IST,
IST,
Highlight
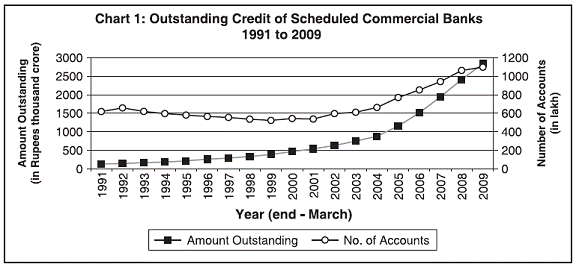
HIGHLIGHTS 1. The Basic Statistical Returns of Scheduled Commercial Banks in India, Volume 38, is based on data collected through BSR 1 and 2 surveys as on March 31, 2009, which covered 81,802 offices of scheduled commercial banks including regional rural banks. These returns are collected from each branch/office of a scheduled commercial banks in India. The salient features are set out below: Outstanding Credit of Scheduled Commercial Banks:- 2. Growth of gross outstanding credit: • At the end of March 2009, gross outstanding credit of scheduled commercial banks amounted to Rs. 28,47,713 crore registering an increase of 17.8 per cent as against an increase of 24.1 per cent in the previous year (Table No.1.3). • The number of borrowal accounts increased to 11.0 crore in 2009 from 10.7 crore in 2008, i.e. by 2.9 per cent (Table No. 1.3).
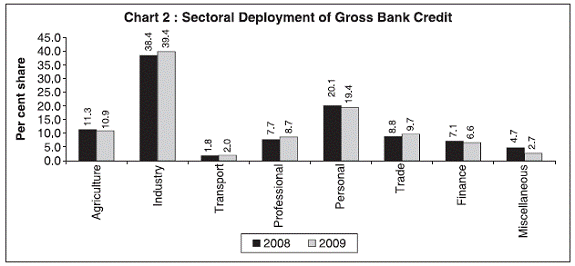
3. Bank group-wise distribution of credit : • The share of the nationalised banks in total bank credit is more than half, showing an increase to 50.5 per cent in 2009 from 48.8 per cent in 2008. The share of ‘private sector banks’ was 18.2 per cent in 2009. The share of foreign banks declined to 5.9 per cent in 2009 from 6.7 per cent a year ago (Table No.1.4). • The nationalised banks had the highest credit growth at 21.8 per cent in 2009. The SBI & Associates and Private sector banks witnessed growth in credit at 21.2 and 9.1 per cent in 2009, respectively. Foreign banks recorded a credit growth of 4.0 per cent, whereas the regional rural banks recorded a growth of 15.4 per cent in 2009. • Of the incremental credit, during 2009, SBI & Associates, Nationalised banks and private sector banks shared 26.7, 59.7 and 10.0 per cent, respectively. 4. Sectoral (occupation-wise) deployment of bank credit: • The share of agriculture credit in gross bank credit declined marginally to 10.9 per cent from 11.3 per cent in 2008. The share of credit to industry increased to 39.8 per cent in 2009 from 38.4 per cent in 2008 (Table 1.11 and Chart 2). • The share of personal loans decreased to 19.4 per cent of gross bank credit in 2009 from the level of 20.1 per cent in the previous year. • The share of credit to trade increased to 9.7 per cent in 2009 as against 8.8 per cent in 2008.
5. Sectoral (Occupation-wise) credit off-take: • The growth rate of bank credit to agriculture decreased to 12.9 per cent in 2009 as against 19.1 per cent in the preceding year (Table 1.9). • The growth of credit to industry declined marginally to 22.2 per cent in 2009 from 25.2 per cent recorded in 2008. • Personal Loans registered a growth of 14.0 per cent in 2009 compared to 12.0 per cent in 2008. Housing loans, which forms a part of personal loans grew by 14.6 per cent compared to 8.5 per cent in the previous year. 6. Incremental Bank Credit (Occupation-wise): • The industry sector, with 39.7 per cent share in the incremental credit in 2008, continued to capture the major share in 2009 at 47.8 per cent. • The agriculture sector absorbed about 8.2 per cent of the incremental credit in 2009 compared to 9.4 in 2008. • The personal loans accounted for 15.8 per cent of incremental credit, in which share of housing loans were 8.4 per cent compared to relatively lower shares of 11.0 per cent and 4.2 per cent respectively registered in the previous year. • The share of credit to professionals in the incremental credit of 14.2 per cent did not change much from 14.0 per cent recorded in 2008. 7. Size-wise distribution of bank credit: • The number of small borrowal accounts (with credit limit up to Rs 2 lakh) contributed 87.0 per cent of total number of accounts as against 88.4 per cent in 2008, while the share of outstanding credit of small borrowal accounts was 12.3 per cent as compared to 13.7 in 2008 (Table No.1.12). • The share of credit with credit limit above Rs. 25 crore increased to 41.2 per cent in 2009 from 35.6 per cent in the previous year. 8. Interest rate on bank credit: • The distribution of outstanding credit according to interest rate ranges (accounts each with credit limit of over Rs.2 lakh) revealed that the proportion of outstanding amount was the highest at 30.7 per cent in the range of 10 – 12 per cent (Table No. 1.13). • The weighted average interest rate in respect of all loans and advances with credit limit of over Rs.2 lakh worked out to be 11.47 per cent as at the end of March 2009 as compared to 12.34 per cent in the previous year. Aggregate Deposits:- 9. Growth in aggregate deposits: • Aggregate deposits amounted to Rs. 39,21,980 crore registering a growth of 20.7 per cent in 2009 as against 25.1 per cent a year ago (Table No.1.18). • The number of deposit accounts in 2009 increased by 13.9 per cent to 66.23 crore from about 58.17 crore in March 2008. 10. Bank group-wise distribution of deposits: • The nationalised banks have a major share in aggregate bank deposits, at 49.4 per cent in 2009. The share of SBI & Associates increased to 24.1 in 2009 as compared to 23.2 per cent in 2008 (Table No.1.4). • The deposits of the SBI & Associates registered the highest growth of 25.6 per cent followed by the nationalised banks (24.1 per cent) and Regional Rural banks (21.6) in 2009. 11. Type of deposits: • The share of term deposits in total deposits increased to 63.5 per cent in 2009 from 61.3 per cent in 2008. The shares of current deposits and saving deposits were at 12.0 per cent and 24.5 per cent, respectively in 2009 as against 13.9 and 24.8 per cent in 2008 (Table No.1.18). 12. Maturity pattern of term deposits: • The share of term deposits with original maturity period of 5 years and above in total term deposits decreased to 7.6 per cent in 2009 from 8.3 per cent in the previous year (Table No.1.24). • The share of term deposit with maturity period 1 to 3 years was 52.1 per cent of the total term deposit amount in 2009 compared to 46.8 per cent in 2008 while deposits for maturity period 6 months to 1 year witnessed decline in their share to 13.6 per cent from 14.2 per cent in the previous year. The share of deposits with maturity period ranging from 3 years to less than 5 years declined to 12.6 per cent in 2009 from 14.8 per cent in 2008. 13. Interest rate on term deposits: • The weighted average interest rate of term deposits outstanding in 2009 worked out to 8.84 per cent, as compared to 8.71 per cent as at end-March 2008 (Table No.1.28). 14. Interest rate spread: • The interest rate spread on bank credit (large borrowal account with credit limit over Rs. 2 lakhs) over term deposits was at 2.63 per cent in 2009 compared to 3.63 per cent in 2008.
Credit - Deposit Ratio:-
15. Population group-wise C-D Ratio: • The All-India C-D ratio was at 72.6 per cent in 2009 compared to 74.4 per cent in 2008. • The population group-wise C-D ratio in respect of rural areas at the end of March 2009 was at 57.1 per cent as per place of sanction of credit. In the case of semi-urban and urban areas the C-D ratios were 50.0 per cent and 55.6 per cent, respectively. The C-D ratios as per place of utilisation for rural, semi-urban and urban areas were 85.1 per cent, 58.7 per cent and 60.6 per cent, respectively. The C-D ratios recorded in metropolitan centres as per place of sanction and utilisation were 86.9 per cent and 78.4 per cent as compared to 87.2 per cent and 75.7, respectively in 2008 (Table No.1.6). 16. Migration of credit among the states: • The analysis of migration of credit among the states has been done through the Credit Deposit (C-D) ratios, calculated as per the place of sanction of credit and place of utilisation of credit (Table No. 1.7 and Chart –3). • Rajasthan, Chandigarh, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu had C-D Ratio, both as per place of sanction and utilisation, above the All-India C-D Ratio (72.6 per cent). • Among these states Chandigarh, Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu had higher C-D ratios as per utilisation than sanction.
|
கடைசியாக புதுப்பிக்கப்பட்ட பக்கம்: