 IST,
IST,
Survey on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) of Mutual Fund (MF) Companies and their Asset Management Companies (AMCs) in India
उत्तर: म्युचुअल फंड कंपनियां प्रत्येक वर्ष 15 जुलाई या उससे पहले प्रश्नावली-4 (Excel प्रारूप) के माध्यम से अपनी प्रतिक्रिया प्रस्तुत कर सकती हैं।
Ans: No. Even if a company’s account closing period is different from reference period (end-March), the ITES survey information should be reported for the survey reference period, based on the company’s internal assessment.
In case of any specific complaint against any bank relating to deficiency in service pertaining to education loan, the same can be filed with the bank concerned. If there is no response to the complaint within one month or non-satisfactory response from the bank, the complaint may be filed under ‘The Reserve Bank - Integrated Ombudsman Scheme, 2021’. Complaints can be filed online through Complaint Management System (CMS) portal of the RBI, at https://cms.rbi.org.in. Complaints can also be filed through the dedicated e-mail or sent in physical mode to the ‘Centralised Receipt and Processing Centre’ set up at Reserve Bank of India, 4th Floor, Sector 17, Chandigarh – 160017, as per the Format provided in the Scheme.
Ans: In terms of revised Master Directions, banks are not required to submit such certificates / Flash Reports to RBI.
ಉತ್ತರ. ಎಎಟಿಎಮ್ /ಎಟಿಎಮ್ ಕಮ್ ಡೆಬಿಟ್ ಕಾರ್ಡ್ಗಳು,ಕ್ರೆಡಿಟ್ ಕಾರ್ಡ್ಗಳು ಹಾಗೂ ಪ್ರಿಪೇಯ್ಡ್ ಕಾರ್ಡ್ಗಳನ್ನು , ನೀಡಿಕೆದಾರರು ಅನುಮತಿಸಿದಂತೆ ,ವಿವಿಧ ವಹಿವಾಟುಗಳಿಗಾಗಿ ಎಟಿಎಮ್ಗಳು /ಡಬ್ಲ್ಯೂಎಲ್ಎಗಳಲ್ಲಿ ಬಳಸಬಹುದು .
Ans. In case a customer does not possess an OVD, he can still open a ‘Small Account’ with a bank. For the purpose, the bank shall obtain a self-attested photograph from the customer and the designated officer of the bank certifies under his signature that the person opening the account has affixed his signature or thumb impression in his presence. The Small Account shall remain operational initially for a period of twelve months and is subject to conditions as given under paragraph 23 of the Master Direction on KYC.
Ans. Provisions related to penalty are contained in paragraph 15 of these Directions. The detailed procedure for premature withdrawal including partial premature withdrawal are determined by the banks in terms of their comprehensive Board approved policy.
Response: Government of India, vide its press release ID 2115009 dated March 25, 2025 has discontinued the Medium and Long Term Government Deposit (MLTGD) components of GMS. Accordingly, the mobilization of a MLTGD, including renewal, has been discontinued with effect from March 26, 2025. There is no change in the provisions pertaining to STBD under GMS.
The initiative involves collaboration between multiple regulators:
-
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) – for banking and payment systems
-
Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) – for securities markets
-
Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority of India (IRDAI) – for insurance products
-
Pension Fund Regulatory and Development Authority (PFRDA) – for pension-related innovations (although PFRDA does not have a separate regulatory sandbox but is a part of the Inter-operable Regulatory Sandbox (IoRS)).
-
International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA) – unified Regulatory authority of Gujarat International Finance Tech-City International Financial Services Centre (GIFT IFSC) for testing in the domain areas as specified in the Annexure I of Framework for FinTech Entity in the International Financial Services Centres.
Yes. REs may formulate an appropriate Board approved policy and adopt a suitable structure of penal charges that is ‘reasonable’ and ‘commensurate’ with the non-compliance of material terms and conditions of the loan contract.
Ans: In terms of MD-TLE dated September 24, 2021, Primary (Urban) Co-operative Banks (PUCBs), State Co-operative Banks (StCBs) and Central Co-operative Banks (CCBs) have been recognised as eligible transferors of stressed loans. The relevant provisions of circular “Guidelines on Sale of Financial Assets to Securitisation Company/Reconstruction Company (SC/RC) by Multi State Urban Cooperative Banks’ dated March 28, 2014, in terms of which only multistate cooperative banks could sell stressed assets to ARCs have been repealed. Accordingly, all cooperative banks are permitted to transfer stressed assets to ARCs in compliance with the provisions of the MD-TLE and other extant regulatory instructions.
-
For calculating the index ratio for a specific date, daily reference WPI values would be linearly interpolated using ‘Ref WPI’ for the first day of the calendar month and the first day of the following calendar month.
-
The formula for computing the reference WPI for a particular day is as under:
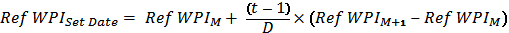
[Ref WPIM = Ref WPI for the first day of the calendar month in which Date falls, Ref WPIM+1 = Ref WPI for the first day of the calendar month following the settlement date, D = Number of days in month (e.g. 31 days in August), and t= settlement date (e.g. August 6)]
- An example of daily reference WPI computed through interpolation is furnished below.
Date |
Ref WPI |
T-1 |
D |
Ref WPI |
1-May-13 |
168.8 |
|
||
2-May-13 |
1 |
31 |
168.85 |
|
3-May-13 |
2 |
31 |
168.90 |
|
4-May-13 |
3 |
31 |
168.95 |
|
5-May-13 |
4 |
31 |
168.99 |
|
6-May-13 |
5 |
31 |
169.04 |
|
7-May-13 |
6 |
31 |
169.09 |
|
8-May-13 |
7 |
31 |
169.14 |
|
9-May-13 |
8 |
31 |
169.19 |
|
10-May-13 |
9 |
31 |
169.24 |
|
11-May-13 |
10 |
31 |
169.28 |
|
12-May-13 |
11 |
31 |
169.33 |
|
13-May-13 |
12 |
31 |
169.38 |
|
14-May-13 |
13 |
31 |
169.43 |
|
15-May-13 |
14 |
31 |
169.48 |
|
16-May-13 |
15 |
31 |
169.53 |
|
17-May-13 |
16 |
31 |
169.57 |
|
18-May-13 |
17 |
31 |
169.62 |
|
19-May-13 |
18 |
31 |
169.67 |
|
20-May-13 |
19 |
31 |
169.72 |
|
21-May-13 |
20 |
31 |
169.77 |
|
22-May-13 |
21 |
31 |
169.82 |
|
23-May-13 |
22 |
31 |
169.86 |
|
24-May-13 |
23 |
31 |
169.91 |
|
25-May-13 |
24 |
31 |
169.96 |
|
26-May-13 |
25 |
31 |
170.01 |
|
27-May-13 |
26 |
31 |
170.06 |
|
28-May-13 |
27 |
31 |
170.11 |
|
29-May-13 |
28 |
31 |
170.15 |
|
30-May-13 |
29 |
31 |
170.20 |
|
31-May-13 |
30 |
31 |
170.25 |
|
1-June-13 |
170.3 |
|
Ans : Yes NBFCs and NBFC-IFCs need to take prior approval from the Reserve Bank for sponsoring IDFs.
Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has authorised various types of payment systems to enable transfer of funds. You may refer to the following link on RBI website to get overview of various payment systems available in India:
Ans: No, there is no limit imposed by the RBI for funds transfer through NEFT system. However, a member bank may place amount limits based on its own risk perception with the approval of its Board.
1 A person resident outside India may hold, own, transfer or invest in Indian currency, security or any immovable property situated in India if such currency, security or property was acquired, held or owned by such person when he was resident in India or inherited from a person who was resident in India.
2 Section 2(v): "person resident in India" means-
(i) a person residing in India for more than one hundred and eighty-two days during the course of the preceding financial year but does not include-
(A) a person who has gone out of India or who stays outside India, in either case-
- for or on taking up employment outside India, or
- for carrying on outside India a business or vocation outside India, or
- for any other purpose, in such circumstances as would indicate his intention to stay outside India for an uncertain period;
(B) a person who has come to or stays in India, in either case, otherwise than-
- for or on taking up employment in India, or
- for carrying on in India a business or vocation in India, or
- for any other purpose, in such circumstances as would indicate his intention to stay in India for an uncertain period;
The accredited banks are paid remuneration by RBI for conduct of State/Central Government transactions. Such remuneration is called Agency Commission. The rates of agency commission applicable at present (from July 1, 2019) are as under:
| No. | Type of Transaction | Unit | Revised Rate | |
| a. | (i) | Receipts – Physical mode | Per transaction | ₹ 40/- |
| (ii) | Receipts – e-mode * | Per transaction | ₹ 9/- | |
| b. | (i) | Payments – Pension | Per transaction | ₹ 75/- |
| (ii) | Payments – Other than pension | Per ₹ 100 turnover | 6.5 paise | |
| *In this context, it may please be noted that ‘Receipts – e-mode’ indicated against Sl. No. a(ii) in the above table would refer to those transactions involving remittance of funds from the remitter’s bank account through internet banking as well as all such transactions which do not involve physical receipt of cash / instruments. | ||||
Ans. On return from a foreign trip, travellers are required to surrender unspent foreign exchange held in the form of currency notes and travellers cheques within 180 days of return. However, they are free to retain foreign exchange up to USD 2,000, in the form of foreign currency notes or TCs for future use or credit to their Resident Foreign Currency (Domestic) [RFC (Domestic)] Accounts.
Ans. No.
Ans. i) Inward remittance through normal banking channels, other than remittances received on account of foreign currency loan or investment received from abroad or received for meeting specific obligations by the account holder;
ii) Payments received in foreign exchange by a 100 per cent Export Oriented Unit or a unit in (a) Export Processing Zone or (b) Software Technology Park or (c) Electronic Hardware Technology Park for supply of goods to similar such units or to a unit in Domestic Tariff Area;
iii) Payments received in foreign exchange by a unit in the Domestic Tariff Area for supply of goods to a unit in the Special Economic Zone (SEZ);
iv) Payment received by an exporter from an account maintained with an authorised dealer for the purpose of counter trade. (Counter trade is an arrangement involving adjustment of value of goods imported into India against value of goods exported from India in terms of the Reserve Bank guidelines);
v) Advance remittance received by an exporter towards export of goods or services;
vi) Payment received for export of goods and services from India, out of funds representing repayment of State Credit in U.S. Dollar held in the account of Bank for Foreign Economic Affairs, Moscow, with an authorised dealer in India;
vii) Professional earnings including directors’ fee, consultancy fee, lecture fee, honorarium and similar other earnings received by a professional by rendering services in his individual capacity;
viii) Re-credit of unutilised foreign currency earlier withdrawn from the account;
ix) Amount representing repayment by the account holder's importer customer in respect of trade related loan/advances granted by the exporter (subject to compliance with the extant guidelines) holding EEFC account; and
x) The disinvestment proceeds received by the resident account holder on conversion of shares held by him to ADRs/GDRs under the Sponsored ADR/GDR Scheme approved by the Foreign Investment Promotion Board of the Government of India.
Ans. “Payment Instruction” is defined as any instrument, authorization or order in any form, including by electronic means, to effect a payment by a person to a participant in a payment system or from one participant in such a system to another participant in that system.
The payment instruction can be communicated either manually i.e. through an instrument like a cheque draft, payment order etc. or through electronic means, so that a payment can be made by either a person to the participant in such a system or between two participants.
Ans: In cases of accounts with ASCL above the cut-off where S4A is implemented, both the sustainable and unsustainable debt (Parts A & B) should be counted towards calculating ASCL.
Restructured accounts where cut-off ASCL is achieved/likely to be achieved due to additional finance under the restructuring package under JLF and other RBI frameworks, should not be subjected to disincentive mechanism for the incremental exposure.
Response
No. Banks are advised not to impose restrictions like age and income criteria of the individual for opening BSBDA.
One can file a complaint with the NBFC Ombudsman by writing on a plain paper and sending it to the concerned office of the NBFC Ombudsman by post/fax/hand delivery. One can also file it by email to the NBFC Ombudsman.
A complaint form along with the scheme is also available on RBI's website, though, it is not mandatory to use this format.
ಪೇಜ್ ಕೊನೆಯದಾಗಿ ಅಪ್ಡೇಟ್ ಆದ ದಿನಾಂಕ:










