IST,
IST,


Economic and Financial Developments in Mizoram
Shri Deepak Mohanty, Executive Director, Reserve Bank of India
Delivered on Dec 19, 2013
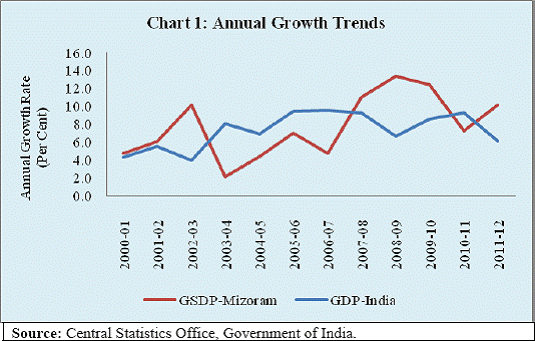
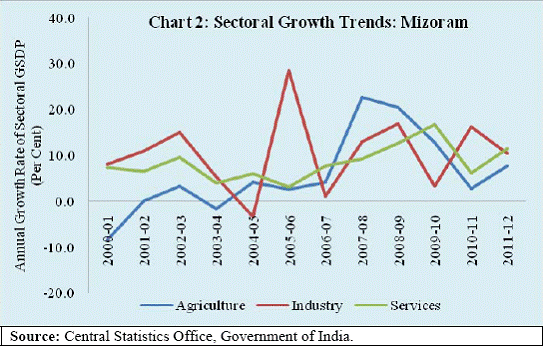
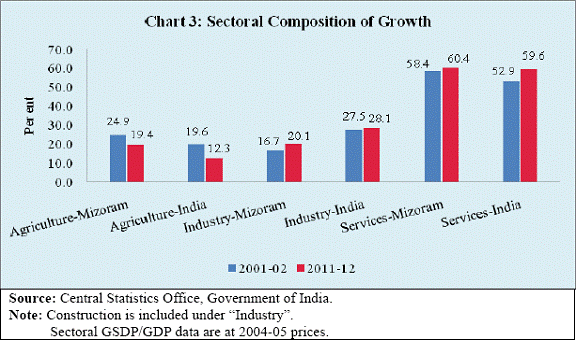
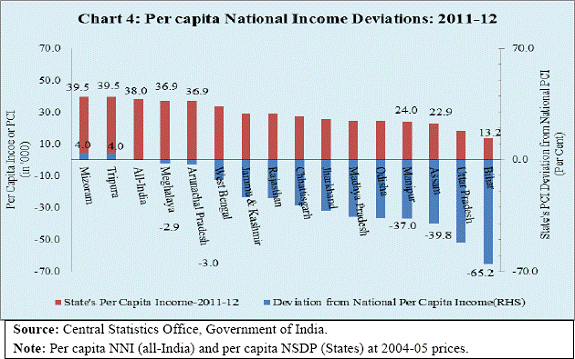
I am happy to be in this picturesque state of Mizoram, the land of rolling hills, valleys, rivers and lakes. The state has a strategic location as it shares much of its border with Bangladesh and Myanmar. It covers 0.6 per cent of the national geographic area and accounts for 0.1 per cent of national population. With second highest literacy rate in the country, the state has great potential for economic development. Access to finance is an important prerequisite for economic development. In the recent years the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has pursued the objective of financial inclusion with renewed vigour. Some progress has been achieved but there are miles to go. Governor Dr. Raghuram G. Rajan has emphasised financial inclusion as one of the five pillars of the RBI’s financial development plank : “… to expand access to finance to small and medium enterprises, the unorganised sector, the poor, and remote and underserved areas of the country, though technology, new business practices and new organisational structure.”1 Financial inclusion poses additional challenges in the north-eastern states given the relatively low level of banking penetration and inadequate infrastructure. Against this background, I briefly delineate the economic and financial structure of the state, highlight our financial inclusion initiatives and conclude with some thoughts on policy challenges on the way forward. Economic Structure India experienced accelerated GDP growth rate in the 2000s. Obviously, this growth experience was shared by many states. In line with the national economy, Mizoram also experienced pick up in its growth. Even as the growth momentum at the national level was dented following the onset of global financial crisis in 2007-08, the performance of Mizoram’s economy was better even in the post-crisis period. Consequently, the share of Mizoram’s gross state domestic product (GSDP) in the all-India GDP rose from 0.08 per cent in 2006-07 to 0.10 per cent during 2011-12 (Chart 1). All the three major sectors of the economy– agriculture, industry and services - contributed to the improved growth performance of the state. There was, however, significant year-to-year fluctuation in sectoral growth rates. While variation in agricultural growth is understandable being weather dependent, volatility in industrial growth needs closer attention, given the low industrial base of the state (Chart 2). The sectoral composition of the Mizoram economy has broadly changed in line with the national economy with declining share of agriculture and increasing share of services. While the share of industry has picked up, it remains significantly below the national average underscoring the scope for further industrialisation (Chart 3). The most significant impact of growth has been improvement of per capita net state domestic product (NSDP) from `26,308 in 2006-07 to `39,546 in 2011-12 at 2004-05 prices, despite a larger decadal population growth rate of 22.8 per cent, which is higher than the rate of growth at 17.6 per cent at the national level. Notably, per capita income of Mizoram was about 4.0 per cent higher than the corresponding average national per capita income during 2011-12 (Chart 4). It is worthwhile to note that while the economy of Mizoram, in line with the national trend, is getting increasingly dominated by industry and services sectors, labour force is still concentrated in the agricultural sector (Table 1). Therefore, creating employment opportunities in the manufacturing and services sectors has become important.
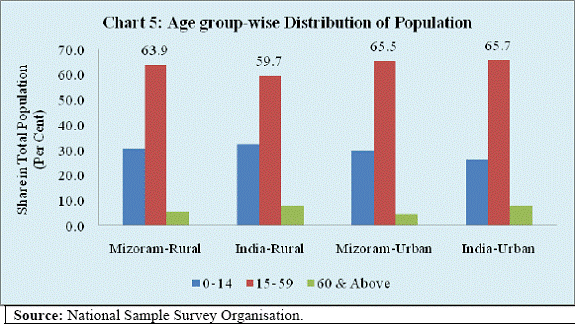
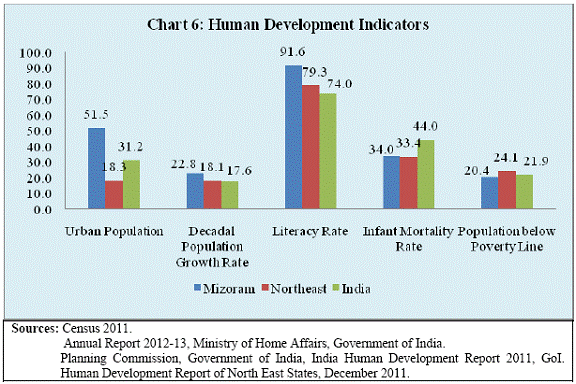
A higher proportion of working age (ages 15-59) population in rural Mizoram as compared to rural India provides a favourable condition for growth (Chart 5). But for this to happen, industry and services sectors should increasingly provide the employment opportunity. Social Indicators With greater urbanisation and higher literacy, indicators of human development in Mizoram are better than the national average (Chart 6). Share of households having access to the basic amenities like electricity, television, computers, telephones and four wheelers are significantly higher in Mizoram than the national average (Table 2). On the other hand, proportion of population having access to banking facilities, although improved during the decade 2001-2011, was below the national level. This is a policy challenge in the context of development with increasing emphasis on financial inclusion.
State Finances Mizoram is one of the 11 special category states which are characterised by low resource base and the cost disabilities due to their geography, sparse terrain and remoteness. In order to overcome these inadequacies, the Centre accords special consideration in devolving resources from the central pool. The revenue account of Mizoram showed significant improvement following a rule-based fiscal policy under Mizoram FRBM Act 2006. However, the correction in revenue account was largely on account of higher transfers from the Centre, since own tax revenue continued to remain around 2.3 per cent of GSDP. From the perspective of growth and employment, a key concern is the decline in capital outlay in terms of GSDP (Table 3).
