|
The external debt data for end-March 2008 have been compiled. As per the current practice, India's external debt statistics for the quarters ending March and June are compiled and released by the Reserve Bank, while the external debt data for quarters ending September and December are compiled and released by the Ministry of Finance, Government of India. A detailed account of external debt in the standard format as at end-March 2008 in rupee and US dollar terms is presented in Statement 1 and Statement 2, respectively.
1. Stock of External Debt
The external debt was placed at US $ 221.2 billion at the end of March 2008 recording an increase of US $ 51.5 billion or 30.4 per cent over the end-March 2007 level (Table 1 and Chart 1). The increase was mainly due to external commercial borrowings (ECBs) that contributed around 39.5 per cent of the increase in total external debt, followed by short term debt (contribution being 34.8 per cent).
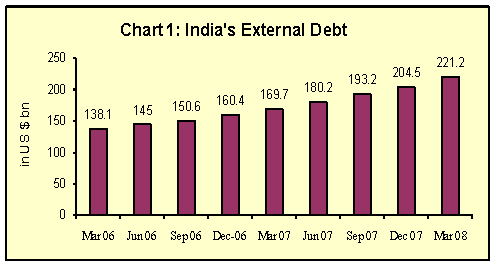
Table 1: External Debt Outstanding
At end of |
Total External Debt
(US $ million) |
Variation (in US $ million) |
Over corresponding
quarter previous year |
Over previous
quarter |
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
March 2006 |
138,133 |
5160 (3.9) |
5,818 (4.4) |
June 2006 |
145,019 |
12,073 (9.1) |
6,886 (5.0) |
September 2006 |
150,622 |
13,813 (10.1) |
5,603 (3.9) |
December 2006 |
160,392 |
28,077 (21.2) |
9,770 (6.5) |
March 2007 |
169,669 |
31,536 (22.8) |
9,277 (5.8) |
June 2007 |
180,179 |
35,160 (24.2) |
10,510 (6.2) |
September 2007 |
193,193 |
42,571 (28.3) |
13,014 (7.2) |
December 2007 |
204,472 |
44,080 (27.5) |
11,279 (5.8) |
March 2008 |
221,212 |
51,543 (30.4) |
16,740 (8.2) |
Note: Figures in parentheses indicate percentage increase.
2. Valuation Changes
Out of the increase of US $ 51.5 billion in external debt during the year 2007-08, valuation effect reflecting the depreciation of the US dollar against other major international currencies and Indian rupee accounted for US $ 9.9 billion of the increase. This would imply that excluding the valuation effects, the stock of external debt as at end-March 2008 increased by about US $ 41.6 billion over the end-March 2007 level.
3. Components of External Debt
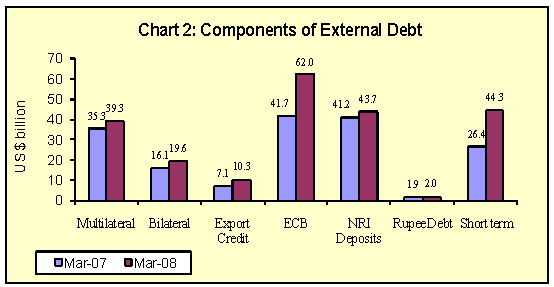
All the components of external debt recorded an increase during the year. External commercial borrowings (ECB) (including FCCBs) at US $ 62.0 billion recorded the maximum increase of US $ 20.4 billion (48.9 per cent) during the year (Table 2 and Chart 2). This was mainly due to the rising financing requirements of the Indian companies on account of their ongoing technological upgradation and capacity expansion. The data on short term debt now includes supplier’s credit up to 180 days with effect from end-March 2005. Short term debt also recorded an increase of US $ 17.9 billion during 2007-08. Under short term debt, while trade related credits rose significantly by around US $ 17.7 billion in line with the rising imports, FII debt investment in government papers rose by about US $ 254 million.
All the other components of external debt also recorded an increase during 2007-08: multilateral debt (US $ 4.0 billion), bilateral debt (US $ 3.6 billion), export credit above one year maturity (US $ 3.2 billion) and NRI deposits (US $ 2.4 billion). Rupee debt recorded a marginal rise of US $ 69 million.
Table 2: Variation in External Debt by Components
Item |
External debt outstanding
at the end-of (US $ million) |
Absolute variation
(US $ million) |
Percentage variation
(US $ million) |
Mar 08 |
Mar 07 |
Mar 06 |
Mar 07 to
Mar 08 |
Mar 06
to
Mar 07 |
Mar 07 to
Mar 08 |
Mar 06
to
Mar 07 |
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
1. Multilateral |
39,312
(17.8) |
35,337
(20.8) |
32,620
(23.6) |
3,975 |
2,717 |
11.2 |
8.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. Bilateral |
19,613
(8.9) |
16,061
(9.5) |
15,761
(11.4) |
3,552 |
300 |
22.1 |
1.9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. IMF |
0
(0.0) |
0
(0.0) |
0
(0.0) |
0 |
0 |
0.0 |
0.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. Export
Credit |
10,267
(4.6) |
7,051
(4.2) |
5,420
(3.9) |
3,216 |
1,631 |
45.6 |
30.1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5.Commercial
Borrowings |
62,019
(28.0) |
41,657
(24.6) |
26,452
(19.1) |
20,362 |
15,205 |
48.9 |
57.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6. NRI
Deposits |
43,672
(19.7) |
41, 240
(24.3) |
36,282
(26.3) |
2,432 |
4,958 |
5.9 |
13.7 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7. Rupee Debt |
2,016
(0.9) |
1,947
(1.1) |
2,059
(1.5) |
69 |
-112 |
3.5 |
-5.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
8. Short term
Debt |
44,313
(20.0) |
26,376
(15.5) |
19,539
(14.1) |
17,937 |
6,837 |
68.0 |
35.0 |
Total Debt
(1 to 8) |
221,212
(100.0) |
169,669
(100.0) |
138,133
(100.0) |
51,543 |
31,536 |
30.4 |
22.8 |
Memo Items |
A. Long-Term
Debt |
176,899
(80.0) |
143,293
(84.5) |
118,594
(85.9) |
33,606 |
24,699 |
23.5 |
20.8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
B. Short-Term
Debt |
44,313
(20.0) |
26,376
(15.5) |
19,539
(14.1) |
17,937 |
6,837 |
68.0 |
35.0 |
Figures in parentheses indicate share to total debt.
4. External Debt by Residual Maturity
While external debt compiled in terms of original maturity helps in comprehending the nature of capital flows, external debt in terms of residual maturity helps to analyse the debt service payments profile and the consequent charge on foreign exchange reserves. Based on residual maturity, long-term debt accounted for US $ 136.4 billion or 62.4 per cent of total debt at end-March 2008. Short-term debt by residual maturity comprises all the components of short-term debt with original maturity of one year or less and repayments due under medium and long-term debt by original maturity during one year reference period. Short-term debt by residual maturity at end-March 2008 stood at US $ 82.1 billion, accounting for 37.6 per cent of the total external debt. The ratio of short-term debt by residual maturity to foreign exchange reserves was 26.5 per cent at end-March 2008 (Table 3).
Table 3: Residual Maturity of External Debt outstanding as at end-March 2008
|
Short term |
Long term |
Total |
Components |
Up to one year |
1 to 2 years |
2 to 3 years |
More than 3 years |
(2 to 5) |
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
|
2,720 |
3,061 |
3,425 |
47,122 |
56,328 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6,881 |
7,327 |
10,636 |
52,706 |
77,550 |
(including export credit) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.NRI deposits (i+ii+iii) |
28,799 |
7,070 |
3,566 |
1,449 |
43,672 |
(i) FCNR(B) |
10,258 |
2,394 |
1,403 |
113 |
14,168 |
(ii) NR(E)RA |
18,541 |
4,676 |
2,163 |
1336 |
26,716 |
(iii) NRO |
NA |
NA |
NA |
NA |
2,788 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.Short term debt |
43,662 |
- |
- |
- |
43,662 |
(Original maturity) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. Total |
82,062 |
17,458 |
17,627 |
101,277 |
221,212 |
Memo Items |
|
|
|
|
|
Short term debt
(Residual maturity as
per cent of total debt |
37.6 |
|
|
|
|
Short term debt
(Residual maturity as
per cent of Reserves) |
26.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Note: 1. Residual Maturity of NRI Deposits is estimated on the basis of the Survey conducted by the Reserve Bank on NRI deposits outstanding as on March 31, 2007.
2. The maturity pattern of NRO Deposits is not available. Therefore, maturity-wise totals given in columns 2 to 5 will not add up to the total given in column 6.
3. FII investment in treasury bills and government dated securities are included under sovereign debt, while FII investment in corporate debt papers and other short-term debt instruments are included under Commercial Borrowings.
5. Currency Composition
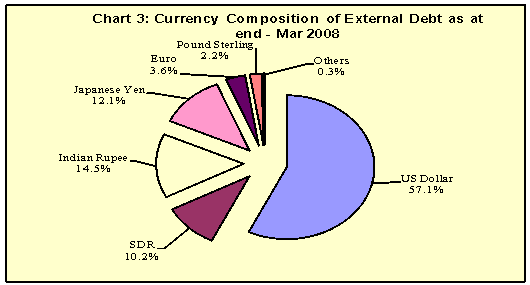
The US Dollar continues to remain the predominant currency accounting for 57.1 per cent of the total external debt stock as at the end of March 2008, followed by the Indian rupee (14.5 per cent), Japanese yen (12.1 per cent) and SDR (10.2 per cent) (Table 4 and Chart 3).
Table 4: Currency Composition of External Debt
(Percentage share in total external debt)
|
At end-March |
Currency |
2004 |
2005 |
2006 |
2007 |
2008 |
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
US Dollar |
40.5 |
48.0 |
49.2 |
52.0 |
57.1 |
SDR |
15.5 |
14.2 |
13.7 |
12.0 |
10.2 |
Indian Rupee |
22.7 |
19.6 |
18.9 |
17.7 |
14.5 |
Japanese Yen |
11.6 |
10.5 |
10.9 |
11.6 |
12.1 |
Euro |
5.8 |
4.6 |
4.4 |
4.0 |
3.6 |
Pound Sterling |
3.4 |
2.6 |
2.6 |
2.4 |
2.2 |
Others |
0.5 |
0.5 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
0.3 |
Total |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
100.0 |
6. Indicators of Debt Sustainability
There has been a perceptible improvement in external debt indicators over the years reflecting the growing sustainability of external debt of India (Table 5).
- External debt to GDP has risen to 18.8 per cent at end-March 2008 from 17.8 per cent at end-March 2007. This ratio was 30.8 per cent at end-March 1995.
- The debt service ratio was placed at 5.4 per cent during 2007-08 as against a double-digit figure till 2003-04.
- Reflecting the rise in short term debt during 2007-08, the ratio of short-term to total debt and short term debt to reserves has risen to 20.0 per cent and 14.3 per cent, respectively.
- The share of concessional debt in total external debt declined to 19.9 per cent at end-March 2008 from 23.3 per cent at end-March 2007 reflecting the continuing increase in non-concessional private debt in India's external debt stock.
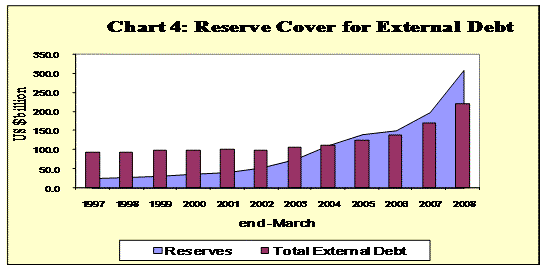
- India’s foreign exchange reserves exceeded the external debt by US $ 88.5 billion providing a cover of 140.0 per cent to the external debt stock at the end of March 2008 (Also see Chart 4).
Table 5: India’s Key ExternalDebt Indicators
Year |
Exter-nal
Debt
($ bn)
|
Ratio of
External
Debt to
GDP
(%) |
Debt
Service
Ratio(%)
|
Ratio of
Foreign
Exchange
Reserves to
Total Debt
(%) |
Ratio of
Concessi-onal
Debt to
Total Debt
(%) |
Ratio of
ShortTerm
Debt to
Foreign
Exchange
Reserves
(%) |
Ratio of
Short Term
Debt to
Total Debt
(%) |
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
(8) |
1990-91 |
83.8 |
28.7 |
35.3 |
7.0 |
45.9 |
146.5 |
10.2 |
1991-92 |
85.3 |
38.7 |
30.2 |
10.8 |
44.8 |
76.7 |
8.3 |
1992-93 |
90.0 |
37.5 |
27.5 |
10.9 |
44.5 |
64.5 |
7.0 |
1993-94 |
92.7 |
33.8 |
25.4 |
20.8 |
44.4 |
18.8 |
3.9 |
1994-95 |
99.0 |
30.8 |
25.9 |
25.4 |
45.3 |
16.9 |
4.3 |
1995-96 |
93.7 |
27.0 |
26.2 |
23.1 |
44.7 |
23.2 |
5.4 |
1996-97 |
93.5 |
24.6 |
23.0 |
28.3 |
42.2 |
25.5 |
7.2 |
1997-98 |
93.5 |
24.3 |
19.5 |
31.4 |
39.5 |
17.2 |
5.4 |
1998-99 |
96.9 |
23.6 |
18.7 |
33.5 |
38.5 |
13.2 |
4.4 |
1999-00 |
98.3 |
22.0 |
17.1 |
38.7 |
38.9 |
10.3 |
4.0 |
2000-01 |
101.3 |
22.5 |
16.6 |
41.7 |
35.4 |
8.6 |
3.6 |
2001-02 |
98.8 |
21.1 |
13.7 |
54.7 |
35.9 |
5.1 |
2.8 |
2002-03 |
104.9 |
20.3 |
16.0* |
72.5 |
36.8 |
6.1 |
4.5 |
2003-04 |
111.6 |
17.8 |
16.1** |
101.2 |
36.1 |
3.9 |
4.0 |
2004-05 |
133.0 |
18.6 |
6.1^ |
106.4 |
30.9 |
12.5 |
13.3 |
2005-06 |
138.1 |
17.2 |
9.9# |
109.8 |
28.6 |
12.9 |
14.1 |
2006-07 |
169.7 |
17.8 |
4.8 |
117.4 |
23.3 |
13.2 |
15.5 |
2007-08 |
221.2 |
18.8 |
5.4 |
140.0 |
19.9 |
14.3 |
20.0 |
* Works out to 12.4 %, with the exclusion of prepayment of external debt of US $ 3,430 million
** Works out to 8.2 % with the exclusion of pre payment of external debt of US $ 3,797 million and redemption of RIBs of US $ 5,549 million.
^ works out to 5.7 % with the exclusion of pre payment of external debt of US $ 381 million.
# works out to 6.3 % with the exclusion of IMD repayments of US $ 7.1 billion and pre payment of external debt of US $ 23.5 million.
Note: NRO deposits are included under NRI deposits from 2005-06 onwards. Suppliers credits up to 180 days and FII investment in short term debt instruments are included under short term external debt since 2004-05.
7. Cross Country Comparison
Comparing the cross country online data on external debt provided by the World Bank up to 2006 for the top twenty debtor countries of the developing world reveal the following (Table 6):
India’s position was fifthin 2006 in terms of external debt stock.
In terms of the ratio of external debt to Gross National Product (GNP), India’s position was second lowest, with China having the lowest ratio of external debt to GNP.
India’s debt service ratio was third lowest with China and Malaysia having first and second lowest debt service ratio, respectively.
The element of concessionality in India’s external debt portfolio was the second highest after Indonesia
In terms of reserves to total debt, India’s position was fifth after China, Malaysia, Thailand and Russia. Table 6: International Comparison of Top 20 Debtor Countries, 2006
Year |
External
Debt
($ bn)
|
External
Debt to
GNP
(%)
|
Debt
Service
ratio
(%)
|
Forex
Reserves
to
Total
Debt
(%) |
Concess-
ional
Debt to
Total
Debt
(%) |
Short
Term to
Total
Debt
(%) |
(1) |
(2) |
(3) |
(4) |
(5) |
(6) |
(7) |
1. China |
323 |
12.1 |
2.5 |
334.8 |
10.9 |
53.7 |
2. Russian Federation |
251 |
26.2 |
13.8 |
121.0 |
0.6 |
16.1 |
3. Turkey |
208 |
51.7 |
33.2 |
30.4 |
1.9 |
20.4 |
4. Brazil |
194 |
18.7 |
37.3 |
44.2 |
1.3 |
10.5 |
5. India |
170 |
17.8 |
4.8 |
117.4 |
23.3 |
15.5 |
6. Mexico |
161 |
19.5 |
18.9 |
47.5 |
0.9 |
4.6 |
7. Indonesia |
131 |
37.5 |
16.6 |
32.5 |
27.1 |
25.2 |
8. Poland |
126 |
38.7 |
24.7 |
38.5 |
0.9 |
17.0 |
9. Argentina |
122 |
58.6 |
31.6 |
26.2 |
1.1 |
28.7 |
10. Hungary |
108 |
102.7 |
33.1 |
20.1 |
1.1 |
13.9 |
11. Kazakhstan |
74 |
103.4 |
33.7 |
25.8 |
1.3 |
17.0 |
12. Philippines |
60 |
47.1 |
19.6 |
38.1 |
20.7 |
8.3 |
13. Thailand |
55 |
27.3 |
9.4 |
121.3 |
12.3 |
32.2 |
14. Romania |
55 |
46.7 |
18.4 |
54.8 |
2.0 |
32.2 |
15. Malaysia |
53 |
36.0 |
4.0 |
157.8 |
8.4 |
30.8 |
16. Ukraine |
50 |
47.6 |
18.1 |
44.8 |
3.6 |
44.8 |
17. Chile |
48 |
37.9 |
20.0 |
40.4 |
0.6 |
19.6 |
18. Venezuela RB |
45 |
24.7 |
13.3 |
82.3 |
0.4 |
26.5 |
19. Colombia |
40 |
26.9 |
31.3 |
38.9 |
2.6 |
12.1 |
20. Croatia |
37 |
90.2 |
33.1 |
30.7 |
1.6 |
14.9 |
Source: Data for India are as published by national authorities for 2006-07 and those for other countries are at end-December 2006 as available in World Bank’s Global Development Finance Online Database.
Alpana Killawala
Chief General Manager
Press Release :2007-2008/1680 |




























