FAQ Page 1 - RBI - Reserve Bank of India
A. Definitions
A Non-Banking Financial Company (NBFC) is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956 or Companies Act, 2013, and engaged in the business of loans and advances, acquisition of shares/stocks/bonds/debentures/securities issued by Government or local authority or other marketable securities of a like nature, leasing, hire-purchase, etc., as their principal business, but does not include any institution whose principal business is that of agriculture activity, industrial activity, purchase or sale of any goods (other than securities) or providing any services and sale/purchase/construction of immovable property. A non-banking institution which is a company and has principal business of receiving deposits under any scheme or arrangement in one lump sum or in installments by way of contributions or in any other manner, is also a non-banking financial company (Residuary non-banking company).
Financial activity as principal business is when a company’s financial assets constitute more than 50 per cent of the total assets (netted off by intangible assets) and income from financial assets constitute more than 50 per cent of the gross income. A company which fulfils both these criteria needs to get registered as NBFC with the Reserve Bank. The term 'principal business' has not been defined in the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. Hence, the Reserve Bank has defined it vide Press Release 1998-99/1269 dated April 08, 1999 so as to ensure that only companies predominantly engaged in financial activity get registered with it and are regulated and supervised by it. Hence, if there are companies engaged in agricultural operations, industrial activity, purchase and sale of goods, providing services or purchase, sale or construction of immovable property as their principal business and are doing some financial business in a small way, they will not be regulated by the Reserve Bank. Interestingly, this test is popularly known as 50-50 test and is applied to determine whether or not a company is into financial business.
Banks and NBFCs are different entities subject to different statutory and regulatory requirements. However, NBFCs lend and make investments and hence these activities are akin to that of banks. The major differences between banks and NBFCs are given below:
i. NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits;
ii. NBFCs do not form part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue cheques drawn on itself;
iii. Deposit insurance facility of Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) is not available to depositors of deposit taking NBFCs.
In terms of Section 45-IA of the RBI Act, 1934, no NBFC can commence or carry on business of a non-banking financial institution without a) obtaining a certificate of registration from the Reserve Bank and without having a Net Owned Funds (NOF) of ₹10 crore with effect from October 01, 2022 (NBFCs seeking registration shall have NOF of ₹10 crore ab initio, and existing NBFCs have timeline upto March 31, 2027 to attain NOF of ₹10 crore). However, in terms of the powers conferred upon the Reserve Bank, to obviate dual regulation, certain categories of NBFCs which are regulated by other regulators are exempted from the requirement of registration with the Reserve Bank viz., Alternative Investment Fund/ Merchant Banking companies/ Stock broking companies registered with SEBI; Insurance Company holding a valid Certificate of Registration issued by IRDA; Nidhi companies as notified under Section 620A of the Companies Act, 1956; Chit companies doing the business of chits as defined in clause (b) of Section 2 of the Chit Funds Act, 1982; Stock Exchange or a Mutual Benefit company, etc.
A ‘company’ desirous of commencing the business of non-banking financial institution as defined under Section 45 I(a) of the RBI Act, 1934 should comply with the following:
i. It should be a company incorporated under Section 3 of the companies Act, 1956 or corresponding Section under the Companies Act, 2013;
ii. It should have a minimum net owned fund of ₹10 crore. (The minimum net owned fund requirements for specialized NBFCs are NBFC-Infrastructure Finance Company (NBFC-IFC) – ₹300 crore; Infrastructure Debt Fund – NBFC (IDF-NBFC) – ₹300 crore; Mortgage Guarantee Company (MGC) – ₹100 crore; Housing Finance Company (HFC) – ₹20 crore, Standalone Primary Dealers (SPDs) which undertake only the core activities – ₹150 crore and SPDs which also undertake non-core activities – ₹250 crore; NBFC-AA – ₹2 crore; and NBFC-P2P – ₹2 crore).
The applicant company is required to apply online on https://pravaah.rbi.org.in and also submit a physical copy of the application along with the necessary documents as per the process prescribed by the Reserve Bank vide its Press Release 2015-2016/2935 dated June 17, 2016 to the Chief General Manager-in-Charge, Department of Regulation, Reserve Bank of India, Central Office, 2nd Floor, Main Office Building, Shahid Bhagat Singh Marg, Fort, Mumbai-400 001.
The application form and an indicative checklist of the documents required to be submitted along with the application is available on Reserve Bank’s website under NBFC Forms.
Over the years, the NBFC sector had evolved considerably in terms of size, complexity, and interconnectedness within the financial sector and hence there was a need to align the regulatory framework for NBFCs keeping in view their changing risk profile. Accordingly, the Reserve Bank has implemented a Scale-Based Regulatory Framework or SBR Framework for regulation of NBFCs w.e.f. October 01, 2022. The SBR Framework which is based on the principle of proportionality takes into account various factors like size, activity, complexity, interconnectedness, etc., within the financial sector for categorising NBFCs into various layers. The degree of regulations increases as one moves from lower to higher layers. SBR Framework classifies NBFCs into four layers. NBFCs in the lowest layer shall be known as NBFC – Base Layer (NBFC-BL). NBFCs in middle layer and upper layer shall be known as NBFC – Middle Layer (NBFC-ML) and NBFC – Upper Layer (NBFC-UL) respectively and are considered to be systemically significant. The Top Layer is ideally expected to be empty and will be known as NBFC - Top Layer (NBFC-TL) which will be populated only if the Reserve Bank is of the opinion that there is a substantial increase in the potential systemic risk from specific NBFCs in the Upper Layer.
B. Entities Regulated by RBI and applicable regulations
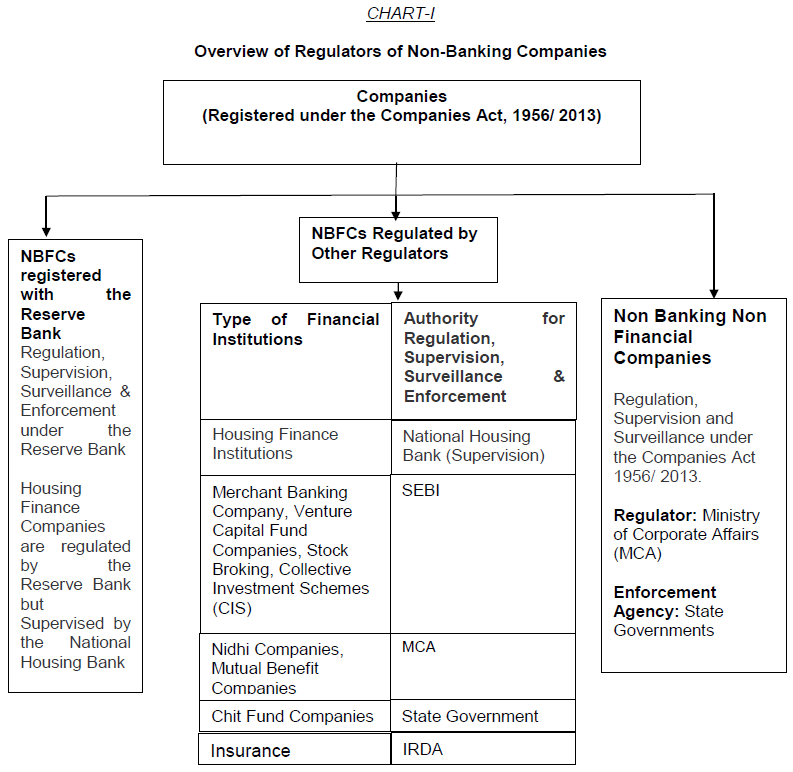
No, the Reserve Bank does not regulate all financial companies. Depending upon the nature of activities, the financial companies may fall under the regulatory purview of other Regulators like SEBI, IRDAI, Government, etc. To name a few, the Merchant Banking Companies/Alternative Investment Fund Company/stock-exchanges/stock brokers/sub-brokers are regulated by Securities and Exchange Board of India, and Insurance companies are regulated by Insurance Regulatory and Development Authority. Similarly, Chit Fund Companies are regulated by the respective State Governments and Nidhi Companies are regulated by Ministry of Corporate Affairs, Government of India. Companies that do financial business but are regulated by other regulators are given specific exemption by the Reserve Bank from its regulatory requirements for avoiding duality of regulation. The categories of NBFCs which are exempted from certain provisions of the RBI Act, 1934 are specified in the ‘Master Direction - Exemptions from the provisions of RBI Act, 1934 dated August 25, 2016.
NBFCs are categorized (a) in terms of the type of liabilities into Deposit and Non-Deposit accepting NBFCs; (b) regulatory structure of NBFCs under Scale Based Regulation into NBFC-Base Layer, NBFC-Middle Layer, NBFC-Upper Layer, and NBFC-Top Layer (as detailed in FAQ no.8 above); and (c) by the kind of activity they conduct.
Based on the type of activities they conduct, the different types of NBFCs are as follows:
I. Investment and Credit Company (ICC): ICC means any company which is a financial institution carrying on as its principal business - asset finance, the providing of finance whether by making loans or advances or otherwise for any activity other than its own and the acquisition of securities; and is not any other category of NBFCs as defined by the Reserve Bank in any of its Master Directions.
II. Housing Finance Company (HFC): HFC shall mean a company that fulfils the following conditions:
(a) It is an NBFC whose financial assets, in the business of providing finance for housing, constitute at least 60% of its total assets (netted off by intangible assets). Housing finance for this purpose shall mean providing finance as stated at clauses (a) to (k) of Paragraph 4.1.16 of the Master Direction – Non-Banking Financial Company – Housing Finance Company (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2021.
(b) Out of the total assets (netted off by intangible assets), not less than 50% should be by way of housing finance for individuals as stated at clauses (a) to (e) of Paragraph 4.1.16 of the aforementioned master directions for HFCs.
III. Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC): IFC is a non-banking finance company (a) which deploys at least 75 per cent of its total assets towards infrastructure lending.
IV. Infrastructure Debt Fund (IDF-NBFC): IDF-NBFC means a non-deposit taking NBFC which is permitted to (a) refinance post commencement operations date (COD) infrastructure projects that have completed at least one year of satisfactory commercial operations; and (b) finance toll operate transfer (TOT) projects as the direct lender.
V. Core Investment Company (CIC): CIC is a NBFC carrying on the business of acquisition of shares and securities which satisfies the following conditions:
(a) It holds not less than 90% of its net assets in the form of investment in equity shares, preference shares, debt or loans in group companies;
(b) Its investments in the equity shares (including instruments compulsorily convertible into equity shares within a period not exceeding 10 years from the date of issue) in group companies and units of Infrastructure Investment Trusts (InvITs) only as sponsor constitutes not less than 60% of its net assets;
(c) Provided that the exposure of such CICs towards InvITs shall be limited to their holdings as sponsors and shall not, at any point in time, exceed the minimum holding of units and tenor prescribed in this regard by SEBI (Infrastructure Investment Trusts) Regulations, 2014, as amended from time to time. It does not trade in its investments in shares, debt or loans in group companies except through block sale for the purpose of dilution or disinvestment;
(d) it does not carry on any other financial activity referred to in Section 45I(c) and 45I(f) of the RBI act, 1934 except (i) investment in bank deposits, money market instruments, government securities, bonds or debentures issued by group companies; (ii) granting of loans to group companies; and (iii) issuing of guarantees on behalf of group companies;
(e) Its asset size is ₹ 100 crore or above; and
(f) It accepts public funds
VI. Micro Finance Institution (NBFC-MFI): “NBFC-MFI” means a non-deposit taking NBFC which has a minimum of 75 percent of its total assets deployed towards “microfinance loans” as defined under Reserve Bank of India (Regulatory Framework for Microfinance Loans) Directions, 2022 as under:
(a) A microfinance loan is defined as a collateral-free loan given to a household having annual household income up to ₹3,00,000. For this purpose, the household shall mean an individual family unit, i.e., husband, wife and their unmarried children.
(b) All collateral-free loans, irrespective of end use and mode of application/ processing/ disbursal (either through physical or digital channels), provided to low-income households, i.e., households having annual income up to ₹3,00,000, shall be considered as microfinance loans.
(c) To ensure collateral-free nature of the microfinance loan, the loan shall not be linked with a lien on the deposit account of the borrower.
(d) The NBFCs shall have a board-approved policy to provide the flexibility of repayment periodicity on microfinance loans as per borrowers’ requirement.
VII. Non-Banking Financial Company – Factors (NBFC-Factors): NBFC-Factor is a non-deposit taking NBFC engaged in the principal business of factoring. The financial assets in the factoring business should constitute at least 50 percent of its total assets and its income derived from factoring business should not be less than 50 percent of its gross income.
VIII. Mortgage Guarantee Companies (MGC): MGC means a company registered as mortgage guarantee company which primarily transacts the business of providing mortgage guarantee i.e., a guarantee for the repayment of an outstanding housing loan and interest accrued thereon up to the guaranteed amount to a creditor institution, on the occurrence of a trigger event. A mortgage guarantee company shall be deemed to primarily transact the business of providing mortgage guarantee when at least 90% of the business turnover is mortgage guarantee business or at least 90% of the gross income is from mortgage guarantee business.
IX. Standalone Primary Dealers (SPDs): SPDs are primarily NBFCs which have been granted authorisation to undertake the Primary Dealer activities in Government Securities. SPDs may undertake a set of core and non-core activities which are clearly defined. SPDs support G- Sec market, (both primary and secondary) through various obligations like participating in primary auctions, market making in G- Secs, predominance of investment in G-Secs, achieving minimum secondary market turnover ratio, etc.
X. Non-Operative Financial Holding Company (NOFHC): NOFHC means a non-deposit taking NBFC referred to in the "Guidelines for Licensing of New Banks in the Private Sector" dated February 22, 2013, issued by the Reserve Bank, which holds the shares of a banking company and the shares of all other financial services companies in its group, whether regulated by the Reserve Bank or by any other financial regulator, to the extent permissible under the applicable regulatory prescriptions.
XI. NBFC – Account Aggregator (NBFC-AA): NBFC-AA means a non-banking financial company as notified under in sub-clause (iii) of clause (f) of section 45-I of the RBI Act, that undertakes the business of an account aggregator, for a fee or otherwise. The “business of an account aggregator” means the business of providing under a contract, the service of, retrieving or collecting such financial information pertaining to its customer, as may be specified by the Reserve Bank from time to time; and consolidating, organizing and presenting such information to the customer or any other financial information user as may be specified by the Bank; Provided that, the financial information pertaining to the customer shall not be the property of the Account Aggregator, and not be used in any other manner.
XII. NBFC – Peer to Peer Lending Platform (NBFC-P2P): NBFC-P2P means a non-banking institution which carries on the business of a Peer to Peer Lending Platform i.e., acting as intermediary providing the services of loan facilitation via online medium or otherwise, to the participants of the platform.
The Reserve Bank has been empowered under the RBI Act 1934 to register, determine policy, issue directions, inspect, regulate, supervise and exercise surveillance over NBFCs that fulfil the principal business criteria or 50-50 criteria of principal business. The Reserve Bank can penalize NBFCs for violating the provisions of the RBI Act or the directions or orders issued by the Reserve Bank under RBI Act. The penal action may also include cancellation of the Certificate of Registration issued to the NBFC.
It is illegal for any person/ entity/ financial company to make a false claim of being regulated by the Reserve Bank to mislead the public to collect deposits and is liable for penal action under the Law. Information in this regard may be forwarded to the nearest office of the Reserve Bank and the Police.
If companies that are required to be registered with the Reserve Bank as NBFCs, are found to be conducting non-banking financial activity, such as, lending, investment or deposit acceptance as their principal business, without obtaining Certificate of Registration from the Reserve Bank, the same would be treated as contravention of the provisions of the RBI Act, 1934 and would invite penal action viz., penalty or fine or even prosecution in a Court of Law. If members of public come across any entity which undertakes non-banking financial activity but does not figure in the list of authorized NBFCs on the Reserve Bank’s website, they should inform the nearest Regional Office of the Reserve Bank, for appropriate action to be taken for contravention of the provisions of the RBI Act, 1934.
The list of registered NBFCs is available on the web site of Reserve Bank (www.rbi.org.in) under ‘Regulation → Non-Banking’. Further, the instructions issued to NBFCs from time to time through circulars and/ or master directions are hosted on the Reserve Bank’s website under ‘Notifications’, and some instructions are issued through Official Gazette notifications and press releases as well.
As part of regulatory framework prescribed by the Reserve Bank for NBFCs, the Reserve Bank prescribes prudential regulations viz., capital adequacy/ leverage, provisioning, corporate governance framework, etc.; conduct of business regulations viz., KYC/ AML regulations, fair practices code, etc.; and other miscellaneous regulations to ensure that NBFCs are financially sound and follow transparency in their operations. The regulations for NBFCs are contained in various master directions and notifications/ circulars issued from time to time, and are available on the website of the Reserve Bank (www.rbi.org.in) under ‘notifications’.
Public funds are not the same as public deposits. Public funds include public deposits, inter-corporate deposits, bank finance and all funds received whether directly or indirectly from outside sources such as funds raised by issue of Commercial Papers, debentures etc. Even though public funds include public deposits in the general course, it may be noted that CICs as also non-deposit taking NBFCs are not allowed to accept public deposits.
Further, indirect receipt of public funds means funds received not directly but through associates and group entities which have access to public funds.
The Reserve Bank has issued detailed directions on prudential norms, vide Master Direction – Reserve Bank of India (Non-Banking Financial Company – Scale Based Regulation) 2023 (as amended from time to time). Applicable regulations vary based on the layer of the NBFC under Scale Based Regulatory Framework for NBFCs. Further, specialised categories of NBFCs viz., NBFC-P2P, NBFC-AA, CICs, SPDs, MGCs and HFCs shall be subject to respective master directions governing them.
The directions, inter alia, prescribe guidelines on income recognition, asset classification and provisioning requirements applicable to NBFCs, exposure norms, disclosures in the balance sheet, requirement of capital adequacy, loan to value (LTV) ratio for NBFCs predominantly engaged in business of lending against gold jewellery, besides others.Para 5.1.25 of Master Direction – Reserve Bank of India (Non-Banking Financial Company – Scale Based Regulation) 2023 (as amended from time to time) defines ‘Owned Fund’ as aggregate of the paid-up equity capital, preference shares which are compulsorily convertible into equity, free reserves, balance in share premium account and capital reserves representing surplus arising out of sale proceeds of asset, excluding reserves created by revaluation of asset; as reduced by accumulated balance of loss, book value of intangible assets and deferred revenue expenditure, if any.
'Net Owned Fund' is defined under Section 45-IA(7) of the RBI Act, 1934. As per this definition, the Net Owned Fund means–
(a) aggregate of the paid-up equity capital and free reserves as disclosed in the latest balance-sheet of the company after deducting there from, accumulated balance of loss, deferred revenue expenditure, and other intangible assets; and
NBFCs shall comply with the provisions of the Master Direction – Reserve Bank of India (Filing of Supervisory Returns) Directions – 2024 (as amended from time to time) for submission of various supervisory returns to the Reserve Bank.
NBFCs shall comply with the regulations contained in para 36 of the Master Direction – Reserve Bank of India (Non-Banking Financial Company – Scale Based Regulation) 2023 (as amended from time to time) while granting loans against security of shares. The regulations include, inter alia, maintaining a Loan to Value (LTV) ratio of 50% at all times, accept only Group 1 securities as collateral for loans of value more than ₹5 lakh where lending is done for investment in capital markets, undertake necessary reporting to stock exchanges on shares pledged in their favour, etc.
In addition to the above, there are other related regulations on NBFCs viz., there shall be ceiling of ₹1 crore per borrower for financing subscription to Initial Public Offer (IPO) and NBFCs can fix more conservative limits. Further, NBFCs are prohibited from lending against security of their own shares and debentures.
The resolution of stressed assets are subject to the provisions of (a) the Prudential Framework for Resolution of Stressed Assets as contained in para 18 and (b) norms on restructuring of advances as contained in para 22, 23, 24 and 25 of the Master Direction – Reserve Bank of India (Non-Banking Financial Company – Scale Based Regulation) 2023 (as amended from time to time). The acquisition of shares due to conversion of debt into equity during a restructuring process will be exempted from regulatory ceilings on capital market exposures.
Loans which are against the collateral of multiple securities and it is specifically agreed to in the agreement that primary security would be something other than shares/ units of mutual funds, LTV as would not be applicable. However, reporting requirements shall remain. In cases where such differentiation is not made (thereby NBFCs can off-load shares at the instance of a default), LTV would be applicable.
The regulations would be applicable and the type of encumbrance created is immaterial.
No, the definition of “companies in the group” is only for the purpose of determining the applicability of prudential norms on multiple NBFCs in a group.
Yes, prior approval would be required in all cases of acquisition/ transfer of shareholding of 26 per cent or more of the paid up equity capital of an NBFC.
Reserve Bank of India has deregulated interest rates to be charged to borrowers by NBFCs. The rate of interest to be charged by the company is governed by the terms and conditions of the loan agreement entered into between the borrower and the NBFCs. However, the NBFCs have to be transparent and the rate of interest and manner of arriving at the rate of interest to different categories of borrowers should be disclosed to the borrower or customer in the application form and communicated explicitly in the sanction letter and on their websites, Key Facts Statement, etc., to enable the borrower to take an informed decision.
IRF may be used to hedge interest rate risk associated with single asset/ liability or a group of assets/ liabilities. Hence, NBFCs are permitted to use duration-based hedging for managing interest rate risk.
As per extant guidelines, NBFCs with asset size of ₹1,000 crore and above are permitted to participate in IRF as trading members duly subject to provisions of ‘Rupee Interest Rate Derivatives (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2019’ dated June 26, 2019 (as amended from time to time). While trading members of stock exchanges are permitted to execute trades on their own account as well as on account of their clients, only banks, SPDs and All India Financial Institutions (AIFIs) have been allowed to act as market-makers. Hence, currently, NBFCs as trading members are permitted to execute only their proprietary trades and are not allowed to undertake transactions on behalf of clients.
C. Residuary Non-Banking Companies (RNBCs)
Residuary Non-Banking Company is a class of NBFC which is a company and has as its principal business the receiving of deposits, under any scheme or arrangement or in any other manner and not being an Investment and Credit Company, a housing finance company, an insurance company, a factor, a mutual benefit company, a mutual benefit financial company and a miscellaneous non-banking company. These companies are required to maintain investments as per directions of the Reserve Bank, in addition to liquid assets. The functioning of these companies is different from those of NBFCs in terms of method of mobilization of deposits and requirement of deployment of depositors' funds as per Directions. Besides, Prudential Norms Directions are also applicable to these companies.
While that there is no ceiling on raising of deposits by RNBCs, it is mandated that every RNBC has to ensure that the amounts deposited with it are fully invested in approved investments. In other words, in order to secure the interests of depositor, such companies are required to invest 100 per cent of their deposit liability into highly liquid and secure instruments, namely, Central/State Government securities, fixed deposits with scheduled commercial banks (SCB), Certificate of Deposits of SCB/FIs, units of Mutual Funds, etc.
The minimum interest an RNBC should pay on deposits should be 5% (to be compounded annually) on the amount deposited in lump sum or at monthly or longer intervals; and 3.5% (to be compounded annually) on the amount deposited under daily deposit scheme. Interest here includes premium, bonus or any other advantage, that an RNBC promises to the depositor by way of return. An RNBC can accept deposits for a minimum period of 12 months and maximum period of 84 months from the date of receipt of such deposit. They cannot accept deposits repayable on demand.
D. Definition of deposits, Eligible / Ineligible Institutions to accept deposits and Related Matters
The term ‘deposit’ is defined under Section 45 I(bb) of the RBI Act, 1934. ‘Deposit’ includes and shall be deemed always to have included any receipt of money by way of deposit or loan or in any other form but does not include:
i. amount raised by way of share capital, or contributed as capital by partners of a firm;
ii. amount received from a scheduled bank, a co-operative bank, a banking company, Development bank, State Financial Corporation, IDBI or any other institution specified by RBI;
iii. amount received in ordinary course of business by way of security deposit, dealership deposit, earnest money, advance against orders for goods, properties or services;
iv. amount received by a registered money lender other than a body corporate;
v. amount received by way of subscriptions in respect of a ‘Chit’.
Para 3(xiii) of the Master Direction – Non-Banking Financial Companies Acceptance of Public Deposits (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2016 (as amended from time to time) defines a ‘public deposit’ as a ‘deposit’ as defined under Section 45I(BB) of the RBI Act, 1934 and further excludes the following:
a. amount received from the Central/ State Government or any other source where repayment is guaranteed by Central/ State Government or any amount received from local authority or foreign government or any foreign citizen/ authority/ person;
b. any amount received from financial institutions specified by RBI for this purpose;
c. any amount received by a company from any other company;
d. amount received and held pursuant to an offer made in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013, towards subscription to any securities, including share application money or advance towards allotment of securities pending allotment, to such extent and for such period as permissible under the Companies (Acceptance of Deposit) Rules, 2014 and as amended from time to time;
e. amount received from directors of a company or from its shareholders by private company or by a private company which has become a public company, provided that the director or shareholder furnishes a declaration in writing that the amount is not given out of funds acquired by borrowing or accepting from others;
f. amount raised by issue of bonds or debentures secured by mortgage of any immovable property or other asset of the company subject to conditions;
fa. any amount raised by issuance of non-convertible debentures with a maturity more than one year and having the minimum subscription per investor at ₹1 crore and above, provided it is in accordance with the guidelines issued by the Bank.
g. the amount brought in by the promoters by way of unsecured loan;
h. amount received from a mutual fund;
i. any amount received as hybrid debt or subordinated debt, the minimum maturity of which is not less than 60 months provided there is no option for recall by the issuer within the period;
j. amount received from a relative of the director of an NBFC;
k. any amount received by issuance of Commercial Paper in accordance with the guidelines issued by the Bank;
l. any amount received by a NBFC-Middle Layer and above, by issuance of ‘perpetual debt instruments’ in accordance with the guidelines issued by the Bank;
m. any amount raised by the issue of infrastructure bonds by an Infrastructure Finance Company as specified in the notification issued by Central Government under Section 80CCF of the Income Tax Act, 1961.
Thus, the directions exclude from the definition of public deposit, amounts raised from certain set of informed lenders who can make independent decision.
Banks, including co-operative banks, can accept deposits. NBFCs (including Housing Finance Companies), which have been issued Certificate of Registration by the Reserve Bank with a specific licence to accept deposits, are entitled to accept public deposit. In other words, not all NBFCs registered with the Reserve Bank are entitled to accept deposits but only those that hold a deposit accepting Certificate of Registration, can accept deposits. Further, these deposit accepting NBFCs can accept deposits, only to the extent permissible. Companies authorized by Ministry of Corporate Affairs under the Companies (Acceptance of Deposits) Rules framed by Central Government under the Companies Act can also accept deposits upto a certain limit. Cooperative Credit Societies can accept deposits from their members but not from the general public. The Reserve Bank regulates the deposit acceptance only of banks, cooperative banks and NBFCs.
It is not legally permissible for other entities to accept public deposits. Unincorporated bodies like individuals, partnership firms, and other association of individuals are prohibited from carrying on the business of acceptance of deposits as their principal business. Such unincorporated bodies are prohibited from accepting deposits even if they are carrying on financial business.
Further, The First Schedule of the ‘The Banning of Unregulated Deposit Schemes Act, 2019’ may be referred for the list of regulated deposit schemes.
All NBFCs are not entitled to accept public deposits. Only those NBFCs that hold a deposit accepting Certificate of Registration, and have a minimum investment grade credit rating of ‘BBB–‘ from any of the SEBI-registered credit rating agencies, are allowed to accept/ hold public deposits up to a limit of 1.5 times of their Net Owned Funds. Presently, the maximum rate of interest an NBFC can offer is 12.5%. The interest may be paid or compounded at rests not shorter than monthly rests. The NBFCs are allowed to accept/ renew public deposits which are repayable after 12 months but not later than 60 months. They cannot accept deposits repayable on demand.
However, as a matter of public policy, Reserve Bank has decided that only banks should be allowed to accept public deposits and as such, has, since 1997, not issued any Certificate of Registration (CoR) to new NBFCs for acceptance of public deposits.
A company which does not have financial assets which are more than 50% of its total assets and does not derive at least 50% of its gross income from such assets is not an NBFC. Its principal business would be non-financial activity like agricultural operations, industrial activity, purchase or sale of goods or purchase/construction of immovable property, and will be a non-banking non-financial company. Acceptance of deposits by a Non-Banking Non-Financial Company are governed by the rules and regulations issued by the Ministry of Corporate Affairs.
The Reserve Bank's overarching concern while regulating/ supervising any financial entity is protection of depositors' interest. Depositors place deposit with any entity on trust unlike an investor who invests in the shares of a company with the intention of sharing the risk as well as return with the promoters. Protection of depositors' interest, thus, is supreme in financial regulation. Further, the deposits of NBFCs do not have insurance from the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation.
The Reserve Bank publishes the list of NBFCs that hold a valid Certificate of Registration for accepting deposits on its website (www.rbi.org.in) under Regulation → Non-Banking → NBFCs. Members of the public are advised to check the list before placing deposits with NBFCs.
NBFCs can accept deposits from NRIs subject to compliance with Foreign Exchange Management (Deposit) Regulations 2016 (as amended from time to time) and also subject to the condition that the rate of interest on these deposits shall not exceed the rate specified by the Reserve Bank for such deposits with scheduled commercial banks.
NBFCs that ought to have sought registration from the Reserve Bank but are functioning without doing so are committing a breach of law. Such companies are liable for action as envisaged under the RBI Act, 1934. To identify such entities, the Reserve Bank has multiple sources of information. These include market intelligence, complaints received from affected parties, industry sources, and exception reports submitted by statutory auditors in terms of Master Direction - Non-Banking Financial Companies Auditor’s Report (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2016 (as amended from time to time). Further, the State Level Co-ordination Committees (SLCC) is convened by the Reserve Bank in all the States/UTs on quarterly basis. The SLCC is now chaired by the Chief Secretary/ Administrator of the concerned State/UT and has, as its members, apart from the Reserve Bank, the Regional Directorate of the MCA/ ROC, local unit of SEBI, NHB, Registrar of Chits, ICAI, Economic Intelligence Unit of the State Police and officials from Law and Home Ministries of the State Government. As all the relevant financial sector regulators and enforcement agencies participate in the SLCC, it is possible to quickly share the information and agree on an effective course of action to be taken against entities indulging in unauthorized and suspect businesses involving funds mobilization from public.
NBFCs are prohibited by the Reserve Bank from associating with any unincorporated bodies. If NBFCs associate themselves with unincorporated entities which are accepting deposits in contravention of RBI Act, they are also liable for penal action under the Act, or action under the Protection of Interest of Depositors (in Financial Establishments) Act, or the Banning of Unregulated Deposit Schemes Act, 2019, as applicable.
Deposits are defined under the RBI Act 1934 as acceptance of money other than that raised by way of share capital, money received from banks and other financial institutions, money received as security deposit, earnest money and advance against goods or services and subscriptions to chits. All other amounts received in any form are treated as deposits. Chit Funds activity involves contributions by members in instalments by way of subscription to the Chit and by rotation each member of the Chit receives the chit amount. The subscriptions are specifically excluded from the definition of deposits and cannot be termed as deposits. While Chit funds may collect subscriptions as above, they are prohibited by the Reserve Bank from accepting deposits from public (except from shareholders) with effect from August 2009.
E. Depositor Protection Issues
Some of the important regulations relating to acceptance of deposits by NBFCs are as under:
-
The NBFCs are allowed to accept/renew public deposits for a minimum period of 12 months and maximum period of 60 months. They cannot accept deposits repayable on demand.
-
NBFCs cannot offer interest rates higher than the ceiling rate prescribed by RBI from time to time. The present ceiling is 12.5 per cent per annum. The interest may be paid or compounded at rests not shorter than monthly rests.
-
NBFCs cannot offer gifts/incentives or any other additional benefit to the depositors.
-
NBFCs should have minimum investment grade credit rating.
-
The deposits with NBFCs are not insured.
-
The repayment of deposits by NBFCs is not guaranteed by RBI.
-
Certain mandatory disclosures are to be made about the company in the Application Form issued by the company soliciting deposits.
A depositor wanting to place deposit with an NBFC must take the following precautions before placing deposits:
i. That the NBFC is registered with the Reserve Bank and specifically authorized by the Reserve Bank to accept deposits. The list of deposit taking NBFCs entitled to accept deposits is available on the web site of the Reserve Bank of India (www.rbi.org.in) under ‘Regulation → Non-Banking’. The depositor should check the above list to know about NBFCs permitted to accept public deposits therein.
ii. NBFCs have to prominently display the Certificate of Registration (CoR) issued by the Reserve Bank at place of business. This CoR should also reflect that the NBFC has been specifically authorized by the Reserve Bank to accept deposits. Depositors must scrutinize the CoR to ensure that the NBFC is authorized to accept deposits.
iii. The maximum interest rate that an NBFC can pay to a depositor should not exceed 12.5% currently. The Reserve Bank keeps altering the interest rates depending on the macro-economic environment and publishes the change in the interest rates on its website (www.rbi.org.in) under ‘notifications’.
iv. The depositor must insist on a proper receipt for every amount of deposit placed with the NBFC. The receipt should be duly signed by an officer authorized by the NBFC and should state the date of the deposit, the name of the depositor, the amount in words and figures, rate of interest payable, maturity date and amount.
v. In the case of brokers/agents, etc., collecting public deposits on behalf of NBFCs, the depositors should satisfy themselves that the brokers/agents are duly authorized by the NBFC.
vi. The depositor must bear in mind that public deposits are unsecured and Deposit Insurance facility is not available to depositors of NBFCs.
vii. The Reserve Bank of India does not accept any responsibility or guarantee about the present position as to the financial soundness of the company or for the correctness of any of the statements or representations made or opinions expressed by the company and for repayment of deposits/discharge of the liabilities by the NBFC.
No. The Reserve Bank does not guarantee repayment of deposits by NBFCs even though they may be authorized to collect deposits. As such, depositors should take informed decisions while placing deposits with an NBFC.
If an NBFC defaults in repayment of deposit, the depositor can approach the Company Law Board (now National Company Law Tribunal) or Consumer Forum or file a civil suit in a Court of Law to recover the deposits. Further, at the level of the State Government, the State Legislations on Protection of Interest of Depositors (in Financial Establishments) empowers the State Governments to take action even before the default takes place or complaints are received from depositors. If there is perpetration of an offence and if the intention is to defraud, the State Government can even attach properties. NBFCs are also advised to lay down an appropriate grievance redressal mechanism as indicated in reply to question 57 below.
When an NBFC fails to repay any deposit or part thereof in accordance with the terms and conditions of such deposit, the CLB/NCLT either on its own motion or on an application from the depositor, direct by order, the NBFC to make repayment of such deposit or part thereof forthwith or within such time and subject to such conditions as may be specified in the order. After making the payment, the company will need to file the compliance with the local office of the Reserve Bank of India.
As explained above, the depositor can approach CLB/NCLT by mailing an application in prescribed form to the appropriate bench of the CLB/NCLT according to its territorial jurisdiction.
The details of addresses and territorial jurisdiction of the bench officers of CLB/NCLT are available on the website https://nclt.gov.in/about-nclt.
An Official Liquidator is appointed by the court after giving the company reasonable opportunity of being heard in a winding up petition. The liquidator performs the duties of winding up of the company and such duties in reference thereto as the court may impose. Where the court has appointed an official liquidator or provisional liquidator, he becomes custodian of the property of the company and runs day-to-day affairs of the company. He has to draw up a statement of affairs of the company in prescribed form containing particulars of assets of the company, its debts and liabilities, names/residences/occupations of its creditors, the debts due to the company and such other information as may be prescribed. The scheme is drawn up by the liquidator and same is put up to the court for approval. The liquidator realizes the assets of the company and arranges to repay the creditors according to the scheme approved by the court. The liquidator generally inserts advertisement in the newspaper inviting claims from depositors/investors in compliance with court orders. Therefore, the depositors should file the claims within due time as per such notices of the liquidator.
With the enactment of the Insolvency and Bankruptcy Code, 2016, the corporate insolvency resolution process can be initiated by the Reserve Bank subject to the provisions of the Code, provided, the asset size of the NBFC is ₹500 crore or more. Thereafter, the resolution process would be undertaken as per the process prescribed under IBC.
The depositor is entitled to approach the relevant authorities as permissible under Law.
It is prescribed that the Board of Directors of NBFCs shall lay down the appropriate grievance redressal mechanism within the organisation and such mechanism shall ensure that all disputes arising out of the decisions of the lending institution’s functionaries are heard and disposed of at least at the next higher level.
Further, NBFCs (excluding Housing Finance Companies) which are authorised to accept deposits; or have customer interface and an asset size of ₹100 crore & above as on the date of the last audited balance sheet, are covered under Reserve Bank - Integrated Ombudsman Scheme, 2021 (as amended from time to time). In case of grievances against NBFCs, which are covered under RBI Ombudsman Scheme, are not redressed within a period of one month, the customer may approach the Ombudsman through its CMS portal accessible on the link https://cms.rbi.org.in/cms/indexpage.html#eng.
Companies registered with MCA but not required to be registered with the Reserve Bank as NBFCs are not under the regulatory domain of the Reserve Bank. Whenever Reserve Bank receives any such complaints about the companies registered with MCA but not registered with the Reserve Bank as NBFCs, it forwards the complaints to the Registrar of Companies (RoC) of the respective state for any action. The complainants are advised that the complaints relating to irregularities of such companies should be promptly lodged with RoC concerned for initiating corrective action. However, in case it comes to the knowledge of the Reserve Bank that those companies were required to be registered with the Reserve Bank but have not done so and have accepted deposits as defined under RBI Act, such action, as is deemed necessary under the provisions of the RBI Act, will be taken.
As per Reserve Bank’s Directions, overdue interest is payable to the depositors in case the NBFC has delayed the repayment of matured deposits, and such interest is payable from the date of receipt of such claim by the NBFC or the date of maturity of the deposit whichever is later, till the date of actual payment. If the depositor has lodged his claim after the date of maturity, the NBFC would be liable to pay interest for the period from the date of claim till the date of repayment. For the period between the date of maturity and the date of claim it is the discretion of the company to pay interest.
In cases where NBFCs are required to freeze the term deposits of customer based on the orders of the Government authorities or the deposit receipts are seized by the Government authorities, they shall follow the procedure as given below:
i. A request letter may be obtained from the depositor on maturity. While obtaining the request letter from the depositor for renewal, NBFCs should also advise him to indicate the term for which the deposit is to be renewed. In case the depositor does not exercise his option of choosing the term for renewal, NBFCs may renew the same for a term equal to the original term.
ii. No new receipt is required to be issued. However, suitable note may be made regarding renewal in the deposit ledger.
iii. Renewal of deposit may be advised by registered letter / speed post / courier service to the concerned Government department under advice to the depositor. In the advice to the depositor, the rate of interest at which the deposit is renewed should also be mentioned.
iv. If overdue period does not exceed 14 days on the date of receipt of the request letter, renewal may be done from the date of maturity. If it exceeds 14 days, NBFCs may pay interest for the overdue period as per the policy adopted by them, and keep it in a separate interest free sub-account which should be released when the original fixed deposit is released.
However, the final repayment of the principal and the interest so accrued should be done only after the clearance regarding the same is obtained by the NBFCs from the respective Government agencies.
An NBFC accepts deposits under a mutual contract with its depositors. In case a depositor requests for pre-mature payment, the Reserve Bank has prescribed regulations for such an eventuality in the Master Direction - Non-Banking Financial Companies Acceptance of Public Deposits (Reserve Bank) Directions, 2016 (as amended from time to time) wherein it is specified that NBFCs cannot grant any loan against a public deposit or make premature repayment of a public deposit within a period of three months (lock-in period) from the date of its acceptance. However, in the event of death of a depositor, the NBFC may, even within the lock-in period, repay the deposit at the request of the joint holders with survivor clause, or to the nominee / legal heir only against submission of relevant proof, to the satisfaction of the NBFC. Further, in order to enable a depositor to meet the expenses of an emergent nature, the NBFC may subject to satisfaction of the NBFC about the circumstances, prematurely repay tiny deposits (i.e., up to ₹10,000/-) and also other deposits, as per the provisions laid down by the Reserve Bank.
An NBFC, which is not a problem company, subject to above provisions, may permit premature repayment of a public deposit after the lock–in period, at its sole discretion, at the rate of interest prescribed by the Reserve Bank.
A problem NBFC is prohibited from making premature repayment of any deposits or granting any loan against public deposits, as the case may be. The prohibition shall not, however, apply in the case of death of depositor or repayment of tiny deposits (i.e. up to ₹ 10,000/-) in order to enable a depositor to meet expenses of an emergent nature, subject to lock in period of 3 months in the latter case.
In terms of Section 45-IB of the RBI Act, 1934, the minimum level of liquid assets to be maintained by deposit taking NBFCs is 15% of public deposits outstanding as on the last working day of the second preceding quarter. Of the 15%, NBFCs are required to invest not less than 10% in approved securities and the remaining 5% can be in unencumbered term deposits with any Scheduled Commercial Bank (SCB)/ SIDBI/ NABARD; or bonds issued by SIDBI or NABARD. Thus, the liquid assets may consist of Government securities, Government guaranteed bonds and term deposits/ bonds, as specified.
The investment in Government Securities should be in dematerialised form which can be maintained in Subsidiary General Ledger (SGL) Account with the Reserve Bank or a Gilt Account with Constituents’ Subsidiary General Ledger (CSGL) Account or a dematerialized account with a depository through a depository participant registered with SEBI. In case of Government guaranteed bonds, the same may be kept in dematerialised form with SCB/ Stock Holding Corporation of India Limited (SHCIL) or in a dematerialised account with a depository through a depository participant registered with SEBI. However, in case Government bonds are in physical form, the same may be kept in safe custody of SCB/SHCIL along with term deposits of SCB/ SIDBI/ NABARD.
NBFCs have been directed to maintain the mandated liquid asset securities at a place where the registered office of the company is situated. However, if an NBFC intends to entrust the securities at a place other than the place at which its registered office is located, it may do so after obtaining the permission of the Reserve Bank in writing. The liquid assets maintained as above are to be utilised for payment of claims of depositors. However, deposits being unsecured in nature, the depositors do not have direct claim on liquid assets.
The Reserve Bank has issued detailed regulations on deposit acceptance, including the quantum of deposits that can be collected, mandatory credit rating, mandatory maintenance of liquid assets for repayment to depositors, manner of maintenance of its deposit books, prudential regulations including maintenance of adequate capital, limitations on exposures, and inspection of the NBFCs, besides others, to ensure that the NBFCs function on sound lines. If the Reserve Bank observes through its inspection or audit of any NBFC or through complaints or through market intelligence, that a certain NBFC is not complying with the Reserve Bank’s directions, it may prohibit the NBFC from accepting further deposits and prohibit it from selling its assets. In addition, if the depositor has complained to the Company Law Board (CLB) [now National Company Law Tribunal (NCLT)] which has ordered repayment and the NBFC has not complied with the CLB/NCLT order, the Reserve Bank can initiate prosecution of the NBFC, including criminal action and winding up of the NBFC.
More importantly, the Reserve Bank initiates prompt action, including imposing penalties and taking legal action against companies which are found to be violating its instructions/norms on the basis of Market Intelligence reports, complaints, exception reports from statutory auditors of the companies, information received through SLCC meetings, etc. The Reserve Bank immediately shares such information with all the financial sector regulators and enforcement agencies in the State Level Coordination Committee Meetings.
As part of its public policy measure, the Reserve Bank has been in the forefront in taking several initiatives to create awareness among the general public on the need to be careful while investing their hard earned money. The initiatives include issue of cautionary notices in print media and distribution of informative and educative brochures/pamphlets and close interaction with the public during awareness/outreach programs, Townhall events, participation in State Government sponsored trade fairs and exhibitions. At times, it even requests newspapers with large circulation (English and vernacular) to desist from accepting advertisements from unincorporated entities seeking deposits. The Reserve Bank has also launched its public awareness initiative with the tag line ‘RBI Kehta Hai’ which may be accessed at https://rbikehtahai.rbi.org.in/.
NBFCs shall obtain credit rating from any of the SEBI-registered credit rating agencies.
The minimum investment grade credit rating issued by any of the SEBI-registered credit rating agencies for deposit taking NBFCs shall be ‘BBB–‘.
In the event of downgrading of credit rating below the minimum specified investment grade rating, the deposit taking NBFC shall stop accepting public deposits and also stop renewing existing deposits with immediate effect, however the existing deposits would be allowed to run off to maturity. The NBFCs shall also report the position within fifteen working days to the Reserve Bank.
The purpose of enacting this law is to protect the interests of the depositors. The provisions of RBI Act are directed towards enabling RBI to issue prudential regulations that make the financial entities function on sound lines. RBI is a civil body and the RBI Act is a civil Act. Both do not have specific provisions to effect recovery by attachment and sale of assets of the defaulting companies, entities or their officials. It is the State government machinery which can effectively do this. The Protection of Interest of Depositors in Financial Establishments Acts, confers adequate powers on the State Governments to attach and sell assets of the defaulting companies, entities and their officials.
Yes, to a large extent. The Act makes offences, such as, unauthorized acceptance of deposits by any entity, firm or company a cognizable offence, that is entities that are indulging in unauthorized deposit acceptance or unlawful financial activities can be immediately imprisoned and prosecuted. Under the Act, the State Governments have been given vast powers to attach the property of such entities, dispose them off under the orders of special courts and distribute the proceeds to the depositors. The widespread State Government / State Police machinery is best positioned to take quick action against the culprits.
Further, Government of India has recently enacted the Banning of Unregulated Deposit Schemes Act, 2019, a Central Legislation, which provides a comprehensive mechanism to ban the unregulated deposit schemes, other than deposits taken in ordinary course of business, and to protect the interest of depositors. This Act has specific provisions for restitution of depositors through various means viz., attachment and sale of property, etc. This Act also provides for enhanced legislative mechanism for handling unregulated deposit schemes viz., constitution of Designated Courts to deal with matters under the Act, powers for investigation (including by Central Bureau of Investigation in case deposits, deposit-takers and properties are located in more than one State or Union Territory, or outside India), search & seizure, penal provisions, etc.
The Reserve Bank is strengthening its market intelligence function and is constantly examining the financials of companies, references for which are received through market intelligence or complaints to the Reserve Bank. As part of initiative of State Level Consultation Committee comprising of Regulators and Government, the Sachet portal (https://sachet.rbi.org.in/) has been launched and members of public are requested to share any relevant information pertaining to unauthorised collection of deposits. In this, context, members of public can contribute a great deal by being vigilant and lodging a complaint immediately if they come across any financial entity that contravenes the RBI Act. For example, if they are accepting deposits unauthorisedly and/conducting NBFC activities without obtaining due permission from the Reserve Bank. More importantly, these entities will not be able to function if members of public start investing wisely. Members of the public must know that high returns on investments will also have high risks. And there can be no assured return for speculative activities. Before investing, the public must ensure that the entity they are investing in is a regulated entity with one of the financial sector regulators.
F. Collective Investment Schemes (CIS) and Chit Funds
No. CIS are schemes where money is exchanged for units, be it profits, income, produce, property etc. Collective Investment Schemes (CIS) do not fall under the regulatory purview of the Reserve Bank and falls under the regulatory purview of SEBI.
Chit Fund companies are regulated under the Chit Fund Act, 1982, which is a Central Act, and is implemented by the State Governments. In order to avoid duality of regulation, companies, doing the business of chit, as defined under Section 2(b) of the Chit Funds Act, 1982 are exempted from the provisions of Section 45-IA, 45-IB and 45-IC of the RBI Act, 1934. Thus, chit fund companies are not required to be registered with the Reserve Bank and would be registered and regulated by the State Government under Chit Funds Act, 1982. However, chit fund companies are subject to other provisions under Chapter IIIB of the RBI Act, 1934 and the Reserve Bank has prohibited chit fund companies from accepting deposits from the public in 2009. In case any Chit Fund is accepting public deposits, the Reserve Bank can prosecute such chit funds
G. Money Circulation/Multi-Level Marketing (MLM)/ Ponzi Schemes/ Unincorporated Bodies (UIBs)
No, Multi-Level Marketing companies, Direct Selling Companies, Online Selling Companies do not fall under the purview of the Reserve Bank. Activities of these companies fall under the regulatory/administrative domain of respective state government. The provisions of the Consumer Protection Act, 2019 and the Consumer Protection (Direct Selling) Rules, 2021 may be referred. The list of regulators and the entities regulated by them are provided in Annex I.
While some of these terms are not formally defined, generally, the money circulation, multi-level marketing / chain marketing or Ponzi schemes are schemes promising easy or quick money upon enrollment of members. Income under multi-level marketing or pyramid structured schemes do not come from the sale of products they offer as much as from enrolling more and more members from whom hefty subscription fees are taken. It is incumbent upon all members to enroll more members, as a portion of the subscription amounts so collected is distributed among the members at the top of the pyramid. Any break in the chain leads to the collapse of the pyramid, and the members lower in the pyramid are the ones that are affected the most. Ponzi schemes are those schemes that collect money from the public on promises of high returns. As there is no asset creation, money collected from one depositor is paid as returns to the other. Since there is no other activity generating returns, the scheme becomes unviable and impossible for the people running the scheme to meet the promised return or even return the principal amounts collected. The scheme inevitably fails, and the perpetrators disappear with the money.
No. Acceptance of money under Money Circulation Schemes, by whatever name called, is not allowed as acceptance of money under those schemes is a cognizable offence under the Prize Chit and Money Circulation (Banning) Act, 1978, and are banned. The Reserve Bank has no role in implementation of this Act, except advising and assisting the Central Government in framing the Rules under this Act.
Money Circulation schemes, by whatever name called, are an offence under the Prize Chits and Money Circulation Schemes (Banning) Act, 1978. The Act prohibits any person or individual to promote or conduct any money circulation scheme or enrol as member to its schemes or anyone to participate in it by either receiving or remitting any money in pursuance of such chit or scheme. Contravention of the provisions of this Act, is monitored and dealt with by the State Governments.
Any information/grievance relating to such schemes should be given to the police / Economic Offence Wing (EOW) of the concerned State Government or the Ministry of Corporate Affairs. If brought to the notice of the Reserve Bank, the same shall be informed to the concerned State Government authorities.
UIBs include an individual, a firm or an unincorporated association of individuals. In terms of provisions of section 45S of RBI Act, these entities are prohibited from accepting any deposit. The Act makes acceptance of deposits by such UIBs punishable with imprisonment or fine or both. The State government has to play a proactive role in arresting the illegal activities of such entities to protect the interests of depositors.
UIBs do not come under the regulatory domain of the Reserve Bank. Whenever the Reserve Bank receives any complaints against UIBs, it immediately forwards the same to the Economic Offences Wing (EOW) of the State Government police agencies. The complainants are also advised to lodge the complaints directly with the State government police authorities (EOW) so that appropriate action against the culprits is taken immediately and the process is hastened.
As per Section 45T of the RBI Act, both the Reserve Bank and the State Governments can apply for search warrant before appropriate Court, and on issue of such warrant, the same shall be executed as per procedure laid down in Law by the enforcement authorities. Nonetheless, in order to take immediate action against the offenders, the information should immediately be passed on to the State Police or the Economic Offences Wing of the concerned State, who can take prompt and appropriate action. Since the State Government machinery is widespread and the State Government is also empowered to take action under the provisions of the RBI Act, 1934, any information on such entities accepting deposits may be provided immediately to the respective State Government’s Police Department/EOW.
Many of the State Governments have enacted the State Protection of Interests of Depositors in Financial Establishments Act, which empowers the State Government to take appropriate and timely action.
The Reserve Bank on its part has taken various steps to curb activities of UIBs which includes spreading awareness through advertisements in leading newspapers to sensitise public, organize various depositor awareness programmes, and keeps close liaison with the law enforcing agencies (Economic Offences Wing).
Before investing in schemes that promise high rates of return, the depositors/ investors must ensure that the entity offering such returns is registered with one of the Financial Sector Regulators and is authorized to accept funds, whether in the form of deposits or otherwise. Depositors/ investors must generally be circumspect if the interest rates or rates of return on deposits/ investments offered are high. Unless the entity accepting funds is able to earn more than what it promises, the entity will not be able to repay the depositor/ investor as promised. For earning higher returns, the entity will have to take higher risks on the investments it makes. Higher the risk, the more speculative would be its investments on which there can be no assured return. As such, members of public should forewarn themselves that the likelihood of losing money in schemes that offer high rates of interest are more.
The two Charts given at Annex I and Annex II depict the activities and the regulators overseeing the same. Further, The First Schedule of the ‘The Banning of Unregulated Deposit Schemes Act, 2019’ may be referred for the list of regulated deposit schemes.
Complaints may hence be addressed to the concerned regulator. If the activity is a banned activity, the aggrieved person can approach the State Police/Economic Offences Wing of the State Police and lodge a suitable complaint.
H. Other/ miscellaneous aspects
Commercial Real Estate (CRE) would consist of loans to builders/ developers/ others for creation/ acquisition of commercial real estate (such as office building, retail space, multi-purpose commercial premises, multi-tenanted commercial premises, industrial or warehouse space, hotels, land acquisition, development and construction etc.) where the prospects for repayment, or recovery in case of default, would depend primarily on the cash flows generated by the asset by way of lease/rental payments, sale etc. Further, loans for third dwelling unit onwards to an individual will be treated as CRE exposure. Exposure shall also include non-fund based limits.
Commercial Real Estate – Residential Housing (CRE–RH) is a sub-category of CRE that consist of loans to builders/ developers for residential housing projects (except for captive consumption). Such projects should ordinarily not include non-residential commercial real estate. However integrated housing project comprising of some commercial spaces (e.g., shopping complex, school etc.) can also be specified under CRE-RH, provided that the commercial area in the residential housing project does not exceed 10 percent of the total Floor Space Index (FSI) of the project. In case the FSI of the commercial area in the predominantly residential housing complex exceed the ceiling of 10 percent, the entire loan should be classified as CRE and not CRE-RH.
No, the group requires to consolidate total assets of only those NBFCs which have been granted Certificate of Registration by the Bank. However, in case unregistered CICs in the group with asset size below ₹100 crore have accessed public funds, the asset size of such CICs shall be consolidated for the above purpose, but it would not change the status of unregistered CICs.
Loans against units of mutual funds (except units of exclusively debt oriented mutual funds) would attract LTV requirements as applicable to loans against shares. Further, the LTV requirement for loans/ advances against units of exclusively debt-oriented mutual funds may be decided by individual NBFCs in accordance with their loan policy.
In this case prior written approval of the Reserve Bank is to be obtained by the NBFC ‘A’. In case NBFC ‘A’ would cease to exist after the merger, the Certificate of Registration shall be surrendered for cancellation. Where ‘B’ is an NBFC, as a result of merger if there is change in control in ‘B’, or change in shareholding pattern of paid-up equity capital of ‘B’ by 26% or more, or change in management in ‘B’ which would result in change in more than 30% of the directors (excluding independent directors), prior written approval of the Reserve Bank is required. If ‘B’ is not an NBFC but is likely to meet Principal Business Criteria (i.e., 50-50 criteria) post-merger, it would also need to approach the Reserve Bank for prior written approval as well as registration as an NBFC.
Where a non-NBFC mergers with an NBFC, prior written approval of the Reserve Bank would be required if such a merger satisfies any one or all of the conditions viz., (i) any change in control in the NBFC due to merger, (ii) any change in the shareholding of the NBFC consequent to the merger which would result in change in shareholding of 26% or more of the paid up equity capital of the NBFC, (iii) any change in the management of the NBFC which would result in change in more than 30% of the directors, excluding independent directors. It may be noted that the NBFC shall continue to fulfil the Principal Business Criteria (i.e., 50-50 criteria) after merger to be eligible to hold the Certificate of Registration as an NBFC.
The NBFCs being amalgamated will require to obtain prior written approval of the Reserve Bank. Depending upon the nature of amalgamation/merger proposal, requisite approvals as per regulations needs to be sought.
Yes, prior approval of the Reserve Bank would have to be obtained before approaching any Court or Tribunal seeking orders for merger/ amalgamation in all such cases which would ordinarily fall under the scenarios explained in FAQs 84, 85 or 86.
Disclaimer: These FAQs are issued by the Reserve Bank for information and general guidance purposes only. The Reserve Bank will not be held responsible for actions taken and/or decisions made on the basis of the same. For clarifications or interpretations, if any, one may be guided by the relevant circulars and notifications issued from time to time.
| Related Press Release | |
| May 31, 2013 | Check before Depositing Money with Financial Entities: RBI Advisory |
Page Last Updated on: December 10, 2022