XV. The Reserve Bank’s Accounts for 2002-03 - ആർബിഐ - Reserve Bank of India
XV. The Reserve Bank’s Accounts for 2002-03
Income And Expenditure
Income
Expenditure
Balance Sheet
Assets
Profit And Loss Account for the Year Ended 30th June 2003
15.1 The key financial results of the Reserve Bank's operations during the year are presented in this section.
15.2 The trends in gross income, expenditure and net disposable income of the Reserve Bank over the last five years are displayed in Table 15.1.
Appropriation of Net Disposable Income
15.3 The net disposable income of the Reserve Bank for the year 2002-03 amounted to Rs.8,838.00 crore (Table 15.2).
(Rupees crore) |
||||||
|
|
||||||
Item |
2002-03 |
2001-02 |
2000-01 |
1999-2000 |
1998-99 |
|
|
|
||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
|
||||||
Total Income (Net) |
15,561.41 |
16,866.39 |
14,941.52 |
14,694.92 |
9,028.09 |
|
Total Expenditure |
6,723.41 |
6,542.39 |
5,587.52 |
5,340.92 |
4,545.09 |
|
Net Disposable Income |
8,838.00 |
10,324.00 |
9,354.00 |
9,354.00 |
4,483.00 |
|
Less : Transfer to Funds * |
4.00 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
4.00 |
|
Surplus transfer to Government |
8,834.00 |
10,320.00 |
9,350.00 |
9,350.00 |
4,479.00 |
|
of which |
||||||
i) Towards Normal Transfer |
7,117.00 |
8,841.00 |
7,871.00 |
7,871.00 |
3,000.00 |
|
ii) Interest differential on account of |
||||||
conversion of special securities into |
||||||
marketable securities |
1,717.00 |
1,479.00 |
1,479.00 |
1,479.00 |
1,479.00 |
|
|
|
||||||
* An amount of Rupees one crore each transferred to NIC (LTO) Fund, NRC(LTO) Fund, NRC(Stabilisation) Fund and NHC(LTO) Fund during each of the five years. |
||||||
Surplus transferable to Government of India
15.4 The surplus transferable to the Central Government for the year 2002-03 amounted to Rs.8,834.00 crore, inclusive of Rs.1,717.00 crore towards interest differential on special securities converted into marketable securities. The transfer on account of interest differential is intended to compensate the Government for the difference in interest expenditure, which the Government had to bear consequent on the conversion.
(Rupees crore) |
||||||
|
|
||||||
Item |
2002-03 |
2001-02 |
2000-01 |
1999-2000 |
1998-99 |
|
|
|
||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
|
||||||
A. |
Foreign Sources |
|||||
Interest, Discount, Exchange, Commission |
9,826.65 |
9,986.46 |
10,086.08 |
6,514.73 |
6,306.59 |
|
B. |
Domestic Sources |
|||||
Interest |
13,064.77 |
14,492.14 |
11,314.12 |
14,928.38 |
12,642.96 |
|
Discount |
0.08 |
10.92 |
211.59 |
323.11 |
87.74 |
|
Exchange |
0.09 |
0.08 |
0.85 |
0.14 |
0.19 |
|
Commission |
279.42 |
189.51 |
210.37 |
185.62 |
175.02 |
|
Rent realised and others |
14.63 |
11.23 |
25.86 |
8.99 |
7.83 |
|
Total – Domestic |
13,358.99 |
14,703.88 |
11,762.79 |
15,446.24 |
12,913.74 |
|
Total Income (Gross) |
23,185.64 |
24,690.34 |
21,848.87 |
21,960.97 |
19,220.33 |
|
15.5 The gross income of the Reserve Bank for the year 2002-03 (July-June), was Rs.23,185.64 crore which was lower by Rs.1,504.70 crore (6.1 per cent) as compared to the previous year's total income of Rs.24,690.34 crore. The fall in income from domestic sources was due to fall in domestic assets and lower interest rates. The fall in income from foreign sources was due to reduction in international interest rates. The sources of income are set out in Table 15.3. 15.6 The share of transfer to Contingency Reserve, Asset Development Reserve and surplus transfer to government as a percentage to total income is given in Table 15.4.
15.6 The share of transfer to Contingency Reserve, Asset Development Reserve and surplus transfer to government as a percentage to total income is given in Table 15.4.
15.7 Income from foreign and domestic sources is compared in Chart XV.1.
Earnings from Foreign Sources
15.8 Data relating to earnings from foreign sources are given in Table 15.5.
(Rupees crore) |
||||
|
|
||||
Particulars |
Amount as on |
Variation |
||
June 30, 2003 |
June 30, 2002 |
Amount |
Percentage |
|
|
|
||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
||||
Foreign Currency Assets (FCA) |
3,65,000.98 |
2,67,333.18 |
97,667.80 |
36.53 |
Gold |
17,182.40 |
16,272.39 |
910.01 |
5.59 |
Special Drawing Rights (SDR) |
6.09 |
46.57 |
(-)40.48 |
(-)86.92 |
Total Foreign Exchange Reserves (FER) |
3,82,189.47 |
2,83,652.14 |
98,537.33 |
34.74 |
Average FCA |
3,17,297.00 |
2,23,565.45 |
93,731.55 |
41.93 |
Net Earnings |
9,826.65 |
9,986.46 |
(-)159.81 |
(-)1.60 |
Capital Gain on Securities |
1,329.28 |
1,335.15 |
(-) 5.87 |
(-)0.44 |
Depreciation on Securities |
(-)392.82 |
(-)549.59 |
156.77 |
28.53 |
Net Capital Gain/Loss on Securities |
936.46 |
785.56 |
150.90 |
19.21 |
Net Earnings excluding Capital Gains/Losses |
8,890.19 |
9,200.90 |
(-)310.71 |
(-)3.38 |
Unrealised Appreciation on Securities |
1,888.12 |
781.81 |
1,106.31 |
141.51 |
|
|
||||
Memo Items : |
||||
|
|
||||
Net Earnings in percentage terms (on average FCA) |
3.10 |
4.47 |
||
Net Earnings in percentage terms |
||||
(excluding Capital Gain/Loss on average FCA) |
2.80 |
4.12 |
||
|
|
||||
15.9 During the year 2002-03, the return on foreign currency assets excluding capital gains less depreciation decreased to 2.8 per cent from 4.1 per cent during 2001-02 because of lower interest rates abroad. However, taking into account the capital gain on securities, the net earnings went up from 2.8 per cent to 3.1 per cent during 2002-03. The foreign securities held in the Reserve Bank's portfolio are valued at the end of every month at the lower of book value or market rate. If the market rate is lower than the book value, depreciation to the same extent is provided for. Appreciation is neither taken to profit and loss account nor to the reserves.
Income from Domestic Sources
15.10 Domestic income decreased by Rs.1,344.89 crore (9.1 per cent) from Rs.14,703.88 crore in 2001-02 to Rs.13,358.99 crore in 2002-03. Data relating to earnings from domestic sources are given in Table 15.6.
(Rupees crore) |
||||
|
|
||||
Particulars |
Amount as on |
Variation |
||
June 30, 2003 |
June 30, 2002 |
Amount |
Percentage |
|
|
|
||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
|
|
||||
Domestic Assets |
1,54,812.91 |
1,86,226.62 |
(-)31,413.71 |
(-)16.87 |
Weekly average of Domestic Assets |
1,56,365.36 |
1,94,553.57 |
(-)38,188.21 |
(-)19.63 |
Net Earnings after depreciation on securities@ |
13,358.99 |
14,703.88 |
(-)1,344.89 |
(-)9.15 |
(642.81) |
(631.90) |
|||
of which : |
||||
(i) Profit on Sale of Securities |
4,798.03 |
3,060.04 |
1,737.99 |
56.80 |
(ii) Interest on Securities |
7,100.29 |
9,004.25 |
(-)1,903.96 |
(-)21.14 |
(iii) Interest on Loan and Advances |
1,013.63 |
2,122.92 |
(-)1,109.29 |
(-)52.25 |
(iv) Other Earnings |
447.04 |
516.67 |
(-)69.63 |
(-)13.48 |
|
|
||||
Memo Items : |
||||
|
|
||||
Net Earnings in percentage terms |
8.54 |
7.56 |
||
(on average domestic assets) |
||||
Net Earnings in percentage terms |
5.47 |
5.98 |
||
(excluding profit on sale of securities) |
||||
|
|
||||
@ : Figures in brackets are depreciation on securities. |
||||
(Rupees crore) |
||||||
|
|
||||||
Item |
2002-03 |
2001-02 |
2000-01 |
1999-2000 |
1998-99 |
|
|
|
||||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
5 |
6 |
|
|
|
||||||
I. |
Interest Payment |
1,990.09 |
2,334.99 |
1,994.80 |
1,971.88 |
1,976.64 |
of which : |
||||||
a) Scheduled Banks |
1,483.02 |
1,838.57 |
1,660.83 |
1,656.18 |
1,652.76 |
|
b) Payment in lieu of service charges |
||||||
on borrowings from IMF payable to |
||||||
Government of India |
– |
– |
– |
7.82 |
45.51 |
|
II. |
Establishment |
1,488.86 |
1,304.36 |
870.85 |
846.75 |
683.59 |
III. |
Non-Establishment |
3,244.46 |
2,903.04 |
2,721.87 |
2,522.29 |
1,884.86 |
of which: |
||||||
a) Agency charges |
1,352.41 |
1,207.84 |
1,160.70 |
1,193.62 |
924.02 |
|
b) Security printing |
1,433.09 |
1,304.49 |
1,122.78 |
1,068.44 |
733.96 |
|
Total [I+II+III] |
6,723.41 |
6,542.39 |
5,587.52 |
5,340.92 |
4,545.09 |
|
|
|
||||||
15.11 Profits booked on sale of securities amounted to Rs. 4,798.03 crore in 2002-03 representing an increase of Rs. 1,737.99 crore over the previous year. The net open market operations sales amounted to Rs.53,780 crore in 2002-03 as compared to Rs.30,335 crore in 2001-02. The interest income on ways and means advances showed decrease of Rs.339.98 crore during 2002-03 from Rs.952.48 crore in 2001-02 to Rs.612.50 crore in 2002-03, reflecting decreased recourse by the Central Government to this facility and also lower bank rate. Interest earnings from loans and advances to banks/financial institutions declined by Rs.769.31 crore from Rs.1,170.44 crore in 2001-02 to Rs.401.13 crore in 2002-03, due to lower utilisation of refinance facility by Primary Dealers/Scheduled Commercial Banks combined with lower interest rates applicable on these advances.
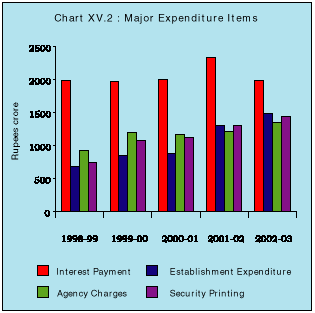
15.12 Total expenditure of the Reserve Bank increased by Rs.181.02 crore (2.8 per cent) from Rs.6,542.39 crore in 2001-02 to Rs.6,723.41 crore in 2002-03 (Table 15.7 and Chart XV.2).
Interest Payment
15.13 Interest payment decreased by Rs.344.90 crore ( 14.8 per cent) from Rs.2,334.99 crore in 2001-02 to Rs.1,990.09 crore in 2002-03 due to reduction in rate of CRR and lower interest rates payable on eligible CRR balances.
Establishment Expenditure
15.14 Establishment expenditure increased by Rs.184.50 crore (14.1 per cent) from Rs.1,304.36 crore in 2001-02 to Rs.1,488.86 crore in 2002-03 as a result of increased provisioning with respect to gratuity and pension funds. As per the actuarial valuation the provisioning in this regard was to the extent of Rs.616.67 crore during 2002-03 as against Rs.440.80 crore during the previous year.
Non-Establishment Expenditure
15.15 Expenditure on security printing, comprising cost of printing of currency notes, cheque forms etc., increased by Rs.128.60 crore (9.9 per cent) from Rs.1,304.49 crore in 2001-02 to Rs.1,433.09 crore in 2002-03, mainly due to upward revision in rates of printing currency notes, increase in quantum of notes printed and larger component of higher denomination notes of Rs.100 and above consistent with the clean note policy.
Liabilities
National Industrial Credit (Long Term Operations) Fund
15.16 There were no operations in the National Industrial Credit (Long Term Operations) Fund (established under Section 46-C of the RBI Act, 1934) during 2002-03 except the credit of Rs.1.0 crore to the Fund out of Reserve Bank's income.
National Housing Credit (Long Term Operations) Fund
15.17 The National Housing Credit (Long Term Operations) Fund was established by the Reserve Bank in terms of Section 46D(1) of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 in January 1989. A token contribution of Rs.1.0 crore was made to the Fund out of Reserve Bank's income during 2002-03.
Deposits - Banks
15.18 'Deposits - Banks' represent balances maintained by the banks in current account with the Reserve Bank mainly for maintaining Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) and as working funds for clearing adjustments.
Deposits - Others
15.19 'Deposits - Others' include deposits from financial institutions, employees' provident fund deposits, surplus earmarked pending transfer to the Government and sundry deposits.
Other Liabilities
15.20 'Other Liabilities' include the internal reserves and provisions of the Reserve Bank and net credit balance in the RBI General Account. These liabilities have increased by Rs.9,112.06 crore (8.3 per cent) from Rs.1,09,243.95 crore as on June 30, 2002 to Rs.1,18,356.01 crore as on June 30, 2003 mainly on account of increase in the levels of internal reserves.
15.21 The reserves, viz., Contingency Reserve, Asset Development Reserve, Currency & Gold Revaluation Account and Exchange Equalisation Account reflected in 'Other Liabilities' are in addition to the 'Reserve Fund' of Rs.6,500 crore held by the Reserve Bank as a distinct balance sheet head.
Currency and Gold Revaluation Account and Exchange Equalisation Account
15.22 Gains/losses on valuation of foreign currency assets due to movements in the exchange rates and/ or prices of gold are not booked in profit and loss account but in a separate account called Currency and Gold Revaluation Account (CGRA), the balance in which represents accumulated net gain on valuation of foreign currency assets and gold. During 2002-03, there was an accretion of Rs.265.64 crore to the CGRA, thus increasing the balance to Rs.51,276.41 crore as on June 30, 2003 from Rs.51,010.77 crore as on June 30, 2002. The CGRA at the end of June 2003 was equivalent to 13.4 per cent of foreign currency assets and gold holdings of the Reserve Bank, as against 18.0 per cent at the end of June 2002. This was mainly on account of increase in the foreign currency assets and also appreciation of the rupee against the US dollar. The balances in Exchange Equalisation Account (EEA) represents provision made for exchange losses arising out of forward commitments. The balance in the EEA as on June 30, 2003 stood at Rs.567.25 crore. The balances in CGRA and EEA which are part of 'Other Liabilities' in the Balance Sheet as at the close of last five accounting years are given in Table 15.8.
Contingency Reserve and Asset Development Reserve
15.23 The Reserve Bank maintains a Contingency Reserve (CR) to enable it to absorb unexpected and unforeseen contingencies. The Reserve Bank has set an indicative target of 12 per cent of the Reserve Bank's total assets to be achieved in phases by the year 2005, subject to review, if considered necessary. The balance in CR has gone up from Rs.48,434.17 crore as on June 30, 2002 to Rs.55,249.29 crore as on June 30, 2003. A sum of Rs.81.20 crore representing unresolved items of credit, which was included under Other Liabilities -Miscellaneous was credited to CR during 2002-03. A transfer of Rs.6733.92 crore was made to CR during 2002-03 from Reserve Bank's income. The balance in CR was sufficient to meet the contingent liabilities.
15.24 In order to meet the internal capital expenditure and make investments in its subsidiaries and associate institutions, the Reserve Bank had created, in 1997-98, a separate Asset Development Reserve (ADR) with the aim of reaching one per cent of the Reserve Bank's total assets within the overall target of 12 per cent set for CR. In the year 2002-03, an amount of Rs.890.31 crore was transferred from income to ADR raising its level from Rs.4,700.54 crore as on June 30, 2002 to Rs.5,590.85 crore as on June 30, 2003. CR and ADR together constituted 11.7 per cent of total assets of the Reserve Bank as on June 30, 2003. The balances in CR and ADR as at the close of last five accounting years are given in Table 15.9.
Foreign Currency Assets
15.25 The foreign currency assets comprise foreign securities held in Issue Department, balances held abroad and investments in foreign securities held in Banking Department. Such assets rose from Rs.2,67,333.18 crore as on June 30, 2002 to Rs.3,65,000.98 crore as on June 30, 2003. The increase in the level of foreign currency assets was mainly on account of market purchases, interest & discount and revaluation gains.
Investment in Government of India Rupee Securities
15.26 Investment in Government of India Rupee Securities which stood at Rs.1,35,067.86 crore as on June 30, 2002 decreased by Rs.29,923.82 crore (22.2 per cent) to Rs.1,05,144.04 crore as on June 30, 2003 mainly on account of substantial open market operations sales during the year.

15.27 The position of foreign currency and domestic assets during the last five years is given in Table 15.10 and Chart XV.3.
Investments in Shares of Subsidiaries and Associate Institutions
15.28 The Reserve Bank's investments in the shares of its subsidiaries and associate institutions have increased by Rs.100.00 crore during 2002-03 on account of an additional investment in capital of the National Housing Bank. The details of Reserve Bank's investments in the shares of its subsidiaries and associate institutions are given in Table 15.11.
Other Assets
15.29 'Other Assets' comprise mainly dead stock, gold holdings in the Banking Department, amounts spent on projects pending completion and staff advances. The level of 'Other Assets' has decreased by Rs.290.78 crore ( 2.3 per cent) from Rs.12,715.34 crore as on June 30, 2002 to Rs.12,424.56 crore as on June 30, 2003.
Auditors
15.30 The accounts of the Reserve Bank for the year 2002-03 were audited by M/s. P.B.Vijayaraghavan & Co., Chennai, M/s. Chandabhoy & Jassoobhoy, Mumbai, M/s. Khimji Kunverji & Co., Mumbai, M/s. P.K.Mitra & Co., Kolkata, M/s. J.L. Sengupta & Co., Kolkata, and M/s. S.N. Nanda & Co., New Delhi appointed by the Central Government.
RESERVE BANK OF INDIA |
|||||||||||
(Rupees Thousands) |
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
2001- 02 |
LIABILITIES |
2002- 03 |
2001- 02 |
ASSETS |
2002- 03 |
||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
Notes held in the |
Gold Coin and Bullion : |
||||||||||
11,18,43 |
Banking Department |
28,16,95 |
13293,30,60 |
(a) Held in India |
14036,76,55 |
||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
259072,77,63 |
Notes in circulation |
292509,85,82 |
(b) Held outside India |
||||||||
169000,00,00 |
Foreign Securities |
255000,00,00 |
|||||||||
259083,96,06 |
Total Notes issued |
292538,02,77 |
|||||||||
182293,30,60 |
Total |
269036,76,55 |
|||||||||
222,78,25 |
228,78,36 |
||||||||||
Government of India |
|||||||||||
76567,87,21 |
Rupee Securities |
23272,47,86 |
|||||||||
Internal Bills of Exchange |
|||||||||||
— |
and other Commercial Paper |
— |
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
259083,96,06 |
Total Liabilities |
292538,02,77 |
259083,96,06 |
Total Assets |
292538,02,77 |
||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
BANKING DEPARTMENT |
|||||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
2001- 02 |
LIABILITIES |
2002- 03 |
2001- 02 |
ASSETS |
2002- 03 |
||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
5,00,00 |
Capital paid-up |
5,00,00 |
11,18,43 |
Notes |
28,16,95 |
||||||
6500,00,00 |
Reserve Fund |
6500,00,00 |
25,80 |
Rupee Coin |
29,02 |
||||||
National Industrial Credit |
20,20 |
Small Coin |
25,25 |
||||||||
11,00,00 |
(Long Term Operations) Fund |
12,00,00 |
Bills Purchased and Discounted : |
||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
National Housing Credit |
(a) |
Internal |
|||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
185,00,00 |
(Long Term Operations) Fund |
186,00,00 |
(b) |
External |
|||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(c) |
Government Treasury Bills |
||||||||||
Deposits |
98168,54,31 |
Balances Held Abroad |
109831,26,17 |
||||||||
(a) Government |
63037,35,48 |
Investments |
86514,01,14 |
||||||||
100,68,63 |
(i) |
Central Government |
100,16,22 |
Loans and Advances to : |
|||||||
41,12,80 |
(ii) |
State Governments |
41,15,13 |
8169,00,00 |
(i) |
Central Government |
9783,00,00 |
||||
5167,88,65 |
(ii) |
State Governments |
3058,92,35 |
||||||||
(b) Banks |
Loans and Advances to : |
||||||||||
55012,21,84 |
(i) |
Scheduled Commercial Banks |
78614,08,82 |
336,12,00 |
(i) |
Scheduled Commercial Banks |
1,05,48 |
||||
(ii) |
Scheduled State Co-operative |
4,80,90 |
(ii) |
Scheduled State Co-operative Banks |
7,06,97 |
||||||
__ |
|||||||||||
1687,88,76 |
Banks |
1643,02,50 |
2,51,00 |
(iii) |
Other Scheduled Co-operative Banks |
||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(iii) |
Other Scheduled Co-operative |
(iv) |
Non-ScheduledStateCo-operativeBanks |
||||||||
1651,31,31 |
Banks |
1548,21,00 |
5654,85,04 |
(v) |
NABARD |
4475,64,84 |
|||||
(iv) |
Non-Scheduled State |
1043,96,39 |
(vi) |
Others |
1004,78,34 |
||||||
41,05,74 |
Co-operative Banks |
47,07,61 |
Loans, Advances and Investments from |
||||||||
1827,55,07 |
(v) |
Other Banks |
2748,21,23 |
National Industrial Credit |
|||||||
18126,96,21 |
(c) Others |
17454,27,45 |
(Long Term Operations) Fund : |
||||||||
53,26,57 |
Bills Payable |
48,81,69 |
(a) Loans and Advances to : |
||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(i) |
Industrial Development |
||||||||||
109243,95,11 |
Other Liabilities |
118356,01,11 |
Bank of India |
||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(ii) |
Export Import Bank of India |
||||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(iii) |
Industrial Investment Bank |
||||||||||
of India Ltd. |
|||||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(iv) |
Others |
||||||||||
(b) Investments in bonds/debentures |
|||||||||||
issued by : |
|||||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(i) |
Industrial Development Bank of India |
||||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(ii) |
Export Import Bank of India |
||||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(iii) |
Industrial Investment Bankof India Ltd. |
||||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(iv) |
Others |
||||||||||
Loans, Advances and Investments |
|||||||||||
from National Housing Credit |
|||||||||||
(Long Term Operations) Fund : |
|||||||||||
175,00,00 |
(a) |
Loans and Advances to National |
175,00,00 |
||||||||
Housing Bank |
|||||||||||
__ |
__ |
||||||||||
(b) |
Investments in bonds/debentures |
||||||||||
issued by National Housing Bank |
|||||||||||
12715,33,84 |
Other Assets |
12424,56,25 |
|||||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
194487,02,04 |
Total Liabilities |
227304,02,76 |
194487,02,04 |
Total Assets |
227304,02,76 |
||||||
|
|
|||||||||||
Significant Accounting Policies and Notes to the Accounts as per Annexure. |
|||||||||||
(Rupees Thousands) |
||||
|
|
||||
2001- 02 |
INCOME |
2002- 03 |
||
|
|
||||
16866,38,78 |
Interest, Discount, Exchange, Commission etc.1 |
15561,40,98 |
||
16866,38,78 |
Total |
15561,40,98 |
||
|
|
||||
EXPENDITURE |
||||
|
|
||||
2334,98,63 |
Interest |
1990,08,87 |
||
1304,35,96 |
Establishment |
1488,85,85 |
||
86,91 |
Directors’ and Local Board Members’ Fees and Expenses |
55,14 |
||
24,78,54 |
Remittance of Treasure |
28,09,43 |
||
1207,83,63 |
Agency Charges |
1352,40,66 |
||
1304,49,25 |
Security Printing (Cheque, Note forms etc.) |
1433,08,53 |
||
27,67,68 |
Printing and Stationery |
26,15,85 |
||
20,96,49 |
Postage and Telecommunication Charges |
17,86,79 |
||
52,48,49 |
Rent, Taxes, Insurance, Lighting etc. |
59,88,44 |
||
88,02 |
Auditors’ Fees and Expenses |
1,00,39 |
||
1,85,37 |
Law Charges |
1,63,67 |
||
125,26,52 |
Depreciation and Repairs to Bank’s Property |
125,52,79 |
||
135,93,29 |
Miscellaneous Expenses |
198,24,57 |
||
6542,38,78 |
Total |
6723,40,98 |
||
10324,00,00 |
Available Balance |
8838,00,00 |
||
Less : Contribution to: |
||||
National Industrial Credit (Long Term Operations) Fund |
1,00,00 |
|||
National Rural Credit (Long Term Operations) Fund2 |
1,00,00 |
|||
National Rural Credit (Stabilisation) Fund2 |
1,00,00 |
|||
National Housing Credit (Long Term Operations) Fund |
1,00,00 |
|||
4,00,00 |
4,00,00 |
|||
|
|
||||
10320,00,00 |
Surplus payable to Central Government |
8834,00,00 |
||
|
|
||||
1. After making the usual or necessary provisions in terms of Section 47 of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. |
||||
2. These funds are maintained by National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD). |
||||
V. S. Das |
K. J. Udeshi |
Rakesh Mohan |
Vepa Kamesam |
Bimal Jalan |
Chief General Manager |
Deputy Governor |
Deputy Governor |
Deputy Governor |
Governor |
REPORT OF THE AUDITIORS
TO THE PRESIDENT OF INDIA
We, the undersigned Auditors of the Reserve Bank of India, do hereby report to the Central Government upon the Balance Sheet of the Bank as at 30th June, 2003 and the Profit and Loss Account for the year ended on that date.
We have examined the above Balance Sheet of the Reserve Bank of India as at 30th June, 2003 and the Profit and Loss Account of the Bank for the year ended on that date and report that where we have called for information and explanations from the Bank, such information and explanations have been given and have been satisfactory. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Bank’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. We conducted our audit in accordance with auditing standards generally accepted in India. Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion and according to the best of our information and explanations given to us and as shown by the books of account of the Bank, the Balance Sheet read with Significant Accounting Policies and Notes to the Accounts is a full and fair Balance Sheet containing all necessary particulars and is properly drawn up in accordance with the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 and Regulations framed thereunder so as to exhibit a true and correct view of the state of the Bank’s affairs, in conformity with the accounting principles generally accepted in India.
M/s. P.B. Vijayaraghavan & Co. |
M/s. P.K. Mitra & Co. |
M/s. Chandabhoy & Jassoobhoy |
Auditors |
Auditors |
Auditors |
M/s. J.L. Sengupta & Co. |
M/s. S.N. Nanda & Co. |
M/s. Khimji Kunverji & Co. |
Auditors |
Auditors |
Auditors |
ANNEXURE
RESERVE BANK OF INDIA
SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND NOTES TO THE ACCOUNTS FOR 2002-03
SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
1. CONVENTION
The financial statements are prepared in accordance with the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 and the notifications issued thereunder and in the form prescribed by the Reserve Bank of India General Regulations, 1949.
Historical cost basis of accounting is used except where it is modified to reflect revaluation.
The accounting practices and policies followed in the statements, unless otherwise stated, are consistent with those followed in the previous year.
2. REVENUE RECOGNITION
Income and expenditure are recognised on accrual basis except penal interest and dividend which are accounted for on receipt basis. Only realised gains are recognised. Provision for outstanding expenditure is made for unpaid bills in each case of Rs. 1 lakh and above.
Balances unclaimed and outstanding for more than three consecutive years in certain transitory accounts including Drafts Payable Account, Payment Orders Account, Sundry Deposits Account, Remittance Clearance Account and Earnest Money Deposit Account are reviewed and written back to the Bank’s income. Claims in this respect are considered and charged against Bank’s income as and when paid.
Income and expenditure in foreign currency are translated on the basis of exchange rates prevailing on the last business day of the preceding week.
3. GOLD AND FOREIGN CURRENCY ASSETS AND LIABILITIES
(a) Gold
Gold is valued at the end of the month at 90 per cent of the daily average price quoted at London for the month. The rupee equivalent is determined on the basis of the exchange rate prevailing on the last business day of the month. Unrealised gains/losses are adjusted to the Currency and Gold Revaluation Account.
(b) Foreign Currency Assets and Liabilities
All foreign currency assets and liabilities are translated at the exchange rates prevailing on the last business day of the week and also on the last business day of the month.
At the year end, assets and liabilities in foreign currencies are translated at the exchange rates prevailing on the last business day except in cases where rates are contractually fixed. Foreign securities other than Treasury Bills are valued at lower of book value or market price prevailing on the last business day of each month. The depreciation is adjusted against current income. Foreign Treasury Bills are valued at cost.
Forward exchange contracts are evaluated half-yearly and net loss, if any, is provided for.
Profit/loss on sale of foreign currency assets is recognised with respect to the book value. Exchange gains and losses arising from translation of foreign currency assets and liabilities are accounted for in Currency and Gold Revaluation Account and remain adjusted therein.
4. RUPEE SECURITIES
Rupee securities, other than Treasury Bills, held in the Issue and Banking Departments, are valued at lower of book value or market price or rates based on the yield curve prevailing on the last business day of the month where the market price for such securities is not available. The depreciation in the value is adjusted against current income. Treasury Bills are valued at cost.
5. SHARES
Investments in shares are valued at cost.
6. FIXED ASSETS
Fixed Assets are stated at cost less depreciation.
Depreciation on computers, motor vehicles, office equipments, furniture and electrical fittings, etc., is charged on a straight-line basis. Depreciation on other assets including premises and fixtures is charged on written-down value basis.
Depreciation on fixed assets is charged only if held for a period of more than six months as at the year end.
7. RETIREMENT BENEFITS
The liability on account of retirement benefits and leave encashment to employees is estimated based on an actuarial valuation.
8. CONTINGENCY RESERVE AND ASSET DEVELOPMENT RESERVE
Contingency Reserve represents the amount provided on a year-to-year basis for meeting unexpected and unforeseen contingencies including depreciation in value of securities, exchange guarantees and risks arising out of monetary/exchange rate policy compulsions.
In order to meet the internal capital expenditure and make investments in subsidiaries and associate institutions a further specified sum is provided and credited to the Asset Development Reserve.
NOTES TO THE ACCOUNTS
1. SURPLUS TRANSFER TO GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
Surplus transferable to the Government includes an amount of Rs.1717 crore representing interest differential pertaining to the period April 1, 2002 –March 31, 2003 on account of conversion of Special Securities into marketable securities.
2. RESERVE FUND
The Reserve Fund comprises initial contribution of Rs. 5 crore made by the Government of India and appreciation of Rs. 6,495 crore on account of revaluation of gold up to October 1990. Subsequent gains/losses on monthly revaluation of gold are taken to Currency and Gold Revaluation Account.
3. DEPOSITS - OTHERS |
|||
(Rupees crore) |
|||
|
|
|||
Particulars |
As at June 30 |
||
|
|
|||
2003 |
2002 |
||
|
|
|||
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|||
I. |
Rupee Deposits from |
||
ForeignCentral Banks and |
|||
Foreign FinancialInstitutions |
3,311.34 |
3,646.43 |
|
II. |
DepositsfromIndian |
||
FinancialInstitutions |
538.73 |
359.79 |
|
III. |
Accumulated RetirementBenefits |
4,447.63 |
3,631.62 |
IV. |
Surplus transferableto |
||
Governmentof India |
8,834.00 |
10,320.00 |
|
V. |
Miscellaneous |
322.57 |
169.12 |
Total |
17,454.27 |
18,126.96 |
|
|
|
|||
4. OTHER LIABILITIES |
|||
(Rupees crore) |
|||
|
|
|||
Particulars |
As at June 30 |
||
|
|
|||
2003 |
2002 |
||
|
|
|||
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|||
I. |
Contingency Reserve |
||
Balance at the beginning of |
|||
the year |
48,434.17 |
36,514.13 |
|
Add : Transfer from National |
|||
Industrial Credit (Long |
|||
Term Operations) Fund |
– |
4,224.00 |
|
Add: Transfer from National |
|||
Housing Credit (Long |
|||
Term Operations) Fund |
– |
700.00 |
|
Add: Transfer from unresolved |
|||
Items of Credit* |
- |
81.20 |
|
Add : Accretion during the year |
6,733.92 |
6,996.04 |
|
Balance at the end of the year |
55,249.29 |
48,434.17 |
|
II. |
Asset Development Reserve |
||
Balance at the beginning of the year |
4,700.54 |
3,872.63 |
|
Add : Accretion during the year |
890.31 |
827.91 |
|
Balance at the end of the year |
5,590.85 |
4,700.54 |
|
III. |
Currency and |
||
Gold Revaluation Account |
|||
Balance at the beginning of the year |
51,010.77 |
29,124.44 |
|
Add : Net Accretion during the year |
265.64 |
21,886.33 |
|
Balance at the end of the year |
51,276.41 |
51,010.77 |
|
IV. |
Exchange Equalisation Account |
||
Balance at the beginning of the year |
51.50 |
49.46 |
|
Transfer from Exchange Account |
1,123.92 |
100.00 |
|
Add : Net Accretion(+)/ |
|||
Net Utilisation(-) |
|||
during the year |
(-)608.17 |
(-)97.96 |
|
Balance at the end of the year |
567.25 |
51.50 |
|
V. |
Provision for net debit entries in |
||
RBI General Account |
63.15 |
63.15 |
|
VI. |
Provision for Outstanding |
||
Expenses |
1,239.12 |
1,367.14 |
|
VII.Miscellaneous (See note 5) |
4,369.94 |
3,616.68 |
|
Total (I to VII) |
1,18,356.01 |
1,09,243.95 |
|
|
|
|||
* The amount of Rs.81.20 crore represents unresolved items of credit included under Other Liabilities - Miscellaneous in the previous year, transferred to Contingency Reserve during 2002-03. |
|||
|
|
|||
5. RBI GENERAL ACCOUNT
Miscellaneous under 'Other Liabilities' includes Rs. 179.40 crore in respect of inter-office transactions and balances under reconciliation. Reconciliation of entries is in progress and necessary adjustments are being effected as and when ascertained.
6. RUPEE INVESTMENTS
Securities sold under LAF-REPO have been reduced from ‘Investments’. Accordingly, the Bank has absorbed the liquidity in the market to the tune of Rs.21,455.00 crore as on June 30, 2003 for which securities amounting to Rs.22,527.75 crore were provided as collateral. These securities were repurchased on July 1, 2003.
7. FOREIGN CURRENCY ASSETS |
||||
(Rupees crore) |
||||
|
|
||||
Particulars |
As at |
As at |
||
June 30, |
June 30, |
|||
2003 |
2002 |
|||
|
|
||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
||
|
|
||||
I. |
Held in Issue Department |
2,55,000.00 |
1,69,000.00 |
|
II. |
Held in Banking Department - |
|||
a) |
Included in Investments |
169.72 |
164.64 |
|
b) |
Balances Held Abroad |
1,09,831.26 |
98,168.54 |
|
Total |
3,65,000.98 |
2,67,333.18 |
||
|
|
||||
Notes: 1. There were outstanding forward exchange contracts as at June 30, 2003 under which the Reserve Bank has to buy US dollar equivalent to Rs.18,634.03 crore as against Rs.4,816.86 crore as at June 30, 2002. There were no outstanding forward sale contracts as at June 30, 2003 as against US dollar equivalent to Rs.6,882.44 crore as at June 30, 2002. 2. Uncalled amount on partly paid shares of the Bank for International Settlement as at June 30, 2003 - Rs. 73.24 crore. |
||||
8. OTHER ASSETS |
|||
(Rupees crore) |
|||
|
|
|||
Particulars |
As at |
As at |
|
June 30, |
June 30, |
||
2003 |
2002 |
||
|
|
|||
1 |
2 |
3 |
|
|
|
|||
I. |
Fixed Assets (net of |
||
accumulated depreciation) |
550.74 |
478.56 |
|
II. |
Gold |
3,145.63 |
2,979.07 |
III. |
Income accrued but not received |
6,621.92 |
6,928.99 |
IV. |
Miscellaneous |
2,106.27 |
2,328.72 |
Total |
12,424.56 |
12,715.34 |
|
|
|
|||
9. INTEREST, DISCOUNT, EXCHANGE, COMMISSION, ETC.
Interest, Discount, Exchange, Commission, etc. include the following items.
(Rupees crore) |
||||
|
|
||||
Particulars |
Year ended |
|||
June 30, |
June 30, |
|||
2003 |
2002 |
|||
|
|
||||
1 |
2 |
3 |
||
|
|
||||
(i) |
Profit on sale of Foreign |
|||
and Rupee Securities |
6,127.32 |
4,395.19 |
||
(ii) |
Rent realised |
11.98 |
10.01 |
|
(iii) |
Net profit on sale of Bank’s property |
2.65 |
1.22 |
|
|
|
||||
10.RETIREMENT BENEFITS
The Bank has made a provision of Rs. 616.67 crore towards pension and gratuity funds during the year based on actuarial valuation.