FAQ Page 1 - ആർബിഐ - Reserve Bank of India
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Some Useful Definitions
Ans: The other capital component (receivables and payables, except equity and participating preference shares investment) of direct investment covers the outstanding liabilities or claims arising due to borrowing and lending of funds, investment in debt securities, trade credits, financial leasing, share application money etc., between direct investors and DIEs and between two DIEs that share the same direct Investor. Non-participating preference shares owned by the direct investor are treated as debt securities & should be included in ‘other capital’.
Domestic Deposits
II. Deposits of Non-Residents Indians (NRIs)
Retail Direct Scheme
Nomination related queries
Business restrictions imposed on Paytm Payments Bank Limited vide Press Releases dated January 31 and February 16, 2024
Aadhar enabled Payment System (AePS)
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
24.1 An investor who purchases a bond can expect to receive a return from one or more of the following sources:
-
The coupon interest payments made by the issuer;
-
Any capital gain (or capital loss) when the bond is sold/matured; and
-
Income from reinvestment of the interest payments that is interest-on-interest.
The three yield measures commonly used by investors to measure the potential return from investing in a bond are briefly described below:
i) Coupon Yield
24.2 The coupon yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the face value. Coupon yield refers to nominal interest payable on a fixed income security like G-Sec. This is the fixed return the Government (i.e., the issuer) commits to pay to the investor. Coupon yield thus does not reflect the impact of interest rate movement and inflation on the nominal interest that the Government pays.
Coupon yield = Coupon Payment / Face Value
Illustration:
Coupon: 8.24
Face Value: ₹100
Market Value: ₹103.00
Coupon yield = 8.24/100 = 8.24%
ii) Current Yield
24.3 The current yield is simply the coupon payment as a percentage of the bond’s purchase price; in other words, it is the return a holder of the bond gets against its purchase price which may be more or less than the face value or the par value. The current yield does not take into account the reinvestment of the interest income received periodically.
Current yield = (Annual coupon rate / Purchase price) X100
Illustration:
The current yield for a 10 year 8.24% coupon bond selling for ₹103.00 per ₹100 par value is calculated below:
Annual coupon interest = 8.24% x ₹100 = ₹8.24
Current yield = (8.24/103) X 100 = 8.00%
The current yield considers only the coupon interest and ignores other sources of return that will affect an investor’s return.
iii) Yield to Maturity
24.4 Yield to Maturity (YTM) is the expected rate of return on a bond if it is held until its maturity. The price of a bond is simply the sum of the present values of all its remaining cash flows. Present value is calculated by discounting each cash flow at a rate; this rate is the YTM. Thus, YTM is the discount rate which equates the present value of the future cash flows from a bond to its current market price. In other words, it is the internal rate of return on the bond. The calculation of YTM involves a trial-and-error procedure. A calculator or software can be used to obtain a bond’s YTM easily (please see the Box III).
| YTM Calculation YTM could be calculated manually as well as using functions in any standard spread sheet like MS Excel. Manual (Trial and Error) Method Manual or trial and error method is complicated because G-Secs have many cash flows running into future. This is explained by taking an example below. Take a two year security bearing a coupon of 8% and a price of say ₹ 102 per face value of ₹ 100; the YTM could be calculated by solving for ‘r’ below. Typically, it involves trial and error by taking a value for ‘r’ and solving the equation and if the right hand side is more than 102, take a higher value of ‘r’ and solve again. Linear interpolation technique may also be used to find out exact ‘r’ once we have two ‘r’ values so that the price value is more than 102 for one and less than 102 for the other value.
Spread Sheet Method using MS Excel In the MS Excel programme, the following function could be used for calculating the yield of periodically coupon paying securities, given the price. YIELD (settlement,maturity,rate,price,redemption,frequency,basis) Wherein; Settlement is the security's settlement date. The security settlement date is the date on which the security and funds are exchanged. Maturity is the security's maturity date. The maturity date is the date when the security expires. Rate is the security's annual coupon rate. Price is the security's price per ₹100 face value. Redemption is the security's redemption value per ₹100 face value. Frequency is the number of coupon payments per year. (2 for Government bonds in India) Basis is the type of day count basis to use. (4 for Government bonds in India which uses 30/360 basis) |
External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits
G. END-USES
Foreign Investment in India
Answer: The following persons can acquire capital instruments on the stock exchanges:
-
FPIs registered with SEBI
-
NRIs
-
Other than (a) and (b) above, a person resident outside India, can acquire capital instruments on stock exchange, subject to the condition that the investor has already acquired and continues to hold the control of such company in accordance with SEBI (Substantial Acquisition of Shares and Takeover) Regulations and subject to conditions specified in Annex I of the Master Direction – Foreign Investment in India.
Indian Currency
C) Different Types of Bank Notes and Security Features of banknotes
Both old and new design notes usually circulate together for a while. The old design notes are then gradually withdrawn from circulation when they become unfit to be re-issued.
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
B. Entities Regulated by RBI and applicable regulations
The regulations would be applicable and the type of encumbrance created is immaterial.
Coordinated Portfolio Investment Survey – India
Contact Details for query related to CPIS
Ans: Queries/clarifications on CPIS may be sought from the RBI at the following address:
International Investment Position Division (IIPD)
Department of Statistics and Information Management (DSIM)
Reserve Bank of India
C-9/5 th Floor, Bandra - Kurla Complex, Bandra East
Mumbai, Maharashtra – 400 051
Email: cpis@rbi.org.in
Core Investment Companies
D. Miscellaneous:
Ans: Anything that has to be repaid to any other legal entity/ person will be an outside liability.
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies
Classification of NBFCs into sub-groups
Domestic Deposits
II. Deposits of Non-Residents Indians (NRIs)
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Some Useful Definitions
Ans: An enterprise is said to have a centre of economic interest and to be a resident unit of a country (economic territory) when the enterprise is engaged in a significant amount of production of goods and/or services in that centre or when it owns land or buildings located in that centre. The enterprise must maintain at least one production establishment in the country and must plan to operate the establishment indefinitely or over a long period of time.
Retail Direct Scheme
Nomination related queries
Business restrictions imposed on Paytm Payments Bank Limited vide Press Releases dated January 31 and February 16, 2024
Money Transfer through UPI/ IMPS
External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits
G. END-USES
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
Day count convention refers to the method used for arriving at the holding period (number of days) of a bond to calculate the accrued interest. As the use of different day count conventions can result in different accrued interest amounts, it is appropriate that all the participants in the market follow a uniform day count convention.
For example, the conventions followed in Indian market are given below.
Bond market: The day count convention followed is 30/360, which means that irrespective of the actual number of days in a month, the number of days in a month is taken as 30 and the number of days in a year is taken as 360.
Money market: The day count convention followed is actual/365, which means that the actual number of days in a month is taken for number of days (numerator) whereas the number of days in a year is taken as 365 days. Hence, in the case of T-Bills, which are essentially money market instruments, money market convention is followed.
In some countries, participants use actual/actual, some countries use actual/360 while some use 30/actual. Hence the convention changes in different countries and in different markets within the same country (eg. Money market convention is different than the bond market convention in India).
Foreign Investment in India
Indian Currency
C) Different Types of Bank Notes and Security Features of banknotes
Central banks the world over change the design of their banknotes and introduce new security features primarily to make counterfeiting difficult and to stay ahead of counterfeiters. India also follows the same policy.
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
B. Entities Regulated by RBI and applicable regulations
No, the definition of “companies in the group” is only for the purpose of determining the applicability of prudential norms on multiple NBFCs in a group.
Coordinated Portfolio Investment Survey – India
Updated: ഡിസം 01, 2023
Special instructions for banks
Ans: No, investments made by branches of your bank located outside India should not be included in CPIS.
Core Investment Companies
D. Miscellaneous:
Ans: The period of 10 years was specified as a prudential measure not necessarily in alignment with a provision of the Companies Act. Moreover, the issue here is not public deposits but Outside Liabilities.
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies
Classification of NBFCs into sub-groups
Retail Direct Scheme
Investment and Account holdings related queries
While the primary auctions are conducted generally on specified days of the week as given in the table below, these days may differ due to holidays or other considerations. Half yearly indicative calendars are published on RBI website for Government of India’s dated securities and Sovereign Gold Bonds whereas quarterly indicative calendars are published for Treasury Bills and State Development loans. For details visit /en/web/rbi
| S. No. | Government security | Primary auction usually held on |
| 1 | Government of India Treasury Bills (T-Bills) | Wednesdays |
| 2 | Government of India dated securities (dated G-Sec) | Fridays |
| 3 | State Development Loans (SDLs) | Tuesdays |
| 4 | Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGB) | Weekly windows announced by RBI in its press release |
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Some Useful Definitions
Ans:
Foreign Subsidiary: An Indian entity is called as a Foreign Subsidiary if a non-resident investor owns more than 50% of the voting power/equity capital OR where a non-resident investor and its subsidiary(s) combined own more than 50% of the voting power/equity capital of an Indian enterprise.
Foreign Associate: An Indian entity is called as Foreign Associate if non-resident investor owns at least 10% and no more than 50% of the voting power/equity capital OR where non-resident investor and its subsidiary(s) combined own at least 10% but no more than 50% of the voting power/equity capital of an Indian enterprise.
Special Purpose Vehicle: A special purpose Vehicle (SPV) is a legal entity (usually a limited company of some type or, sometimes, a limited partnership) created to fulfil narrow, specific or temporary objectives. SPV have little or no employment, or operations, or physical presence in the jurisdiction in which they are created by their parent enterprises, which are typically located in other jurisdictions (economies). They are often used as devices to raise capital or to hold assets and liabilities and usually do not undertake significant production.
Domestic Deposits
III. Advances
Business restrictions imposed on Paytm Payments Bank Limited vide Press Releases dated January 31 and February 16, 2024
Money Transfer through UPI/ IMPS
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
It is calculated as per the following formula

External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits
G. END-USES
Foreign Investment in India
Indian Currency
C) Different Types of Bank Notes and Security Features of banknotes
The security features in MG Series 2005 and MG (New) Series banknotes are as under:
i. Security Thread: The silver-coloured machine-readable security thread in ₹10, ₹20 and ₹50 denomination banknotes is windowed on front side and fully embedded on reverse side. The thread fluoresces in yellow on both sides under ultraviolet light. The thread appears as a continuous line from behind when held up against light. ₹100 and above denomination banknotes have machine-readable windowed security thread with colour shift from green to blue when viewed from different angles. It fluoresces in yellow on the reverse and the text will fluoresce on the obverse under ultraviolet light.
ii. Intaglio Printing: The portrait of Mahatma Gandhi, Reserve Bank seal, Guarantee and promise clause, Ashoka Pillar emblem, RBI’s Governor's signature and the identification mark for the visually impaired persons are printed in intaglio in denominations ₹100 and above.
iii. See through register: On the left side of the note, a part of the numeral of each denomination is printed on the obverse (front) and the other part on the reverse. The accurate back-to-back registration makes the numeral appear as one when viewed against light.
iv. Water Mark and electrotype watermark: The banknotes contain the portrait of Mahatma Gandhi in the watermark window with a light and shade effect and multi-directional lines. An electrotype mark showing the denominational numeral in each denomination banknote also appears in the watermark widow and these can be viewed better when the banknote is held against light.
v. Colour Shifting Ink: The numeral 200, 500 & 2000 on the ₹200, ₹500, and ₹2000* banknotes are printed in a colour-shifting ink. The colour of these numerals appears green when the banknotes are held flat but would change to blue when the banknotes are held at an angle.
vi. Fluorescence: The number panels of the banknotes are printed in fluorescent ink. The banknotes also have dual-coloured optical fibres. Both can be seen when the banknotes are exposed to ultra-violet lamp.
vii. Latent Image: In the banknotes of ₹20 and above in the MG-2005 Series, the vertical band next to the (right side) Mahatma Gandhi’s portrait contains a latent image, showing the denominational value. The value can be seen only when the banknote is held horizontally, and light allowed to fall on it; otherwise, this feature appears only as a vertical band. In the MG (New) Series banknotes, the latent image exists in denominations ₹100 and above.
viii. Micro letterings: This feature appears at different places on the banknotes and can be seen better under a magnifying glass.
ix. Additional Features introduced since 2015:
• New Numbering Pattern
The numerals in both the number panels of the banknotes are in ascending size from left to right while the first three alpha-numeric characters (prefix) will remain constant in size.
• Angular Bleed Lines and Increase in the size of Identification Marks
Angular Bleed Lines have been introduced in banknotes - 4 lines in 2 blocks in ₹100, 4 angular bleed lines with two circles in between in ₹200, 5 lines in 3 blocks in ₹500, 7 in ₹2000*. In addition, the size of the identification marks in denominations ₹100 and above have been increased by 50 percent.
Information about the above security features present in the Indian banknotes denomination-wise is also available on the website www.rbi.org.in>>press releases. Alternately, information can also be accessed from https://website.rbi.org.in/web/rbi/-/notifications/master-circular-detection-and-impounding-of-counterfeit-notes-11610.
*₹2000 denomination notes continue to be legal tender. For more details, please refer to our press release 2023-2024/851 dated September 01, 2023 (https://rbi.org.in/web/rbi/-/press-releases/withdrawal-of-%E2%82%B92000-denomination-banknotes-status-56301).
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
B. Entities Regulated by RBI and applicable regulations
Yes, prior approval would be required in all cases of acquisition/ transfer of shareholding of 26 per cent or more of the paid up equity capital of an NBFC.
Coordinated Portfolio Investment Survey – India
Updated: ഡിസം 01, 2023
Special instructions for banks
Ans: Yes, it should be included.
Core Investment Companies
D. Miscellaneous:
Ans: The term used in the CIC Master Direction is block sale and not block deal which has been defined by SEBI. In the context of the Master Direction, a block sale would be a long term or strategic sale made for purposes of disinvestment or investment and not for short term trading. Unlike a block deal, there is no minimum number/value defined for the purpose.
Domestic Deposits
III. Advances
An illustrative list of Intermediary Agencies is as under;
-
State Sponsored organizations for on-lending to Weaker Sections@
-
Distributors of agricultural inputs/ implements.
-
State Financial Corporations (SFCs)/ State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDCs) to the extent they provide credit to weaker sections.
-
National Small Industries Corporation (NSIC).
-
Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC)
-
Agencies involved in assisting the decentralized sector.
-
Housing and Urban Development Corporation Ltd. (HUDCO)
-
Housing Finance Companies approved by National Housing Bank (NHB) for refinance.
-
State sponsored organization for SCs/STs (for purchase and supply of inputs to and/or marketing of output of the beneficiaries of these organizations).
-
Micro Finance Institutions/ Non-Government Organizations (NGOs) on lending to SHGs.
@ ‘Weaker Sections’ in Priority Sector includes following:
-
Small and marginal farmers with land holdings of 5 acres and less, landless labourers, tenant farmers and share-croppers;
-
Artisans, village and cottage industries where individual credit requirements do not exceed Rs.25,000/-.
-
Small and marginal farmers, sharecroppers, agricultural and non-agricultural labourers, rural artisans and families living below the poverty lines are the beneficiaries. The family income should not exceed Rs.11,000/- per annum.
-
Scheduled Castes and Scheduled Tribes.
-
Beneficiaries are persons whose family income from all sources does not exceed Rs.7200/- per annum in urban or semi urban areas or Rs.6400/- per annum in rural areas. They should not own any land or the size of their holding does not exceed one acre in the case of irrigated land and 2.5 acres in the case of unirrigated land (land holding criteria do not apply to SC/ST).
-
Beneficiaries under Scheme of Liberation and Rehabilitation of Scavengers (SLRs).
-
Advances granted to Self-Help Groups (SHGs) for reaching the rural poor.
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies
Time frame for compliance of regulations
Retail Direct Scheme
Investment and Account holdings related queries
G-Secs are credit risk free instruments in domestic currency. However, there are market risks if you sell before maturity. You may refer to ‘Government Securities Market- A primer’, published on RBI website, to understand various risks associated with government securities.
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Some Useful Definitions
Ans: Participating preference shares are those shares which have one or more of the following rights:
(a) To receive dividend, out of surplus profit after paying the dividend to equity shareholders.
(b) To have share in surplus assets remaining after the entire capital is paid in case of winding up of the company.
On the other hand, non-participating preference shares are those shares which do not have any of the above said rights.
Business restrictions imposed on Paytm Payments Bank Limited vide Press Releases dated January 31 and February 16, 2024
Paytm Payments Bank Business Correspondent
External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits
G. END-USES
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
27.1 Duration (also known as Macaulay Duration) of a bond is a measure of the time taken to recover the initial investment in present value terms. In simplest form, duration refers to the payback period of a bond to break even, i.e., the time taken for a bond to repay its own purchase price. Duration is expressed in number of years. A step by step approach for working out duration is given in the Box IV below.
| Calculation for Duration First, each of the future cash flows is discounted to its respective present value for each period. Since the coupons are paid out every six months, a single period is equal to six months and a bond with two years maturity will have four time periods. Second, the present values of future cash flows are multiplied with their respective time periods (these are the weights). That is the PV of the first coupon is multiplied by 1, PV of second coupon by 2 and so on. Third, the above weighted PVs of all cash flows is added and the sum is divided by the current price (total of the PVs in step 1) of the bond. The resultant value is the duration in no. of periods. Since one period equals to six months, to get the duration in no. of year, divide it by two. This is the time period within which the bond is expected to pay back its own value if held till maturity. Illustration: Taking a bond having 2 years maturity, and 10% coupon, and current price of ₹101.79, the cash flows will be (prevailing 2 year yield being 9%):
Duration in number of periods = 379.28/101.79 = 3.73 Duration in years = 3.73/2 = 1.86 years |
More formally, duration refers to:
-
The weighted average term (time from now to payment) of a bond's cash flows or of any series of linked cash flows.
-
The higher the coupon rate of a bond, the shorter the duration (if the term of the bond is kept constant).
-
Duration is always less than or equal to the overall life (to maturity) of the bond.
-
Only a zero coupon bond (a bond with no coupons) will have duration equal to its maturity.
What is Modified Duration?
27.2 Modified duration (MD) is a modified version of Macaulay Duration. It refers to the change in value of the security to one per cent change in interest rates (Yield). The formula is
Illustration
In the above example given in Box IV, MD = 1.86/(1+0.09/2) = 1.78
Duration is useful primarily as a measure of the sensitivity of a bond's market price to interest rate (i.e., yield) movements. It is approximately equal to the percentage change in price for one percent change in yield. For example the duration is the approximate percentage by which the value of the bond will fall for a 1% per annum increase in market interest rate. So, a 15-year bond with a duration of 7 years would fall approximately 7% in value if the interest rate increased by 1% per annum. In other words, duration is the elasticity of the bond's price with respect to interest rates. This ignores convexity explained in para 24.7
What is PV 01?
27.3 PV01 describes the actual change in price of a bond if the yield changes by one basis point (equal to one hundredth of a percentage point). It is the present value impact of 1 basis point (0.01%) (1%=100 bps) movement in interest rate. It is often used as a price alternative to duration (a time measure). Higher the PV01, the higher would be the volatility (sensitivity of price to change in yield).
Illustration
From the modified duration (given in the illustration under 27.2), we know that the security value will change by 1.78% for a change of 100 basis point (1%) change in the yield. In value terms that is equal to 1.78*(101.79/100) = ₹ 1.81.
Hence the PV01 = 1.81/100 = ₹0.018, which is 1.8 paise. Thus, if the yield of a bond with a Modified Duration of 1.78 years moves from say 9% to 9.05% (5 basis points), the price of the bond moves from ₹101.79 to ₹101.70 (reduction of 9 paise, i.e., 5x1.8 paise).
What is Convexity?
27.4 Calculation of change in price for change in yields based on duration works only for small changes in yields. This is because the relationship between bond price and yield is not strictly linear. Over large variations in yields, the relationship is curvilinear i.e., the reduction in option free bond price is less than the change calculated based only on duration for yield increase, and increase in option free bond price will be more than the change calculated based only on duration for yield decrease. This is measured by a concept called convexity, which is the change in duration of a bond due to change in the yield of the bond.
Foreign Investment in India
Indian Currency
C) Different Types of Bank Notes and Security Features of banknotes
In addition to the security features listed above, banknotes issued after introduction of MG series-2005 have the year of printing on the reverse of the banknotes which is not present in the pre-2005 series.
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
B. Entities Regulated by RBI and applicable regulations
Reserve Bank of India has deregulated interest rates to be charged to borrowers by NBFCs. The rate of interest to be charged by the company is governed by the terms and conditions of the loan agreement entered into between the borrower and the NBFCs. However, the NBFCs have to be transparent and the rate of interest and manner of arriving at the rate of interest to different categories of borrowers should be disclosed to the borrower or customer in the application form and communicated explicitly in the sanction letter and on their websites, Key Facts Statement, etc., to enable the borrower to take an informed decision.
Coordinated Portfolio Investment Survey – India
Updated: ഡിസം 01, 2023
Special instructions for banks
Ans: No, it should not be included, as it will be considered as resident to resident transaction.
Core Investment Companies
D. Miscellaneous:
Ans: Adjusted net worth (ANW) is a concept akin to capital requirement wherein the ANW should not be less than 30% of the risk weighted assets (RWA). In cases where asset size is aggregated, all the CICs within the group will be registered as CIC and ANW will be applicable individually.
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Some Useful Definitions
Ans: If the Indian entity has issued the shares to non-resident entities under the FDI scheme in India, then it is a FDI and should be reported under the Foreign Direct Investment in India (Liabilities) of the return.
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies
Credit Rating
- The NBFCs in the category of equipment leasing and hire purchase finance companies having Rating of less than the Investment Grade as mentioned below are no longer entitled to accept fresh public deposits :
Name of rating agencies | Level of minimum investment |
EL/HP Cos. | LC/ICs |
CRISIL | A- (A MINUS) |
ICRA | A- (A MINUS) |
CARE | BBB (FD) |
DCR India | BBB- (BBB minus) |
The Loan and Investment Companies having Rating of less than `A are no longer entitled to accept fresh deposits.
It may be added that A- is not equivalent to A; AA- is not equivalent to AA and AAA- is not equivalent to AAA.
Retail Direct Scheme
Investment and Account holdings related queries
The returns on Government securities are dependent on various features of the securities. You may refer to ‘Government Securities Market- A primer’, published on RBI website, to understand the factors affecting the returns on government securities.
Domestic Deposits
III. Advances
Yes. The banks are free to determine the rates of interest without reference to BPLR and regardless of the size, in respect of following loans:
(i) a. Loans for purchase of consumer durables.
b. Loans to individuals against shares and debentures/ bonds
c. Other non-priority sector personal loans.
d. Advances/ overdrafts against domestic/ NRE/ FCNR(B) deposits with the bank, provided that the deposit/s stands/ stand either in the name(s) of the borrower himself/ borrowers themselves, or in the names of the borrower jointly with another person.
e. Finance granted to intermediary agencies (excluding those of housing) for on lending to ultimate beneficiaries and agencies providing input support.
f. Finance granted to housing finance intermediary agencies for on lending to ultimate beneficiaries
g. Discounting of Bills
h. Loans/Advances/Cash Credit/Overdrafts against commodities subject to Selective Credit Control
ii. Loans covered by participation in interest refinancing schemes of term lending institutions. | Banks are free to charge rates as per stipulations of the refinancing agencies without reference to BPLR |
Business restrictions imposed on Paytm Payments Bank Limited vide Press Releases dated January 31 and February 16, 2024
Accounts frozen, lien marked etc.
Any lien or freeze (full or partial) marked as per the instructions of any law enforcement or judicial authorities on the account/wallet of a customer with Paytm Payments Bank will continue to be governed by the orders passed by such authorities
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
28.1 For Cooperative banks, investments classified under 'Held to Maturity' (HTM) category need not be marked to market and will be carried at acquisition cost unless it is more than the face value, in which case the premium should be amortized over the period remaining to maturity. The individual scrip in the ‘Available for Sale’ (AFS) category in the books of the cooperative banks will be marked to market at the year-end or at more frequent intervals. The individual scrip in the ‘Held for Trading’ (HFT) category will be marked to market at monthly or at more frequent intervals. The book value of individual securities in AFS and HFT categories would not undergo any change after marking to market.
28.2 RBI vide FMRD.DIRD.7/14.03.025/2017-18 dated March 31, 2018 has notified that Financial Benchmark India Pvt. Ltd (FBIL) has been advised to assume the responsibility for administering valuation of Government securities with effect from March 31, 2018. From this date, FIMMDA has ceased to publish prices/yield of Government securities and this role has been taken over by FBIL. FBIL had commenced publication of the G-Sec and SDL valuation benchmarks based on the extant methodology. Going forward, FBIL will undertake a comprehensive review of the valuation methodology. RBI regulated entities, including banks, non-bank financial companies, Primary Dealers, Co-Operative banks and All India Financial Institutions who are required to value Government securities using prices published by FIMMDA as per previous directions may use FBIL prices with effect from March 31, 2018. Other market participants who have been using Govt. securities prices/yields published by FIMMDA may use the prices/yields published by FBIL for valuation of their investment portfolio.
28.3 State Development Loans were previously valued by applying YTM method by marking it up by a spread of 25 basis points on the Central G-Sec yield of the corresponding residual maturity, whereas for corporate bonds the spreads given by the FIMMDA need to be added. RBI vide its notification DBR.BP.BC.No.002 /21.04.141/2018-19 dated July 27, 2018 decided that securities issued by each state government, i.e., State Development Loans (SDLs), shall be valued in a manner which would objectively reflect their fair value based on observed prices/yields and Financial Benchmarks India Pvt. Ltd. (FBIL) shall make available prices for valuation of SDLs based on the above principles. Brief details of valuation methodology is provided in Box V.
| A framework in this regard has been formulated by FBIL having the following elements: (a) On any business day, the secondary market prices/YTM of SDLs and the auction prices/YTM of SDLs, as available, will be used for their valuation. However, the secondary market trades that are referred to the Dispute Resolution Committee (DRC) of the Fixed Income Money Market and Derivatives Association of India (FIMMDA) and the reversed trades when they occur, will be excluded, (b) Interpolation/ extrapolation technique will be used in respect of the remaining SDLs which do not trade on that day, and (c) Consistency/market alignment check, as applicable, will be applied in respect of all traded prices/YTM. The methodology seeks to strike a judicious and prudent balance between two opposing considerations: Since the number of actual/observed prices in respect of SDLs are very small, the opportunity cost of not including any actual/observed price is high (consequence of the so-called Type 1 error). However, sufficient care has been exercised, by way of the imposition of a set of objective criteria, to make sure that (i) off-market data are excluded, and (ii) no incentive for market manipulation is provided (reducing the possibility of the so called Type 2 error). The detailed valuation methodology along with illustrations is provided on FBIL website at link https://www.fbil.org.in/uploads/general/FBIL-SDL_Valuation_Methodology.pdf |
28.4 In the case of corporate bonds, the spread that need to be added to the corresponding yield on central G-Sec will be published by the FIMMDA from time to time. FIMMDA gives out the information on corporate bond spreads for various ratings of bonds. While valuing a bond, the appropriate spread has to be added to the corresponding CG yield and the bond has to be valued using the standard ‘Price’ formula.
External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits
G. END-USES
Foreign Investment in India
Indian Currency
C) Different Types of Bank Notes and Security Features of banknotes
The Mahatma Gandhi (New) Series banknotes have a sharp colour contrast scheme to facilitate identification by the partially visually challenged. The banknotes from ₹100 denomination onwards, have angular bleed lines (4 lines in 2 blocks in ₹100, 4 angular bleed lines with two circles in between in ₹200, 5 lines in 3 blocks in ₹500, 7 in ₹2000*) and identification mark for the benefit of the visually challenged. There is an identification mark on the front side of each note which is in raised print (intaglio) and has different shapes for different denominations for e.g. Horizontal rectangle for ₹2000, circle for ₹500, raised Identification mark H for ₹200, triangle for ₹100. Further, in these denominations, numerals are prominently displayed in the central area of the notes in raised print.
*₹2000 denomination notes continue to be legal tender. For more details, please refer to our press release 2023-2024/851 dated September 01, 2023 (https://rbi.org.in/web/rbi/-/press-releases/withdrawal-of-%E2%82%B92000-denomination-banknotes-status-56301).
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
B. Entities Regulated by RBI and applicable regulations
IRF may be used to hedge interest rate risk associated with single asset/ liability or a group of assets/ liabilities. Hence, NBFCs are permitted to use duration-based hedging for managing interest rate risk.
Core Investment Companies
D. Miscellaneous:
Ans: The total assets of all NBFCs (Including Standalone Primary Dealer (SPD), Infrastructure Debt Fund-Non-Banking Financial Company (IDF-NBFC) and NBFCs which will always remain in Base Layer, viz., NBFC-Peer to Peer Lending Platform (NBFC-P2P), NBFC-Account Aggregator (NBFC-AA), Non-Operative Financial Holding Company (NOFHC) and NBFC without public funds and customer interface) in a Group, including all the registered Core Investment Companies (CICs) and unregistered CICs with asset size less than ₹100 crore which have raised public funds, shall be consolidated to determine the threshold for classification of other group NBFCs (NBFC- Investment and Credit Company (NBFC-ICC), NBFC- Micro Finance Institution (NBFC-MFI), NBFC- Factor and NBFC- Mortgage Guarantee Company (NBFC-MGC)) into middle layer. However, the consolidation of asset of unregistered CICs for the above purpose would not change the status of unregistered CICs.
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies
Credit Rating
Domestic Deposits
III. Advances
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Some Useful Definitions
Ans: Under FLA return, calculation of market value of equity capital for unlisted companies is done using the Own Funds at Book Value (OFVB) method, in accordance with IMF’s guidelines under the compilation of CDIS data for a country. It is calculated as follows:
Market value of equity capital held by Non- resident at OFBV for current year/previous year
= (Net worth of the company for current year/previous year) * (% non-resident equity holding for current year/previous year)
where, Net worth of the company
= (Paid up Equity & Participating Preference share capital of company + Reserves & Surplus - Accumulated losses)
Retail Direct Scheme
Investment and Account holdings related queries
| S. No. | Government security | Minimum investment amount/quantity (as on Nov 12, 2021) |
| 1 | Government of India Treasury Bills (T-Bills) | ₹10,000 |
| 2 | Government of India dated securities (dated G-Sec) | ₹10,000 |
| 3 | State Development Loans (SDLs) | ₹10,000 |
| 4 | Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGB) | One gram of gold |
Business restrictions imposed on Paytm Payments Bank Limited vide Press Releases dated January 31 and February 16, 2024
Accounts frozen, lien marked etc.
The bank has been directed to allow withdrawal or transfer to another bank account of the customer, upto the available balance in the account / wallets.
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
G-Secs are generally referred to as risk free instruments as sovereigns rarely default on their payments. However, as is the case with any financial instrument, there are risks associated with holding the G-Secs. Hence, it is important to identify and understand such risks and take appropriate measures for mitigation of the same. The following are the major risks associated with holding G-Secs:
29.1 Market risk – Market risk arises out of adverse movement of prices of the securities due to changes in interest rates. This will result in valuation losses on marking to market or realizing a loss if the securities are sold at adverse prices. Small investors, to some extent, can mitigate market risk by holding the bonds till maturity so that they can realize the yield at which the securities were actually bought.
29.2 Reinvestment risk – Cash flows on a G-Sec includes a coupon every half year and repayment of principal at maturity. These cash flows need to be reinvested whenever they are paid. Hence there is a risk that the investor may not be able to reinvest these proceeds at yield prevalent at the time of making investment due to decrease in interest rates prevailing at the time of receipt of cash flows by investors.
29.3 Liquidity risk – Liquidity in G-Secs is referred to as the ease with which security can be bought and sold i.e. availability of buy-sell quotes with narrow spreads. Liquidity risk refers to the inability of an investor to liquidate (sell) his holdings due to non-availability of buyers for the security, i.e., no trading activity in that particular security or circumstances resulting in distressed sale (selling at a much lower price than its holding cost) causing loss to the seller. Usually, when a liquid bond of fixed maturity is bought, its tenor gets reduced due to time decay. For example, a 10-year security will become 8 year security after 2 years due to which it may become illiquid. The bonds also become illiquid when there are no frequent reissuances by the issuer (RBI) in those bonds. Bonds are generally reissued till a sizeable amount becomes outstanding under that bond. However, issuer and sovereign have to ensure that there is no excess burden on Government at the time of maturity of the bond as very large amount maturing on a single day may affect the fiscal position of Government. Hence, reissuances for securities are generally stopped after outstanding under that bond touches a particular limit. Due to illiquidity, the investor may need to sell at adverse prices in case of urgent funds requirement. However, in such cases, eligible investors can participate in market repo and borrow the money against the collateral of such securities.
Risk Mitigation
29.4 Holding securities till maturity could be a strategy through which one could avoid market risk. Rebalancing the portfolio wherein the securities are sold once they become short term and new securities of longer tenor are bought could be followed to manage the portfolio risk. However, rebalancing involves transaction and other costs and hence needs to be used judiciously. Market risk and reinvestment risk could also be managed through Asset Liability Management (ALM) by matching the cash flows with liabilities. ALM could also be undertaken by matching the duration of the assets and liabilities.
Advanced risk management techniques involve use of derivatives like Interest Rate Swaps (IRS) through which the nature of cash flows could be altered. However, these are complex instruments requiring advanced level of expertise for proper understanding. Adequate caution, therefore, need to be observed for undertaking the derivatives transactions and such transactions should be undertaken only after having complete understanding of the associated risks and complexities.
External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits
G. END-USES
Foreign Investment in India
Indian Currency
C) Different Types of Bank Notes and Security Features of banknotes
Mobile Aided Note Identifier (MANI) is a mobile application launched by the Reserve Bank for aiding visually impaired persons to identify the denomination of Indian Banknotes. The free of cost application, once installed, does not require internet and is capable of identifying the denominations of Mahatma Gandhi Series and Mahatma Gandhi (New) series banknote by checking front or reverse side/part of the note including half folded notes at various holding angles and in a broad range of light conditions (normal light/day light/low light etc).
Note: This mobile application does not authenticate a note as being either genuine or counterfeit.
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
B. Entities Regulated by RBI and applicable regulations
As per extant guidelines, NBFCs with asset size of ₹1,000 crore and above are permitted to participate in IRF as trading members duly subject to provisions of ‘Rupee Interest Rate Derivatives (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2019’ dated June 26, 2019 (as amended from time to time). While trading members of stock exchanges are permitted to execute trades on their own account as well as on account of their clients, only banks, SPDs and All India Financial Institutions (AIFIs) have been allowed to act as market-makers. Hence, currently, NBFCs as trading members are permitted to execute only their proprietary trades and are not allowed to undertake transactions on behalf of clients.
Core Investment Companies
D. Miscellaneous:
Ans: Yes. As per the present directions for CICs, they are permitted to make investments in money market instruments, including money market mutual funds. Since Liquid Funds are also mutual funds with the underlying being money market instruments; CICs are permitted to invest their surplus funds in Liquid Fund Schemes also.
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies
Credit Rating
Domestic Deposits
III. Advances
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Some Useful Definitions
Ans: If the Indian reporting entity is listed, then their closing share price as on reference period, i.e., end-March of previous and current year is used for valuation of non-resident equity investment.
Retail Direct Scheme
Investment and Account holdings related queries
For dated G-Sec, T-Bills and SDLs – The following limits apply if you purchase these securities through the non-competitive segment of primary auctions:
| S. No. | Government security | Maximum investment amount/quantity (as on Nov 12, 2021) |
| 1 | Government of India Treasury Bills (T-Bills) | The aggregate allocation of all non-competitive bids will be restricted to a maximum of 5% of the aggregate nominal amount of the issue within the notified amount as specified by the Government of India, or any other percentage determined by RBI. |
| 2 | Government of India dated securities (dated G-Sec) | ₹2 crore (face value) per security per auction. |
| 3 | State Development Loans (SDLs) | 1% of notified amount (face value) per auction |
For Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs) – An individual may not subscribe to more than 4 kg of SGBs per fiscal year. The annual ceiling will include bonds subscribed under different tranches during initial issuance by Government and those purchased from the Secondary Market.
Business restrictions imposed on Paytm Payments Bank Limited vide Press Releases dated January 31 and February 16, 2024
Onboarding of new customers
The business restriction dated March 11, 2022, prohibiting Paytm Payments Bank from onboarding any new customers for any of its services continues to be in force. Hence, Paytm Payments Bank cannot onboard any new customers after March 11, 2022.
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
30.1 While the G-Secs market generally caters to the investors with a long-term investment horizon, the money market provides investment avenues of short term tenor. Money market transactions are generally used for funding the transactions in other markets including G-Secs market and meeting short term liquidity mismatches. By definition, money market is for a maximum tenor of one year. Within the one year, depending upon the tenors, money market is classified into:
i. Overnight market - The tenor of transactions is one working day.
ii. Notice money market – The tenor of the transactions is from 2 days to 14 days.
iii. Term money market – The tenor of the transactions is from 15 days to one year.
What are the different money market instruments?
30.2 Money market instruments include call money, repos, T- Bills (for details refer para 1.3), Cash Management Bills (for details refer para 1.4), Commercial Paper, Certificate of Deposit and Collateralized Borrowing and Lending Obligations (CBLO).
Call money market
30.3 Call money market is a market for uncollateralized lending and borrowing of funds. This market is predominantly overnight and is open for participation only to scheduled commercial banks and the primary dealers.
Repo market
30.4 Repo or ready forward contact is an instrument for borrowing funds by selling securities with an agreement to repurchase the said securities on a mutually agreed future date at an agreed price which includes interest for the funds borrowed.
30.5 The reverse of the repo transaction is called ‘reverse repo’ which is lending of funds against buying of securities with an agreement to resell the said securities on a mutually agreed future date at an agreed price which includes interest for the funds lent.
30.6 It can be seen from the definition above that there are two legs to the same transaction in a repo/ reverse repo. The duration between the two legs is called the ‘repo period’. Predominantly, repos are undertaken on overnight basis, i.e., for one day period. Settlement of repo transactions happens along with the outright trades in G-Secs.
30.7 The consideration amount in the first leg of the repo transactions is the amount borrowed by the seller of the security. On this, interest at the agreed ‘repo rate’ is calculated and paid along with the consideration amount of the second leg of the transaction when the borrower buys back the security. The overall effect of the repo transaction would be borrowing of funds backed by the collateral of G-Secs.
30.8 The repo market is regulated by the Reserve Bank of India. All the above mentioned repo market transactions should be traded/reported on the electronic platform called the Clearcorp Repo Order Matching System (CROMS).
30.9 As part of the measures to develop the corporate debt market, RBI has permitted select entities (scheduled commercial banks excluding RRBs and LABs, PDs, all-India FIs, NBFCs, mutual funds, housing finance companies, insurance companies) to undertake repo in corporate debt securities. This is similar to repo in G-Secs except that corporate debt securities are used as collateral for borrowing funds. Only listed corporate debt securities that are rated ‘AA’ or above by the rating agencies are eligible to be used for repo. Commercial paper, certificate of deposit, non-convertible debentures of original maturity less than one year are not eligible for this purpose. These transactions take place in the OTC market and are required to be reported on FIMMDA platform within 15 minutes of the trade for dissemination of trade information. They are also to be reported on the clearing house of any of the exchanges for the purpose of clearing and settlement.
Triparty Repo
"Tri-party repo" means a repo contract where a third entity (apart from the borrower and lender), called a Tri-Party Agent, acts as an intermediary between the two parties to the repo to facilitate services like collateral selection, payment and settlement, custody and management during the life of the transaction. Funds borrowed under repo including tri-party repo in government securities shall be exempted from CRR/SLR computation and the security acquired under repo shall be eligible for SLR provided the security is primarily eligible for SLR as per the provisions of the Act under which it is required to be maintained.
Tri Party Repo Dealing System (TREPS) facilitates, borrowing and lending of funds, in Triparty Repo arrangement. CCIL is the Central Counterparty to all trades from TREPS and also perform the role and responsibilities of Triparty Repo Agent. All the repo eligible entities are entitled to participate in Triparty Repo. The entity type admitted include, Public Sector Banks, Private Banks, Foreign Banks, Co-operative Banks, Financial Institutions, Insurance Companies, Mutual Funds, Primary Dealers, Bank cum Primary Dealers, NBFCs, Corporates, Provident/ Pension Funds, Payment Banks, Small Finance Banks, etc.
TREPS Dealing System is an anonymous order matching System provided by CCDS (Clearcorp Dealing Systems (India) Ltd) to enable Members to borrow and lend funds. It also disseminates online information regarding deals concluded, volumes, rate etc., and such other notifications as relevant to borrowing and lending under Triparty Repo by the members. The borrowing and/ or lending can be done for settlement type T+0 and T+1.
Commercial Paper (CP)
30.13 Commercial Paper (CP) is an unsecured money market instrument issued in the form of a promissory note and held in a dematerialized form through any of the depositories approved by and registered with SEBI. A CP is issued in minimum denomination of ₹5 lakh and multiples thereof and shall be issued at a discount to face value No issuer shall have the issue of CP underwritten or co-accepted and options (call/put) are not permitted on a CP. Companies, including NBFCs and AIFIs, other entities like co-operative societies, government entities, trusts, limited liability partnerships and any other body corporate having presence in India with net worth of ₹100 cr or higher and any other entities specifically permitted by RBI are eligible to issue Commercial papers subject to conditions specified by RBI. All residents, and non-residents permitted to invest in CPs under Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA), 1999 are eligible to invest in CPs; however, no person can invest in CPs issued by related parties either in the primary or secondary market. Investment by regulated financial sector entities will be subject to such conditions as the concerned regulator may impose.
RBI has issued Reserve Bank Commercial Paper Directions 2017 - FMRD.DIRD.01/CGM (TRS) - 2017 dated August 10, 2017
Certificate of Deposit (CD)
30.14 Certificate of Deposit (CD) is a negotiable money market instrument and issued in dematerialised form or as a Usance Promissory Note, for funds deposited at a bank or other eligible financial institution for a specified time period. Banks can issue CDs for maturities from 7 days to one year whereas eligible FIs can issue for maturities from 1 year to 3 years.
External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits
H. REFINANCING OF ECB
Foreign Investment in India
Indian Currency
C) Different Types of Bank Notes and Security Features of banknotes
The processes and systems followed for production of Indian banknotes are at par with the best practices adopted globally. In line with the same, banknote quality is maintained well within the various tolerance parameters for dimension, placement of design, print features etc. A press release issued by RBI in this regard can be accessed at the following link: https://rbi.org.in/web/rbi/-/press-releases/rbi-clarifies-on-quality-control-measures-in-currency-note-printing-41364.
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
C. Residuary Non-Banking Companies (RNBCs)
Residuary Non-Banking Company is a class of NBFC which is a company and has as its principal business the receiving of deposits, under any scheme or arrangement or in any other manner and not being an Investment and Credit Company, a housing finance company, an insurance company, a factor, a mutual benefit company, a mutual benefit financial company and a miscellaneous non-banking company. These companies are required to maintain investments as per directions of the Reserve Bank, in addition to liquid assets. The functioning of these companies is different from those of NBFCs in terms of method of mobilization of deposits and requirement of deployment of depositors' funds as per Directions. Besides, Prudential Norms Directions are also applicable to these companies.
Core Investment Companies
D. Miscellaneous:
Yes, activities such as trading or rendering services to the group companies are not restricted for CICs, provided such activities are carried out purely in the nature of a non-financial activity, and they do not lead the CIC to carry on any other financial activity not permitted under the extant instructions within the group or on behalf of the group entities. Such activities should not ultimately render creation of any financial asset which the CICs are not permitted to hold within/outside the group. Further, CICs cannot enter into commodity derivative contracts or hold any non-financial assets other than real estate or other fixed assets which are required for effective functioning of the CIC outside the group within the limit of 10% of net assets.
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies
Credit Rating
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Some Useful Definitions
Ans: A related party is a person or entity that is related to the entity that is preparing its financial statements (referred to as the ‘reporting entity’).
A person or a close member of that person’s family is related to a reporting entity if that person:
(i) has control or joint control over the reporting entity.
(ii) has significant influence over the reporting entity; or
(iii) is a member of the key management personnel of the reporting entity or of a parent of the reporting entity.
In the definition of a related party, an associate includes subsidiaries of the associate and a joint venture includes subsidiaries of the joint venture. Therefore, for example, an associate’s subsidiary and the investor that has significant influence over the associate are related to each other.
Retail Direct Scheme
Investment and Account holdings related queries
There are two ways to buy Government securities through Retail Direct platform:
-
By placing a bid in the primary auctions of dated G-Sec, T-Bills and SDLs (Non-competitive segment only, i.e., by only entering the desired amount of securities, without entering a price). For Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGBs), you may place a bid during the subscription windows announced by RBI on its website. For step-by-step details on bidding in auctions, you may refer to the User Manual on the Retail Direct Portal.
-
By placing a buy quote in the secondary market portal.
Domestic Deposits
III. Advances
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
31.1 The Fixed Income Money Market and Derivatives Association of India (FIMMDA), an association of Scheduled Commercial Banks, Public Financial Institutions, Primary Dealers and Insurance Companies was incorporated as a Company under section 25 of the Companies Act,1956 on June 3, 1998. FIMMDA is a voluntary market body for the bond, money and derivatives markets. FIMMDA has members representing all major institutional segments of the market. The membership includes Nationalized Banks such as State Bank of India, its associate banks and other nationalized banks; Private sector banks such as ICICI Bank, HDFC Bank; Foreign Banks such as Bank of America, Citibank, Financial institutions such as IDFC, EXIM Bank, NABARD, Insurance Companies like Life Insurance Corporation of India (LIC), ICICI Prudential Life Insurance Company, Birla Sun Life Insurance Company and all Primary Dealers.
31.2 FIMMDA represents market participants and aids the development of the bond, money and derivatives markets. It acts as an interface with the regulators on various issues that impact the functioning of these markets. FIMMDA also plays a constructive role in the evolution of best market practices by its members so that the market as a whole operates transparently as well as efficiently.
31.3 Financial Benchmarks India Pvt. Ltd (FBIL) was incorporated in 2014 as per the recommendations of the Committee on Financial Benchmarks. FBIL has taken over existing benchmarks such as Mumbai Inter-Bank Outright Rate (MIBOR) and option volatility and introduced new benchmarks such as Market Repo Overnight Rate (MROR), Certificate of Deposits (CDs) and T-Bills yield curves. The development of FBIL as an independent organisation for administration of all financial market benchmarks including valuation benchmarks is important for the credibility of these benchmarks and integrity of financial markets. FBIL has assumed the responsibility for administering valuation of Government securities with effect from March 31, 2018.
FBIL has also assumed the responsibility for computation and dissemination of the daily “Reference Rate” for Spot USD/INR and other major currencies against the Rupee, which was previously being done by the Reserve Bank.
External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits
H. REFINANCING OF ECB
Foreign Investment in India
Answer: Downstream investment made in accordance with the guidelines in existence prior to February 13, 2009 would not require any modification to conform to these regulations. All other investments, after the said date, would come under the ambit of FEMA 20(R). Downstream investments made between February 13, 2009 and June 21, 2013 which were not in conformity with these regulations should have been intimated to the Reserve Bank by October 3, 2013, for treating such cases as compliant with these regulations.
Indian Currency
D) Soiled, Mutilated and Imperfect Banknotes
(i) A ‘soiled note’ means a note which has become dirty due to normal wear and tear and includes a two-piece note pasted together wherein both the pieces presented belong to the same note and form the entire note with no essential feature missing.
(ii) “Mutilated banknote” is a banknote, of which a portion is missing, or which is composed of more than two pieces.
(iii) “Imperfect banknote” means any banknote, which is wholly or partially, obliterated, shrunk, washed, altered or indecipherable but does not include a mutilated banknote.
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
C. Residuary Non-Banking Companies (RNBCs)
While that there is no ceiling on raising of deposits by RNBCs, it is mandated that every RNBC has to ensure that the amounts deposited with it are fully invested in approved investments. In other words, in order to secure the interests of depositor, such companies are required to invest 100 per cent of their deposit liability into highly liquid and secure instruments, namely, Central/State Government securities, fixed deposits with scheduled commercial banks (SCB), Certificate of Deposits of SCB/FIs, units of Mutual Funds, etc.
Core Investment Companies
D. Miscellaneous:
The number of layers of CICs within a Group (including the parent CIC) shall be restricted to two, irrespective of the extent of direct or indirect holding/ control exercised by a CIC in the other CIC. For instance, if a group consists of a parent CIC namely HCo which is holding 100 per cent equity capital in three other CICs namely A, B and C, the layers in the group shall be as follows.
- HCo shall be considered as first layer of CIC
- A,B and C shall be considered as second layer of CICs.
- Any cross holdings, directly or indirectly through other entities in the group, by CICs in the second layer in any other CIC in the group shall be considered as creation of third layer of CIC/s in the group structure which is a violation of the extant instructions. However, investment by second layer CICs in non-CIC group companies is not a violation to the extant CIC regulations. Further, no restriction is placed on number of CICs in a horizontal layer.
Indian Currency
D) Soiled, Mutilated and Imperfect Banknotes
Reserve Bank of India has been continuously making efforts to make good quality banknotes available to the members of public. To help RBI and the banking system towards this objective, the members of public are requested to ensure the following:
-
Not to staple the banknotes;
-
Not to write/put rubber stamp or any other mark on the banknotes;
-
Not to use banknotes for making garlands/toys, decorating pandals and places of worship or for showering on personalities in social events, etc.
The Reserve Bank of India has issued a press release on March 12, 2008, appealing members of public not to use banknotes for making garlands, decorating pandals and places of worship or for showering on personalities in social events, etc. Press Release issued in this regard is available at the following link:
https://rbi.org.in/web/rbi/-/press-releases/respect-your-banknotes-rbi-appeals-to-public-18026.
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies
Credit Rating
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
C. Residuary Non-Banking Companies (RNBCs)
Retail Direct Scheme
Investment and Account holdings related queries
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Some Useful Definitions
Ans: Any domestic liabilities or assets (even if it is in foreign currency) should not be reported in the FLA return.
Domestic Deposits
III. Advances
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
32.1. RBI financial market watch - /en/web/rbi/financial-markets/other-links/financial-market-watch
This site provides links to information on prices of G-Secs on NDS-OM, money market and other information on G-Secs like outstanding stock etc.
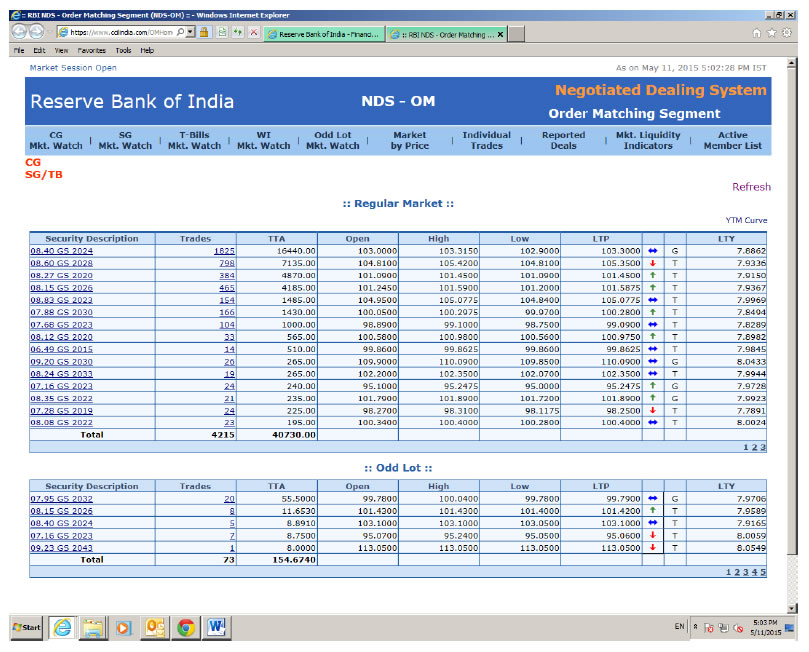
32.2. NDS-OM market watch https://www.ccilindia.com/OMHome.aspx
This site provides real-time information on traded as well as quoted prices of G-Secs, both in Order matching and Reporting segment. In addition, prices of When Issued (WI) (whenever trading takes place) segment are also provided.
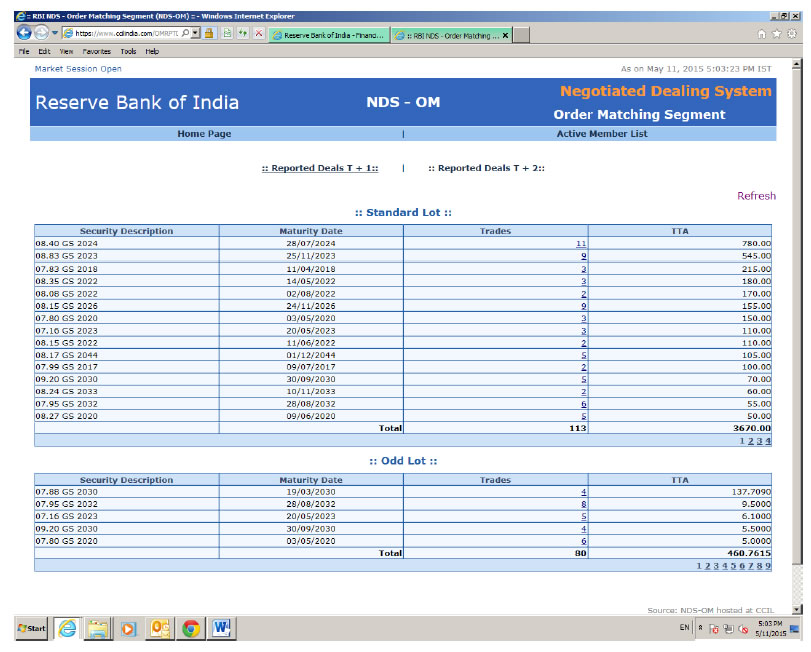
32.3. Reported deals on NDS-OM: https://www.ccilindia.com/OMRPTDeals.aspx
This site provides information on prices of G-Secs in OTC market as reported. One can see chronological traded price levels and quantity in various securities.
32.4 FBIL – www.fbil.org.in
Financial Benchmark India Private Ltd (FBIL) was jointly promoted by Fixed Income Money Market & Derivative Association of India (FIMMDA), Foreign Exchange Dealers’ Association of India (FEDAI) and Indian Banks’ ‘Association (IBA). It was incorporated on 9th December 2014 under the Companies Act 2013. It was recognised by Reserve bank of India as an independent Benchmark administrator on 2nd July 2015.
The company is run by a Board of Directors, assisted by an oversight committee. The main object of the company is to act as the administrators of the Indian interest rate and foreign exchange benchmarks and to introduce and implement policies and procedures to handle the benchmarks. It also will make policies for possible cessation of any benchmark and to follow steps for ensuring orderly transition to the new benchmarks. FBIL will review each benchmark to ensure that the benchmarks accurately represent the economic realities of the interest that it intends to measure. It will take up/consider such other benchmarks as may be required from time to time by periodically assessing the emerging needs of the end -users.
32.5 FIMMDA - http://www.fimmda.org/
This site provides a host of information on market practices for all the fixed income securities including G-Secs. Accessing information from this site requires a valid login and password which are provided by FIMMDA to the eligible entities.















