IST,
IST,
Report on Foreign Exchange Reserves
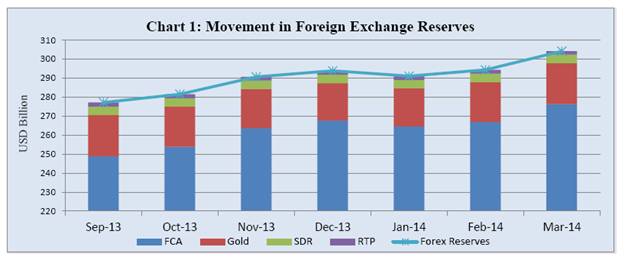
Developments during the Half Year ended March, 2014 The Reserve Bank of India publishes half-yearly reports on management of foreign exchange reserves for bringing about more transparency and enhancing the level of disclosure. These reports are prepared half yearly with reference to the position as at end-March and end-September each year. The present report (22nd in the series) is with reference to the position as at end-March, 2014. The report is divided into two parts: Part I contains the developments regarding movement of reserves and information on the external liabilities vis-à-vis the foreign exchange reserves, Financial Transaction Plan (FTP) of the IMF, adequacy of reserves, etc. during the half-year under review. Objectives of reserve management, statutory provisions, risk management practices, information on transparency and disclosure practices followed by the RBI with regard to reserve management are covered in Part II. Part- I The reserves stood at USD 277.2 billion as at end-September, 2013. During the half year under review, reserves have risen consistently from USD 281.5 billion as at end-October, 2013 to USD 293.8 billion as at end-December, 2013. It came down to USD 291.1 billion as at end-January, 2014, after which it increased to USD 304.2 billion as at end-March, 2014 (Table 1 & Chart 1). Although both US dollar and Euro are intervention currencies and the Foreign Currency Assets (FCA) are maintained in major currencies like US dollar, Euro, Pound Sterling, Japanese Yen etc., the foreign exchange reserves are denominated and expressed in US dollar only. Movements in the FCA occur mainly on account of purchases and sales of foreign exchange by RBI in the foreign exchange market, income arising out of the deployment of the foreign exchange reserves, external aid receipts of the Central Government and the effects of revaluation of the assets.
The net forward liability of the Reserve Bank in domestic foreign exchange market stood at USD 31,030 million as at the end of March, 2014. I.4. External Liabilities vis-à-vis Foreign Exchange Reserves India’s International Investment Position (IIP), which is a summary record of the stock of country’s external financial assets and liabilities, as at end-March, 2014, is furnished in Table 2.
The net IIP as at end-March, 2014 was negative at USD 331.6 billion, implying that our external liabilities are more than the external assets. The net IIP as at end-March, 20131 and end-September, 20132 was USD (-) 326.7 billion and USD (-) 302 billion respectively. At the end of March, 2014, the import cover increased to 7.8 months from 6.6 months at end-September, 2013. The ratio of short-term debt3 to the foreign exchange reserves, which was 34.2 per cent at end-September, 2013, declined to 29.3 per cent at end-March, 2014. The ratio of volatile capital flows (defined to include cumulative portfolio inflows and short-term debt) to the reserves declined from 97.2 per cent as at end-September, 2013 to 90.4 per cent as at end-March, 2014. I.6. Management of Gold Reserves The Reserve Bank held 557.75 tonnes of gold, of which 265.49 tonnes are held overseas in safe custody with the Bank of England and the Bank for International Settlements. It formed about 6.9 per cent of the total foreign exchange reserves in value terms (USD) as at end-March, 2014. I.7 Investment Pattern and Earnings of the Foreign Currency Assets The foreign currency assets are invested in multi-currency, multi-asset portfolios as per the existing norms, which are similar to the best international practices followed in this regard. As at end-March, 2014, out of the total foreign currency assets of USD 276.4 billion, USD 171.3 billion was invested in securities, USD 89.7 billion was deposited with other central banks, Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF) and remaining USD 15.3 billion comprised deposits with foreign branches of commercial banks and funds placed with the External Asset Managers (EAMs) (Table 3). I.8.1 Financial Transaction Plan (FTP) of the IMF During September, 2013-March, 2014, there was one purchase transaction for US$ 81.71 million and seven repurchase transactions amounting to USD 438.54 million. I.8.2 Investments under Note Purchase Agreement (NPA) and New Arrangements to Borrow (NAB) with IMF The IMF’s amended and expanded New Arrangements to Borrow (NAB) became effective on March 11, 2011. India has committed to provide resources up to SDR 8,740.8 million to the IMF under this arrangement. Under NAB, the Government of India is the participant while the RBI holds the NAB notes. The RBI has subscribed to notes equivalent to SDR 1261.1 million under NAB till end-March 2014. In terms of the Note Purchase Agreement 2012, entered into between RBI and IMF, RBI has agreed to invest an amount equivalent to USD 10 billion in SDR denominated Notes issued by IMF. I.8.3 Bilateral Swap Arrangement between India and Japan RBI had entered into a bilateral currency swap arrangement (BSA) with Bank of Japan for an amount of USD 15 billion on Dec 4, 2012 for a period of three years. Subsequently, RBI has signed an amended agreement with Bank of Japan to increase the swap amount to USD 50 billon. I.8.4 Investment in bonds issued by IIFC (UK) The Reserve Bank has the mandate to invest up to USD 5 billion, in the bonds issued by the India Infrastructure Finance Company (UK) (IIFC) Limited. As at end-March, 2014, the amount invested in IIFC bonds stood at USD 1181 million. I.8.5 Transfer of SDR Holdings of GoI with IMF to RBI A Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed between the Government of India (GoI) and the Reserve Bank of India on March 20, 2014 for the transfer of GoI’s SDR holdings in its SDR account with the IMF to RBI in a phased manner. The first tranche of SDRs equivalent of USD 820 million was transferred to RBI on March 24, 2014. Part-II II.1. Objectives of Reserve Management The guiding objectives of foreign exchange reserve management in India are similar to those of many central banks in the world. The demands placed on the foreign exchange reserves may vary widely depending upon a variety of factors including the exchange rate regime adopted by the country, the extent of openness of the economy, the size of the external sector in a country's GDP and the nature of markets operating in the country. While liquidity and safety constitute the twin objectives of reserve management in India, return optimisation becomes an embedded strategy within this framework. II.2. Legal Framework and Policies The Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934 provides the overarching legal framework for deployment of reserves in different foreign currency assets (FCA) and gold within the broad parameters of currencies, instruments, issuers and counterparties. The essential legal framework for reserve management is provided in sub-sections 17 (6A), 17(12), 17(12A), 17(13) and 33 (6) of the above Act. In brief, the law broadly permits the following investment categories:
The broad strategy for reserve management including currency composition and investment policy is decided in consultation with the Government of India. The risk management functions are aimed at ensuring development of sound governance structure in line with the best international practices, improved accountability, a culture of risk awareness across all operations, efficient allocation of resources and development of in-house skills and expertise. The risks attendant on deployment of reserves, viz., credit risk, market risk, liquidity risk and operational risk and the systems employed to manage these risks are detailed in the following paragraphs. The Reserve Bank has been sensitive to the credit risk it faces on the investment of foreign exchange reserves in the international markets. The Reserve Bank's investments in bonds/treasury bills represent debt obligations of highly rated sovereigns, central banks and supranational entities. Further, deposits are placed with central banks, the Bank for International Settlements (BIS) and foreign branches of commercial banks. RBI has framed requisite guidelines stipulating criteria for selection of issuers/counterparties with a view to enhancing the safety and liquidity aspects of the reserves. The Reserve Bank continues to apply stringent criteria for selection of counterparties. Credit exposure vis-à-vis sanctioned limit in respect of approved counterparties is monitored continuously. Developments regarding counterparties are constantly under watch. The basic objective of such an on-going exercise is to assess whether any counterparty's credit quality is under potential threat. Market risk for a multi-currency portfolio represents the potential change in valuations that result from movements in financial market prices, for example, changes in interest rates, foreign exchange rates, equity prices and commodity prices. The major sources of market risk for central banks are currency risk, interest rate risk and movement in gold prices. Gains/losses on valuation of FCA and gold due to movements in the exchange rates and/or price of gold are booked under a balance sheet head named the Currency and Gold Revaluation Account (CGRA).The balances in CGRA provide a buffer against exchange rate/gold price fluctuations which in recent times have shown sharp volatility. Foreign dated securities are valued at market prices prevailing on the last business day of each month and the appreciation/depreciation arising therefrom is transferred to the Investment Revaluation Account (IRA). The balance in IRA is meant to provide cushion against changes in the security prices over the holding period. Currency risk arises due to movements in the exchange rates. Decisions are taken on the long-term exposure to different currencies, depending on the likely movements in exchange rates and other considerations in the medium and long-term (e.g., maintenance of major portion of reserves in the intervention currency, benefit of diversification, etc.). The decision making procedure is supported by reviews of the strategy on a regular basis. The crucial aspect of the management of interest rate risk is to protect the value of the investments as much as possible from adverse impact of interest rate movements. The interest rate sensitivity of the portfolio is identified in terms of the benchmark duration and the permitted deviation from the benchmark. Liquidity risk involves the risk of not being able to sell an instrument or close a position when required without facing significant costs. The reserves need to have a high level of liquidity at all times in order to be able to meet any unforeseen and emergency needs. Any adverse development has to be met with reserves and, hence, the need for a highly liquid portfolio is a necessary constraint in the investment strategy. The choice of instruments determines the liquidity of the portfolio. For example, in some markets, treasury securities could be liquidated in large volumes without much distortion of the price in the market and, thus, can be considered as liquid. Except fixed deposits with the BIS, overseas branches of commercial banks and central banks and securities issued by supranationals, almost all other types of investments are highly liquid instruments which could be converted into cash at short notice. The Reserve Bank closely monitors the portion of the reserves, which could be converted into cash at a very short notice, to meet any unforeseen/emergency needs. II.3.3 Operational Risk and Control System In tune with the global trend, considerable attention is paid to strengthen the operational risk control arrangements. Key operational procedures are documented. Internally, there is total separation of the front office and the back office functions and the internal control systems ensure several checks at the stages of deal capture, deal processing and settlement. The deal processing and settlement system, including generation of payment instructions, is also subject to internal control guidelines based on the principle of one-point data entry. There is a system of concurrent audit for monitoring compliance in respect of all the internal control guidelines. Further, reconciliation of accounts is done regularly. In addition to internal annual inspection and statutory audit of accounts by external auditors, there is also a system of audit of the dealing room operations by external auditors. There is a comprehensive reporting mechanism covering significant areas of activity / operations relating to reserve management. These are provided to the senior management periodically, viz., on daily, weekly, monthly, quarterly, half-yearly and yearly intervals, depending on the type and sensitivity of information. The Reserve Bank uses SWIFT as the messaging platform to settle its trades and send financial messages to its counterparties, banks with whom nostro accounts are maintained, custodians of securities and other business partners. II.4 Transparency and Disclosures The Reserve Bank has been making available in the public domain data relating to foreign exchange reserves, its operations in foreign exchange market, position of the country’s external assets and liabilities and earnings from deployment of foreign currency assets and gold through periodic press releases of its Weekly Statistical Supplements, Monthly Bulletins, Annual Reports, etc. The Reserve Bank's approach with regard to transparency and disclosure closely follows international best practices in this regard. The Reserve Bank is among the 71 central banks across the globe which have adopted the Special Data Dissemination Standards (SDDS) template of the IMF for publication of the detailed data on foreign exchange reserves. Such data are made available on monthly basis on the Reserve Bank's website. 1& 2 Partially revised figures and may not tally with figures published in the previous report. 3 Redefined in 2005-06 by including suppliers’ credit up to 180 days and FII investments in the Government of India Treasury Bills and other instruments and further in March, 2007 by including external debt liabilities of the banking system and the investments in the Government Treasury bills by foreign central banks and international institutions. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
கடைசியாக புதுப்பிக்கப்பட்ட பக்கம்: