2 The complainant was maintaining a current account and approached the bank to convert his current account to cash credit account. For the said purpose he had pledged NSC amounting to Rs.1,20,000/-. Subsequently the bank neither sanctioned him a cash credit limit nor returned the certificates. In the meantime the certificates were matured for payment and he requested the bank to return the certificates. The bank failed to return the certificates stating that the certificates had been misplaced. The complainant approached us with a request to redress his grievances. On taking up the matter with the bank, the bank assured to take up the matter with the post office for issue of duplicate NSCs. On receipt of the duplicate NSCs from the concerned post office, the complainant was compensated for the loss of the original certificates. The complainant submitted a letter of satisfaction to the BO. Case 3 A complaint relating to non-credit of cheque amount into the account of the complainant was received. The complainant had reportedly taken up the matter with the bank several times but there was no response by the bank towards credit of the cheque amount. The complainant approached the BO for resolution of his grievances. On receipt of the complaint, BO questioned the bank as to what action had been taken on the complaint by them. The bank reported that the cheque in question was lost in transit resulting in non-credit of the cheque amount to the complainant’s account. At the instance of BO, the bank took up the matter with UTI Mutual Fund, Patna by submitting letter of undertaking and death certificate. The Mutual Fund issued a duplicate cheque and the amount was credited to the complainant’s account. The complainant submitted a letter of satisfaction. Case 4 A complainant approached the BO alleging that the bank from which he had availed a housing loan had been charging a higher rate of interest . Initially he applied for a housing loan of Rs.8,50,000/- at the fixed rate of interest. The rate of interest applicable on the loan was 9.25% as per the brochure provided by the bank. However, the complainant alleged that the loan was sanctioned at an interest rate of 9.75% without explaining about the terms and conditions of the loan at the time of sanction. On taking up the case with the bank, the bank informed BO that the higher rate of interest charged on the loan had since been rectified by the bank’s data center and excess interest charged on the loan was adjusted and credited to the complainant’s account. Case 5 BO received a complaint where the complainant alleged that on her husband’s death, she approached the concerned bank on November 27, 2008 for payment of family pension and all the formalities were completed as required by the bank. The Treasury Officer had converted the pension into family pension and advised the bank on October 18, 2008 to make payment to the widow. Though she had been approaching the bank there was no response from the bank. BO questioned the bank as to what action had been taken by them on the complaint. On persuasion, the bank redressed the grievances and paid the family pension to the complainant. Case 6 The complainant was maintaining Priority Banking Savings accounts with a private sector bank. This account was opened a year back with average quarterly balance requirement of Rs.1 lakh and the customer was promised several services, which were allegedly not provided to him. These services included cheque collection from his residence, valet parking at the branch, use of office for personal meetings, credit card facility, demat services, portfolio services and timely response to transaction queries. It was observed that the bank had introduced the priority banking service product without first ensuring that its branches were properly equipped to provide the promised services to all such customers. The bank was also found deficient in as much as it had not communicated to the customer the various conditions linked to the promised services. It was not considered fair that the customer was made to maintain an average quarterly balance of Rs. 1 lakh without providing all the promised services. Thus, had the customer maintained a normal savings bank account with average quarterly balance requirement of Rs.5000/-, he would have had an opportunity to invest Rs.95,000/- in fixed deposit to earn higher interest. BO passed an award against the bank for payment of interest at fixed deposit rate of interest applicable at the time of opening the account plus 2% (with quarterly compounding) from the date of opening of account to the date on which the bank pays the interest. Case 7 A cheque drawn by the EPF Department on the ABC Bank’s Nasik branch for Rs.21.36 lakh was sent to XYZ Bank, New Delhi for credit to the account of the complainant. The amount was not credited to the complainant’s account advising that it had not received the cheque. The complainant, however, obtained the Proof of Delivery from Post Office in support of the claim that it was delivered to the XYZ bank.. It transpired that the XYZ bank had actually misplaced the cheque before sending it for collection to ABC Bank and it had already furnished an affidavit to the EPF Department reporting the misplacement of the cheque and requesting for a duplicate cheque. With the intervention of BO, the bank credited an amount of Rs.18,894/- as interest on the delayed payment since date of deposit of the cheque. Case 8 The complainant was holding a credit card of a foreign bank. He complained that a caller from the bank persisted in selling Medical Insurance Benefit Scheme to the card holder though he as well as his family members did not require the same. After a few days he received a policy in the name of his son and daughter without taking his approval. When he called up the bank in June 2006, he was assured that the policies would be cancelled and later it was confirmed as well. But after a few days, he was advised to send a cancellation request by fax. The statement received showed unpaid balance. The complainant again sent two faxes in August and September 2006 for cancellation of the policies. In the conciliation meeting held by BO on 19 January 2009, the bank official stated that there was a recorded telephonic conversation with an Insurance Company and the bank had debited the account of the customer on the mandate received by the Insurance Company. There was no written mandate with the bank from the customer for debiting his account for premium of the policies of the Insurance Company. The bank failed to resolve the complaint for 2/3 years. However, with the intervention of BO, the debits of Rs.23,246/- were reversed. Case 9 The complainant maintaining an account at Bank A attempted a withdrawal of Rs.25,000/- from Bank B’s ATM, but no cash was dispensed. However, his account was debited. He immediately complained to Bank A and then to Banking Ombudsman subsequently. Bank A retrieved the JP log of 20.4.2008 from Bank B, which was not legible and confirmed that the transaction was successful. However, BO observed that the JP log appeared to be of 20.1.2008 and not of 20.4.2008, the reply was that actually the digit was 4 but appearing as 1 because of faulty printing. As we were still not convinced and insisted for a legible copy of JP log, Bank A informed after one month that they had received the amount from Bank B and the complainant’s account had been credited. In fact, Bank B had possibly misinformed Bank A. Case 10 An employee of a PSU had availed a housing loan of Rs 385000/- from XYZ Bank, under the tie-up arrangement between the bank and the PSU. The loan was offered at fixed rate of 7.5%. The bank subsequently increased the rate of interest from 7.5% to 8.5% and changed the EMI. When the matter was taken up with the bank, he was informed that as per the terms and conditions and the MOU, the fixed rate applicable for housing loan is ‘adjusted interest rate’ on the date of the agreement. The ‘adjusted interest rate’ was ‘quoted rate’ +/- changes in the BPLR of the bank on the date of agreement between the bank and the employees of the PSU. At the time of sanction of the loan, the BPLR was 11.50% so the ‘adjusted interest rate’ would be 8.5% and therefore the bank had charged the interest accordingly which would be reset after 5 years i.e. from 26.9.2006. As the bank’s response was not convincing, he approached the BO. On calling for their comments, the bank informed that they were charging the interest in terms of the MOU entered between the bank and the PSU and that it was in sync with the terms and conditions of the loan. BO advised the bank to furnish copies of the sanction letter, agreement with the complainant and copy of the MOU. On scrutinizing the aforesaid documents, it was observed that the rate of interest mentioned in the agreement at clause 7 was 8.5% (Fixed) and at clause 6 which was applicable to Floating rate, no entries were made. The sanction letter indicated 8.5% at fixed rate for 5 years to be reset after 5 years. Scrutiny of housing loan passbook disclosed that the bank was charging 7.5 % fixed interest from November 26, 2006 for 168 months at an EMI of Rs 3710/-. The bank had not carried out the documentation of the loan properly, as there was a discrepancy in the housing loan passbook and the agreement with respect to rate of interest. The increase in EMI was not justifiable. Therefore, BO passed the benefit of doubt to the complainant and directed the bank to consider the rate of interest at 7.5% fixed for 5 years and reset thereafter and refund the excess EMI recovered. Bank complied with the order of BO. Case 11 A complaint was received by BO from an exporter in China. They had consigned Mulberry Silk to a company at Bangalore during May 2008. The payment was to be made by the ABC Bank, Bangalore on DP basis. Payment was not forthcoming despite requests and personal visits. The matter was taken up with senior officials of the bank with a view to uphold the image of the country and the Indian financial system. With the intervention of this forum, the payment of USD 78466.77 was made by the bank in a short span of time not withstanding the fraud of larger proportion at the branch. The overseas exporter overwhelmed by the involvement of all functionaries, appreciated BO profusely. Case12 A complainant approached the BO regarding return of her ECS payment despite holding sufficient balance in her account. Two banks were involved in the complaint. The receiving bank maintained that the ECS was not honoured by the complainant’s banker and produced a copy of return memo. Subsequently, on the complainant taking up the matter, the complainant’s banker issued a certificate that credit has been passed to the receiving bank. However, the receiving bank denied having received the credit. Because of the dispute between the two banks, the complainant was left high and dry. BO called the officials of both the banks and held a meeting and advised them to investigate the matter immediately. The complainant’s banker at last located the credit which was lying with their service branch. Thus, it came to light that the bank had issued the certificate without conducting adequate internal enquiry. The complainant’s banker was, therefore, advised to pay interest for the period of delay besides tendering apology to the complainant for misrepresentation of facts and inconvenience caused to its customer (complainant) Case 13 A complaint was lodged by a borrower of a nationalized bank who had availed a housing loan of Rs.5.00 lakh along with her husband as a joint applicant during the year 2004. In the year 2005, the bank had introduced a mortgage redemption insurance scheme and directed the complainant to insure themselves under the scheme as it was compulsory and debited their HL account with Rs.15746/- and EMI was accordingly readjusted. After the demise of her husband in 2008, she approached the bank with a request to adjust the insurance cover taken by them and close the loan account. However, the bank replied that the premium debited to her HL was not remitted to LIC of India inadvertently and hence no policy was issued. Further, they also stated that as per their Head Office instructions on the subject only the first borrower was covered under the scheme i.e. the borrower herself. Since the matter was not resolved, a conciliation meeting was held. The bank argued that the scheme was introduced in 2005 and it was not compulsory as stated by the complainant, but was optional. BO enquired the bank as to whether this fact was brought to the notice of the complainant for which the bank replied that there were no records available in the bank to indicate that contents of the scheme were brought to the notice of the complainant. BO took a stand that the details of the scheme should have been brought to the notice of all the eligible constituents of the bank and observed that there was wide communication gap in the bank. Further, BO wanted to know why the premium recovered from the borrower was not remitted to the LIC of India and where was the premium recovered from the complainant parked during the three years. The bank stated that the premium was held in their ‘Suspense A/c’. BO took the stand that the bank was grossly negligent in not remitting the premium recovered from the complainant. It should have shown more diligence and asked the bank to credit the insured amount to the HL account of the complainant for closing as on the date of death of her husband and refund any excess amount remitted/charged thereafter to the complainant within 15 days. Since the bank did not comply with the resolution, BO later passed an award. Case 14 The complainant was a school teacher. His salary account was maintained with a bank branch. The bank issued an ATM Card to the complainant. One day he found that his ATM Card along with a slip having the PIN was lost. Immediately, he lodged an FIR at the nearest Police Station. He reported the matter at the concerned bank branch requesting for deactivation of the Card. The branch informed him that the lost card had been deactivated and issued him a new ATM card. Two months later, a loan was sanctioned to him by the branch and the amount was credited to his account. However, he found that the entire loan amount was withdrawn by somebody by using the lost card. He immediately made a complaint at the bank branch and claimed from the bank the amount withdrawn by miscreant using the lost card. The bank branch, however, rejected his claim stating that he was in fault for divulging the PIN to fraudster deliberately or intentionally violating the standing instruction regarding the secrecy of the PIN, which was stated to be a contributory negligence on the part of the complainant. Being unsatisfied with the response of the bank, he lodged a complaint before the BO against the branch. On hearing both the sides, the BO came to the conclusion that, the bank branch failed to de-activate the lost card as soon as the matter was brought to their notice. The mis-deed could have been averted if the bank had de-activated the lost card immediately which was, however, de-activated only after fraudulent withdrawals were brought to the notice of the bank. BO passed an Award in favour of the complainant ordering the bank to pay the compensation to the complainant to the extent of amount of unauthorized withdraws along with interest with Fixed Deposit rate on the amount for the period from the date of fraudulent withdraws till the date of the payment of compensation. Case 15 A complainant (a firm) alleged that the bank suddenly debited Rs. 2.42 lakh in December 2007 and Rs. 6.75 lakh in January 2008 in its current account towards service charges (transaction charges, cash denomination charges etc.) as against usual monthly charge of Rs. 0.15 lakh. On enquiry, the bank told that the service charges were revised in the month of October 2007. The complainant claimed that the bank did not inform revision of charges in advance. Further, when the complainant wanted to change the account type to the one having lesser charges, the bank told it to wait till the end of quarter as the change will be effective from start of a quarter. The bank charged him Rs. 12 lakh (approx) till March 2008. The bank claimed that it informed the revised charges through notice placed on its notice board. In the conciliation meeting the bank failed to furnish any supporting document to substantiate its claim of having informed revised charges in advance. The bank was unable to justify its stand that the customer can change the account type only w.e.f start of a quarter as in the instant case it led to forced payment of charges till end of quarter. The bank was directed to not levy revised charges from October 2007 till March 2008 as it is deficient in not intimating the complainant in advance about the revision in charges for the services rendered by it. The bank complied with the order. Case 16 A complainant claimed that she had Rs. 5.56 lakh in her SB account in May 2006 and when she checked the balance after a year, more than Rs. 5.5 lakh is withdrawn without her knowledge. She claimed that she was out of the city during the period and she did not withdraw the amount. The bank claimed that the amount was withdrawn in regular installments between 25th August and 17th November 2006 through ATM. The complainant claimed that she neither applied for ATM card nor used it. The bank stated that it issued the ATM card on verbal request from account holder. The PIN for the ATM card was delivered to the person who approached the bank for the same along with the ATM card and claiming to be the husband of the account holder. As the bank issued the ATM card and the PIN without any request / authorization from the account holder, it was directed to make good the loss suffered by the account holder. The bank complied with the order. Case 17 A bank sanctioned term loan of Rs 2.25 crore to the complainant at 8% rate of interest with the condition that interest shall be repriced every year on the anniversary date of disbursement and it will be linked to the 364 days T-bill rate on the date of repricing. The first reprising was to be done after two years. The complainant alleged that the bank increased the rate of interest six times in three years. The bank claimed that in accordance with the provision in the loan agreement for the bank to revise the terms of loan repayment, it changed the linkage of loan to BPLR instead of T-Bill and it had informed the complainant through a letter sent by courier though it could not produce the POD or any other document. The complainant denied receipt of the letter. We concluded that a provision in agreement to change repayment terms of loan does not entitle the bank to unilaterally change the mode of repricing loan and it failed to inform complainant before effecting the change. Thus, complainant had no opportunity to exit the loan when the terms are changed by bank to his disadvantage. The bank’s action was not in keeping with the terms of loan sanction accepted by the borrower and the terms were changed by the bank without the consent of the borrower and it was directed to pay the difference in interest charged on the loan availed by the complainant. Bank paid an amount of Rs 11, 85,309.29 to the complainant. Case 18 Two complainants, husband and wife invested Rs. Five lakh and Rs. Ten lakh respectively under Capital Gains Account Scheme 1988 (CGAS 1988) for three years, with ‘C’ bank on July 20, 2004, being the proceeds of sale of property. They alleged that the rate of interest offered at the time of investment was 10.5% p.a. and the same was also stated in the FD receipts duly signed by the bank officials. However, at maturity, the bank claimed that the rate of interest on FD receipts was mistakenly stated as 10.5% p.a. and it paid interest at 5.5% p.a. only. The complainants sought relief that the bank be directed to pay them the amount of difference in interest and a reasonable compensation for the mental agony. ‘C’ bank submitted that the complainants initially deposited the subject amount in Fixed Deposit (FD) for a period of 91 days which carried an interest rate of 5.5% p.a. The deposits were foreclosed before maturity and kept in the CGAS for a period of 3 years. The interest rate was mistakenly mentioned as 10.5% p.a. in the said fixed deposit receipts since the interest rate was not corrected from the old rate of 10.5% p.a. to the ruling rate of 5.5% p.a. (applicable for the Capital Gains Account) in the computer (system). The bank acknowledged its mistake. The bank also contended that the rate of interest on the CGAS deposits made for a period of three years was fixed at 5.5% p.a. w.e.f. 01.01.2004 as applicable for other deposits. The said rate of interest was applicable till 14.11.2004. They invested the sale proceeds of their property in CGAS to avail tax benefit from Capital Gains Tax. The scheme does not provide for double benefit by way of tax exemption and higher rate of interest for the investment. As per the RBI guidelines, with effect from October 22, 1997, banks were free to fix their own interest rates on domestic term deposits of 30 days and above and the RBI has directed that individual banks should adopt uniform rates at all their branches and for all customers. The bank cannot discriminate the payment of interest among its own customers as per the RBI guidelines. The issue to be decided was whether the bank should pay the committed rate of interest to the customer as claimed by the complainants or the claim of a bonafide mistake by the bank be accepted. It was observed from both the application forms for deposit submitted by the complainants to the bank and the deposit receipts issued by the bank that Capital Gains Account was clearly mentioned thereon. Thus, the complainants intended to avail the benefit of tax exemption on capital gains on the proceeds of the sale as per the Capital Gains Account Scheme formulated by the Central Government. As per Para 8 of the said Scheme, interest rate on the deposit is to be specified by the RBI from time to time. Further, in terms of RBI Circular DBOD No.Dir.BC.121 / 13.01.01 / 97 dated October 21, 1997 banks have been granted freedom to fix the rate of interest for term deposits of 30 days and above including under CGAS, 1988. On taking into account the facts that subject amounts were initially parked in another deposit account and subsequently deposited under the Capital Gains Account Scheme and that Capital Gains Account was mentioned on the deposit application forms and the deposit receipts, it was clear that the depositors were aware of the provisions of the Capital Gains Account Scheme. It was ascertained from certain other public sector banks that they were also offering interest rates in the range of 5.5% to 5.75% on such deposits in the relevant period. Payment of interest at a rate other than the uniform interest rate fixed by the bank for specific deposit accounts would lead to discrimination amongst depositors. Thus, even though the bank was at fault for not paying the committed amount, the complaint was rejected under clause 13(d) of Banking Ombudsman Scheme, 2006 as otherwise, it would lead to violations of the provisions of the RBI instructions to bank vide circular DBOD No.120 / 13.01.01 / 97 dated October 21, 1997 in terms of which banks have to adopt uniform interest rates at all their branches and for all customers. Case 19 A logistic management company preferred a complaint before the Banking Ombudsman against a bank that it has unreasonably and unilaterally recovered from them exorbitant amount of pre closure charges at the time of preclosure of the credit facilities availed by it and requested for refund of the excess preclosure amount. The bank stated that it charged pre closure charges as the term loan was pre-closed by the complainant after six months of sanction of the same, whereas the tenure of the loan was 5 years. The bank charged higher quantum of pre-closure charges due to the extraordinary economic condition prevailing at the time of loan closure. The bank had high cost of funds at the time of sanction of the facility and it faced low rates of return at the time of loan closure. Hence, higher rate of pre closure charge was levied on the complainant to cover the loss between cost of funds and returns thereon. The bank submitted its calculation sheets etc. In the loan agreement the pre closure charge is stated as 1% of the outstanding amount of loan. The bank tried to establish its claim for charging higher pre closure charges than the rate agreed to by the customer on the basis of the indemnity clause in sanction letter signed by the customer. As the loan agreement specifically states 1% pre closure charge, any higher rate charged by the bank is violation of the agreement. The bank was directed to consider the issue afresh and refund the excess amount of pre closure charges received from the complainant. The bank confirmed having refunded Rs.28,47,873.90 to the complainant towards the excess prepayment charges levied and the balance service tax amount will be refunded on receipt of the same from the tax authorities. Case 20 The complainant represented that the payment of insurance premium had not been authorized by her. Further, she informed that the insurance officials had not contacted her and she had not signed any insurance proposal papers. The bank officials informed that the bank had investigated the complaint and that the signature of the complainant appearing on the insurance company’s ‘authorization for payment through credit card’ tallied with the signature appearing on the application for credit card. On a careful examination of the complaint and the bank’s reply thereto, the BO observed that i) The card issuer (bank) debited the credit card account of the complainant solely on the basis of the ‘authorization for payment through credit card’ reportedly signed by the card holder and received by the bank/card issuer from the insurance company. ii) The signature appearing on the photocopy of the ‘authorization for payment through credit card furnished by the bank did not match with the signature of the card holder appearing on the other documents including the copy of the card application form submitted to this Office by the bank. The bank’s stand that the cardholder had signed the authorization was, therefore, not found substantiated. iii) The ‘authorization for payment through credit card’ form indicated the contact number of the cardholder as 9230506205, which was different from the phone number (9830159299) on the credit card application form. The bank was unable to convince the complainant that she had authorized the bank to debit the card account on account of the transaction in question as envisaged in para 8.14.1 (d) of the Code of Bank’s Commitment to Customers (BCSBI). Case 21 The dispute related to non-issuance of NOC by AB bank for which the complainant lodged a complaint with this Office. The complainant availed a loan from the AB bank in February 2006 which was to be repaid in 36 EMIs. The complainant made regular payment of EMIs but in respect of one EMI of Rs.1700/- for the month of July 2006 through the SB a/c of the complainant with another bank i.e. CD bank was debited by the same was not remitted to AB bank. Although all the EMIs were paid by the complainant, due to non-receipt of EMI of July 2006, AB bank declined to issue the NOC. A conciliation meeting was held in the BO Office in which the AB bank reiterated its stance. The CD bank's representatives admitted that they had debited the SB a/c of the complainant towards the EMI of July 2006 but due to some internal reasons it was not remitted to AB bank. The BO observed that due to delay in interbank correspondence the complainant/ bank's customer should not suffer and he directed the banks to settle the dispute between themselves amicably, if necessary, after due consultation with the higher authorities of respective banks. Immediately the CD bank's representative consulted his controlling authority over phone and told AB bank that it would remit the claimed amount in question to AB bank also, after consulting its higher authority, agreed for the settlement between the banks. Then the dispute was settled and within a week AB bank handed over the NOC to the complainant. Case 22 The complainant had alleged that a deposit of Rs 20,000/- made in his account by a known person was kept under lien by the bank and later on debited from his account without his knowledge. He had approached the BO requesting for direction to the bank for immediate credit of the amount to his account as it was illegally debited by the bank without prior intimation to him. The matter was taken up with the bank. The bank in its submission had stated that an amount of Rs 20,000/- was deposited by one person in favour of Y. The depositor had inadvertently mentioned the account number of the complainant instead of that of Y in the deposit slip. The bank had accordingly credited the money to the account number indicated in the deposit slip which happened to be that of the complainant. Subsequently, on receipt of a request letter from the depositor the bank could recognize its mistake and immediately marked a lien on the amount in the account of the complainant. The complainant’s account was thereafter debited under intimation to him. On perusal of the evidences such as deposit slip, request letter of the depositor etc. it was observed that the depositor’s name mentioned by the complainant was different from the name indicated in the deposit slip. Further, the amount was intended to be credited to another person although the account number of the complainant was inadvertently mentioned in the deposit slip. The bank instead of matching the name and account number while effecting the credit had relied on the account number mentioned in the deposit slip which was considered as a bonafide mistake. Therefore, a view was taken that the bank has every right to rectify an error committed by it provided it is a bonafide mistake and is backed by the mandate of the depositor. The fact that the amount was kept under lien for almost a month and the complainant was aware of it was found sufficient to establish that the bank’s action was with the full knowledge of the complainant. The matter was disposed in terms of clause 13 (d) of BOS 2006. Case 23 The complainant claimed to have lost his cheque book and one of his cheques for an amount of Rs 1,00,000/ was encashed within 3 hrs at a branch of the same bank located 100 kilometers away from the place where he had reportedly lost his cheque book. The complainant had lodged a FIR in the nearby police station on the same day. Accordingly, he demanded that the money may be refunded to him by the bank since it was fraudulently encashed by someone else without his knowledge. The bank submitted that the honour of the cheque by the bank was a valid one since the signature in the alleged lost cheque tallied with the specimen signature recorded at the bank. The bank received the information from the complainant regarding the loss after a lapse of three days. The bank also showed the video clippings of CCTV to the complainant to recognize the person taking the payment but he failed to identify the person. On the basis of the documents and submission made by the bank a view was taken that the matter required investigation from criminal angle and genuineness of the signature could be established only by making a reference to GEQD. Since adjudication of the matter would have required consideration of elaborate documentary and oral evidence the complaint was disposed in terms of clause 13 ( c) of BOS 2006. Case 24 In terms of an arrangement with X, the bank had collected an amount of Rs 20,47,007/- to be deposited in the account of X. A dacoity occurred just outside the premises of X and the entire amount was looted by the culprits. The bank had fled a criminal case in respect of the dacoity and decided not to credit the amount to the account of X since it was an unforeseen event and the matter was under investigation. Since the representatives of the bank had acknowledged the receipt of cash, X had taken up the matter with the bank requesting it to credit the said amount with interest to its current account. As the bank failed to credit the amount to its account despite repeated follow up X had preferred to lodge a complaint with the BO.. On perusal of the documents submitted by both the complainant and the bank, BO observed that the fact of acceptance of the cash by the bank is clearly established. The terms of the agreement between both the parties did not spell out the position for any unforeseen circumstances. The bank is expected to have obtained the transit insurance for such transactions. Accordingly, the bank’s stand to disown the liability was not in order. More ever, crediting the amount to the account of X is neither dependent upon the completion of the investigation by the police nor settlement of the claim by the Insurance company.Accordingly, an award was passed directing the bank to compensate the loss of X by crediting an amount of Rs 20,47,007/ along with the interest from the date of receipt till the date of credit in the account of X. The bank appealed before the Appellate Authority against the award which was dismissed and the award passed by the BO was accepted with a modification directing bank to credit only the amount in question( not the interest) to the account of X. The award has since been implemented. Case 25 The Credit Card Company had issued an additional credit card to the complainant who had never opted for it. The card holder had contacted the local card office and had requested for return of the card as he had never transacted on the original one and as such did not require the additional card. One person claiming to be an officer of the card company collected the card from him through his agent and assured to hand over a copy of the cancellation letter. However, the cancellation letter was never received by him. On the other hand he received a demand for payment of Rs.19487.50 for purchasing petrol from different petrol pumps of the city. The complainant had also received a legal notice from the card company on account of bouncing of a cheque supposedly issued by him on Indus Ind bank where he did not even have an account. Since the complainant did not get any relief from the Card Company he had sought the intervention of the BO to resolve the issue . As the reply of Card Company was not found to be satisfactory a conciliation meeting was convened to resolve the issue. During the conciliation meeting the Card Company admitted that the matter was a clear case of fraud. Accordingly a view was taken that since the complainant had no fault in the entire matter, the matter may be resolved by waiving the entire outstanding amount in the card account. The grievance was settled by mutual agreement.Case 26 The complainant had alleged that despite making full payment of the outstanding amount on his card account and request for closure of the card the Card company was issuing monthly statement showing outstanding dues and giving constant telephone calls. The Card company had even served a legal notice causing harassment to him. The response of the Card company to his pleas have been quite evasive. He had accordingly sought relief by way of direction to the Card company to close the card and compensation to the tune of Rs 1,00,000/ as compensation for harassment. The conciliation meeting convened to resolve the matter clearly indicated the lack of coordination between the accounts and the collection wings of the Card company. Relying on the evidence of full payment of dues by the complainant, request for closure, copy of legal notice and absence of any written response to the complainant, BO observed that the approach of the Card company has been very lukewarm to the customer. Issuance of legal notice by the Card company after receipt of a communication from the BO regarding the dispute also reflects the lack of sensitivity of the card company to customer grievances and it is desirable that it desists from such practices. Accordingly, the card Company was directed to pay an amount of Rs.5000 to the complainant as compensation for the harassment which was agreed by the Card company and the matter was treated as settled and closed. Case 27 One complainant applied for a home loan of Rs.20 lakh and deposited Rs.11020/- as processing fee along with other required documents. Later, he complained to this Office requesting for refund of the processing fee paid by him to the bank, as the bank had not disbursed the loan. After taking up the matter with the bank, they informed that the complainant had himself refused to accept the sanction letter. The bank expressed its inability to refund the processing fee for the above reason as also because the fee was ‘non-refundable’, levied to cover the cost involved in sanction of the loan application. This was not considered tenable by BO. After putting a great deal of pressure on the bank, the processing fee was refunded to the complainant. Case 28 One complaint was lodged by a nominee of a Fixed Deposit (FD) account holder regarding non-payment of interest at FD rate for delay on the part of the bank in settlement of death claim on the FD account. The bank advised BO that on receipt of claim papers from the complainant, the same were forwarded by them to their Head Office for approval. Further, the records pertaining to nomination had been destroyed during the foods a few years ago in South Gujarat, which resulted in delay in payment. The bank, however, had offered interest at the Savings Bank rate for the delayed period. On scrutiny of both the submissions, it was observed by BO that, despite having nomination registered in the name of the complainant, the bank had asked for additional papers and documents and had sent these to their Head Office for sanction. In terms of the ‘Code of Bank’s Commitments to its Customers’ payment is to be released in such cases to the nominee within 15 days from the date of receipt of the claim along with required documents. The bank was advised to pay FD interest applicable for the delayed period, instead of paying interest at SB rate, and resolve the grievances of the complainant. Case 29 A complaint was lodged regarding non-payment of an applicable enhanced family pension as recommended by the Sixth Pay Commission. On examination of the complaint and the bank's reply, it was observed that the bank has been paying normal family pension to the complainant, even though she was eligible for an enhanced family pension as per the recent instructions of her employer institution (Western Railways). We had referred the clarificatory circular issued by the Railways in this regard and observed that the bank was not paying the enhanced family pension since January 2007. As deficiency in banking services was observed, the bank was advised to pay the difference between eligible enhanced family pension payable to her since January 2007 and normal minimum family pension being paid to her as arrears and update the records at their centralized computer centre. Case 30 The complainant had constantly followed up with the bank with an intention to make payment of outstanding dues on her credit card account. She was constantly requesting the bank to provide relevant statements concerning the dues. In support, she had produced various logs viz. diary of events, relevant correspondence with the bank, gist of telecons, SMS etc. The complaint was forwarded to the bank. In response the bank clarified that the complainant had not paid the dues regularly and missed out certain EMIs that attracted the late payment charges, interest etc. on card account. A conciliation meeting was held between the complainant and the bank's Nodal officer. The bank procured a copy of an e-mail dated April 2, 2009, sent to the complainant (copy not endorsed to this office). In the said mail the bank had stated that the charges of Rs.36604/- levied to her account were reversed, CIBIL record would be updated showing nil dues and waiver of an amount of Rs.2862 towards basic purchases. The complainant was surprised to see a copy of the mail produced by the bank and denied having received the same. The BO had also called for a detailed statement of dues showing the details i.e. due date of payment and actual date of payment. However, the statement submitted by the bank at the meeting did not reflect these two columns. On examination it was observed that the mail dated April 02, 2009 was a fake mail sent on non-existent e-mail ID. The explanation was called for from the bank for dragging the customer for two years for not providing the correct information about the outstanding dues which has resulted in harassment. There was considerable loss of time, energy and expenditure on the part of the complainant in making follow up. BO issued a show cause notice to the bank requiring the bank to pay Rs.20,000/- as compensation in addition to reversal of Rs.36604/-charges and an apology letter to be issued to the complainant. The bank paid Rs.20000/- compensation to the complainant and also effected the reversal of charges. Case 31 The complainant had kept deposit of Rs. 6 lakh for one year in bank’s special deposit Scheme. After completion of 10 months, he requested the bank for premature closure of the said deposit. The branch initially refused to pay the said deposit before maturity. Later on its central office allowed the branch premature payment, however, without any interest. The complainant filed complaint with us for non-payment of any interest for run period of 10 months. The bank invited complainant’s attention towards features of Special Deposit Scheme that the fixed deposit was not supposed to be prematurely withdrawn, the bank had initially denied the payment. However, taking into consideration the urgent need of the complainant the deposit was paid without considering payment of interest. In this regard the complainant’s contention was that these terms and conditions were neither explained to him at the time of accepting deposit nor mentioned in the fixed deposit receipt issued to him. He contended that the bank had accepted the discharged deposit receipt on the counter and informed him that the interest due would be credited to his account. On examination of complaint it was observed that the bank did not maintain transparency while accepting deposits under special deposit scheme as the terms and conditions were not made clear to customer. It had also changed rules of the scheme after 4 months. The revisions brought in the scheme were disadvantageous to depositors who had invested in the scheme prior to July 19, 2007; these were not informed to customers in writing. On the above background contents of the RBI circular DBOD.No.Dir. BC.39/13.03.00/ 2007-2008 dated October 25, 2007 concerning issues related to deposits accepted under ‘lock-in period’ were brought to the notice of the bank. In the said circular the RBI has clarified that the special schemes, with lock-in periods and other features referred to at paragraph 1 in the circular, were flouted by some banks; these were not in conformity with RBI’s instructions. Further, provisions of clause 2.23 of RBI Master Circular dated July 2, 2007 read as - “Deposit Mobilisation Schemes were also brought to the notice of the bank. On the above background the bank’s action was not in conformity with RBI’s instructions. The bank was, therefore, advised to settle the interest claim in terms of bank’s policy on premature payment of term deposits to regular category and report compliance. The bank settled the complainant’s claim by effecting payment of interest as applicable to regular term deposit schemes.
Case 32 On scrutiny of complaints received against one of the banks it was observed that the complaints concerning levy of charges for not maintenance of AQB were on rise. It was more so in respect of special products, in which the accounts were up-graded from ordinary Savings Bank category without seeking clear mandate from the account holders. It was observed that the bank wassending certain communication to the customers seeking their approval for transformation of existing product to up-graded one along with a copy of response note to be signed by him. This note was seeking his confirmation on the bank’s intent. However, irrespective of receipt of any confirmation from the customer (presumably within prescribed period) the bank was inescapably implementing up-gradation formula and thereafter penalizing the customers for non compliance of terms and conditions of the up-graded product, including levy of charges for non maintenance of AQB. In our view bank’s such action was in violation of clause 4.d of BCSBI and hence needed remolding immediately. This aspect was unfolded through a complaint of such nature registered vide above referred number. In this regard it was observed that the bank had reversed charges levied to the complainant’s account only after his raising the issue before BO. The bank in response to BO, had conveniently stated that the charges were reversed only as a service gesture. In our opinion, the bank had not done any favour to the customer in reversing the charges; it had simply corrected its wrongdoings. The more distressing factor in the matter was that the bank was resorting to this practice since long and hence there was scope to apprehend that the bank might have penalized many such accounts. The bank was advised to do away with such practices and ensure that the BCSBI codes accepted by the banks were religiously followed. Incidentally the bank’s attention was also invited to RBI circular dated February 22, 2007; the bank was advised to initiate action for elimination of complaints as outlined in the said circular. DISCLAIMER The Reserve Bank of India does not vouch the correctness, propriety or legality of orders and awards passed by Banking Ombudsmen. The object of placing this compendium is merely for the purpose of dissemination of information on the working of the Banking Ombudsman Scheme and the same shall not be treated as an authoritative report on the orders and awards passed by Banking Ombudsmen and the Reserve Bank of India shall not be responsible or liable to any person for any error in its preparation. Break up of Bank wise (Scheduled Commercial Banks) complaints received in the year 2008-09
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||