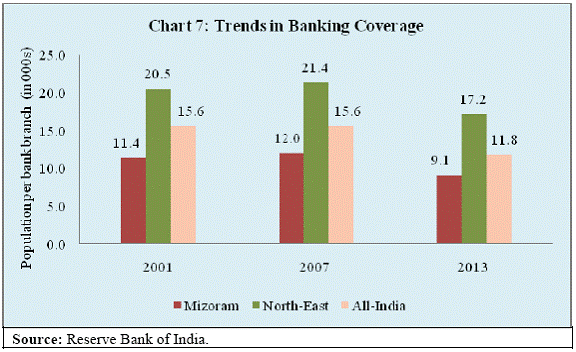
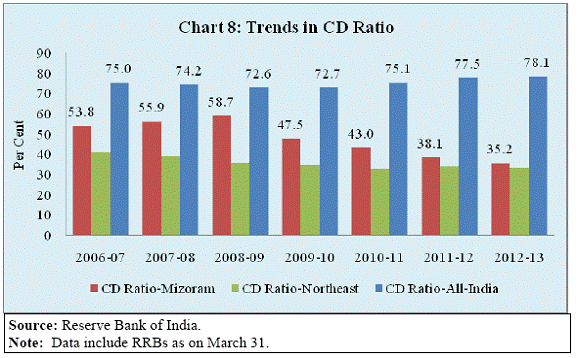
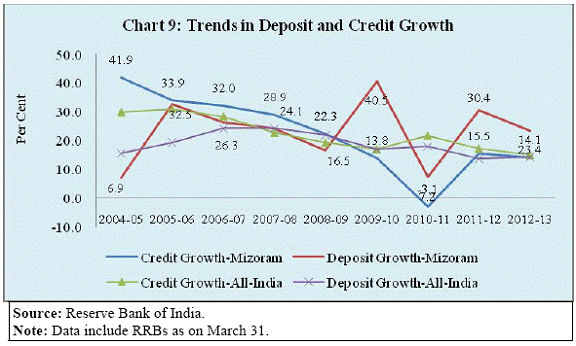
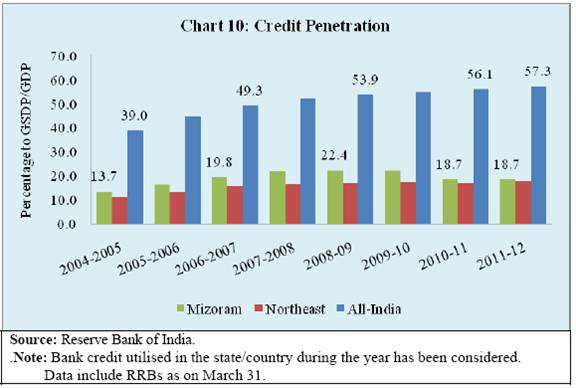
Banking Developments The banking sector penetration in Mizoram may be seen in the context of its special characteristics of difficult terrain and economic structure. Agriculture is characterised by hill and mountain cultivation and industry is dominated by micro and small units. The population per bank branch in Mizoram declined from 11,400 in June 2001 to 9,100 by June 2013 and thus was much lower than the all-India average of 11,800 (Chart 7) reflecting better coverage of banking services. However, Credit-Deposit (C-D) ratio remained significantly lower than the all-India average (Chart 8). Moreover, C-D ratio in Mizoram has declined in the more recent years. It could partly be that deposits have grown faster. The annual deposit growth rate of Mizoram was significantly higher than the national average. However, the credit growth rate has fallen short of the national average after 2007-08 (Chart 9). This underscores the need for a deeper analysis of credit information: Is it lack of demand or lack of supply which is constraining credit flow? The lower credit flow is also mirrored by credit to GDP ratio which is another measure of financial deepening. The credit-GSDP ratio in Mizoram has improved more modestly from 13.7 per cent in 2004-05 to 18.7 per cent in 2011-12, as compared to the increase from 39.0 per cent to 57.3 per cent at the national level (Chart 10). Financial Inclusion The Reserve Bank is committed to Financial Inclusion (FI) so that the banking services touch every section of our society. It is imperative to bring the poor and under-privileged section of population under the banking fold for inclusive growth and development. In this regard, the Reserve Bank has adopted a structured approach towards financial inclusion predominantly through a bank-led model by leveraging appropriate technology, changing the mode of delivery and increasing financial literacy. In this context, I may highlight four key elements. First, ensuring branch expansion in the rural areas by giving full freedom to the banks to open branches in villages. In fact, recently the branch authorisation policy has been fully liberalised subject to banks opening at least 25 per cent of their branches in the rural areas. In addition, the Reserve Bank has enabled commercial banks to operate through their Business Correspondents (BCs) thus taking banking to the door step in the rural areas. Second, for providing universal coverage and facilitating Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) by leveraging Aadhar identification, banks have been advised to draw up their Financial Inclusion Plans (FIPs) for the period 2013-16 with greater emphasis on opening of branches in unbanked rural centres. Third, provision of suitable financial products aimed towards the vulnerable section of population such as no-frill account, credit through General Credit Card (GCC) and Kisan Credit Card (KCC). Moreover, Know Your Customer (KYC) norm required for opening of a bank account has been relaxed especially for rural and under-privileged population. Finally, efforts are made towards spread of financial literacy including internet based curriculum for financial literacy in schools and organising financial literacy camps. In this direction, banks have covered all the unbanked villages with population over 2,000. The second phase of this movement aims to achieve the target of financial inclusion in about 4,90,000 villages with population less than 2,000. The identified villages have been allotted to various banks to ensure availability of at least one banking outlet in each village. The detailed achievement in the recent financial inclusion drive is summarised in Table 4.
Progress of financial inclusion in Mizoram Keeping in mind the topographic challenges and locational disadvantages for the development of extensive banking outreach, banks have been advised to adopt special measures for FI in the north-eastern region of India. Since December 2009, the domestic scheduled commercial banks in the country, excluding RRBs, were permitted to open branch in any location in the region without taking permission from the Reserve Bank. Let me now turn specifically to progress of financial inclusion in Mizoram. As a part of the Financial Inclusion Plan (FIP) adopted in Mizoram, all the unbanked villages in the state with population of 2,000 or more have been covered by banking facility by end-March 2012. Another 700 villages having population below 2,000 have already been identified. Out of these villages, 106 have been proposed to be covered through brick and mortar model while rest would be covered through Business Correspondence (BC) model. As at end-September 2013, there were 2, 27,812 Basic Saving Bank Deposit Accounts (BSBDAs) in Mizoram, while another 10,777 such accounts with overdraft facilities are targeted to be opened during the year 2013-14. In addition, 11,642 KCC and GCC are targeted to be provided to the households during 2013-14. Out of the 8 districts in the State, so far 5 financial literacy centres (FLCs) have been opened. As of end-September 2013 cumulatively 3,063 Self Help Groups (SHGs) were credit-linked and have been provided with total credit of `1,650 lakh. Policy Challenges Mizoram economy has performed well in the recent years. However, keeping in view the young population and high literacy and strategic location, there is considerable scope for growth and development. Let me conclude by drawing attention to a few challenges. First, the dominant feature of the hill and mountain farming in Mizoram is sloping marginal farmlands under rain-fed farming. Subsistence farming on these lands is pervasive. Expansion of land for cultivation in an environmentally sustainable manner may be limited. The emphasis in agriculture, therefore, may shift towards high value added horticulture for which there is tremendous potential. This will also require greater penetration of credit in agriculture. Second, industrial development in Mizoram started late in the 1990s, mainly after attaining statehood. The industrial landscape is dominated by micro and small industries. There is a need to reinforce this process by facilitating access to markets and formal credit. Third, weak market linkages with the rest of India coupled with lack of good quality road and absence of railway network inhibits the effective marketing of goods. Therefore, priority should be given to the development of infrastructure, especially roads and also provision of post harvest management, cold storage and processing facilities. There is also the need to further harness the hydro-power capacity. Better accessibility will also help develop the services sector, particularly tourism, which could become a significant source of employment and revenue. Finally, the topography of the state and infrastructure bottlenecks together work as a deterrent for the development of physical banking and financial infrastructure. Hence, greater reliance may need to be placed on technology to make banking more accessible to the majority of the population. This will require improvement in telecommunication facility. I thank you for inviting me to share my thoughts on financial inclusion in the state. Tomorrow, I hope to see some of you at our outreach programme at Tanhril village. With the combined effort of state administration, banks and the Reserve Bank we could together make a significant impact in financial inclusion. *Speech by Shri Deepak Mohanty, Executive Director, Reserve Bank of India at the Aizawl Club on December 19, 2013. The assistance provided by P.K. Nayak, S. Suraj and S. Nath is acknowledged. 1“The Five Pillars of RBI’s Financial Sector Policies”, speech by Governor Raghuram G. Rajan at BANCON 2013 held at Mumbai on November 15, 2013. RBI Monthly Bulletin, December 2013. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Page Last Updated on: