 IST,
IST,
Indian Coinage
An Overview
India has been one of the earliest issuers of coins in the world (circa 6th Century BC). Few countries rival India for the sheer diversity of its coinage be it minting techniques, motifs, sizes, shapes, the metals used or for that matter the monetary history arising from the Monetary Standards India has experienced (Tri-metallism, Bi-metallism, the Silver Standard, the Gold Exchange Standard as well as fiat money).
In history, Indian coins have played a crucial role in documenting political and economic changes over time. Foreign coin hoards found in India throw light on Indian trade patterns in ancient, medieval, and late pre-colonial times. The Motifs on coins have been impacted upon by the cultural ethos of different regions at different time periods.
Our coinage pages attempt to give a sampler of Indian Coins down the ages and are by no means exhaustive. We propose to supplement the pages in the days to come. We welcome contributions of the public/viewers.
To identify these coins we invite you to browse through our pages.
Among the earliest issues were those by the Bank of Hindostan (1770-1832), the General Bank in Bengal and Bahar (1773-75, established by Warren Hastings), the Bengal Bank (1784-91), amongst others. Few of these notes survive.
The Paper Currency Act of 1861 conferred upon Government of India the monopoly of Note Issue bringing to an end note issues of Private and Presidency Banks. Paper currency in India owed much to the intellectual stimulus and personal dynamism of Sir James Wilson, the first Finance Member in the Executive Council of the Viceroy of India. With the early death of Sir James, the task of issuing Government Paper Money in India devolved upon his successor Samuel Laing who substantially modified Wilson's original proposals.
Government of India continued to issue currency notes till the Reserve Bank of India was established on 1st April, 1935. When the one rupee note was reintroduced as a war time measure in August, 1940, it was issued by Government of India with the status of a coin. Government of India continued to issue Rupee one notes till 1994.
The motifs appearing on Indian currency notes reflect the changing socio-cultural ethos and the world-view of the times: buccaneering mercantilism, colonial consolidation, domineering imperialism, the grandeur of empire, to the symbols of National Independence followed up by allegories of progress and finally in the latest series, reminiscing Gandhian values.
To understand these issues we invite you to browse through our pages.
Currency Timeline



India Paper Money A Retrospect : 1770-1998
Financial Instruments and 'Hundies' in India have a venerable history. Paper Money, in the modern sense, traces its origins to the late eighteenth century with the issues of private banks as well as semi-government banks (the Bank of Bengal, the Bank of Bombay and the Bank of Madras alluded to as the Presidency Banks).
Hundies
Hundis refer to financial instruments evolved on the Indian sub-continent used in trade and credit transactions. They were used
• as remittance instruments (to transfer funds from one place to another),
• as credit instruments (to borrow money [IOUs]),
• for trade transactions (as bills of exchange).
Technically, a Hundi is an unconditional order in writing made by a person directing another to pay a certain sum of money to a person named in the order. Hundis, being a part of the informal system have no legal status and are not covered under the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881. Though normally regarded as bills of exchange, they were more often used as equivalents of cheques issued by indigenous bankers.
Hundis: Specimens





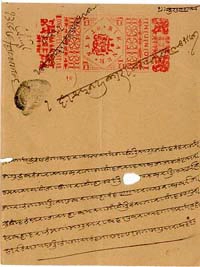

A Representative Darshani Hundi.
Early 20th Century
Nisani Hamare Gharu khate nam mandna.
Dastkhat Brijkishore Bhargava ke hundi likhe mujib sikar desi.
'SRI RAMJI
Sidh sri Patna subhastane chiranjeeva bhai Rikhabchand Bridhichan yog sri Jaipur se likhi Brijkishore Bhargava kee asis banchna, apranch hundi aik rupia 2,000 akshare rupia do hazar ke nime rupia aik hazar ka duna yahan rakha sah Sri Punamchandji Harakchandji pas miti Mangsir bad baras (12th) puga turat sah-jog rupia chalan ka dena. Sambat 1990, Miti Mangsir bad baras,
Rs.2,000
Neme Neme rupia panchsau ka chauguna pura do hazar kardejo.
'1' Chiranjeeva Rikhabchand Bridhichand, Patna.
Translation
Place it to the debit of our account.
Signature: Honour the Hundi written by Brijkishore Bhargava.
Greetings to Messrs. Rikhabchand Bridhichand, son of the fair city of Patna on whom the Hundi for Rs 2,000 (in words Rupees Two thousand only) is written by Brij Kishore Bhargava from Jaipur. Rupees one thousand if doubled make the sum of the hundi. The hundi has been drawn from here in favour of Messrs. Punamchand Harackchand on 12th Mangsir 1990, which please honour on presentation in the current money.
Rs.2,000
Four times of Rs. 500 make the sum of Rs. 2,000 for which the hundi is drawn.
Watermark on Hundis

Revenue Seals appearing on Hundis






GP Notes, Bonds & Shares





The Advent of Modern Banking in India: 1720 to 1850s
| Established | Failed (F) or Merged (M) | Bank | Place |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1720 | 1770 | Bank of Bombay | Bombay |
| 1770 | F 1832 | Bank of Hindostan | Calcutta |
| 1773 | F 1775 | General Bank of Bengal and Bihar | Calcutta |
| 1784 | F 1791 | Bengal Bank | Calcutta |
| 1786 | F 1791 | General Bank of India | Calcutta |
| 1788 | Unknown | The Carnatic Bank | Unknown |
| 1806 | M 1920 | Bank of Calcutta Bank of Bengal, 1808 | Calcutta |
| 1819 | F 1828 | The Commercial Bank | Calcutta |
| 1824 | F 1829 | The Calcutta Bank | Calcutta |
| 1828 | Unknown | Bank of India | |
| 1829 | F 1848 | The Union Bank | Calcutta |
| 1833 | Unknown | The Government Savings Bank | Calcutta |
| 1833 | F 1866 | The Agra & United Service Bank Ltd. (Earlier The Agra Bank and later The Agra and Masterman's Bank, London) | Agra |
| 1835 | F 1837 | The Bank of Mirzapore | Mirzapur |
| 1836 | Still Born | Bank of India (London) | |
| 1840 | F 1859 | North Western Bank of India | Mussoorie |
| 1840 | M 1920 | Bank of Bombay: Re-formed in 1868 | |
| 1841 | 1842 | Bank of Asia | London |
| 1841 | M 1849 | The Bank of Ceylon (Taken over by the Oriental Banking Corporation) | Colombo |
| 1842 | Still Born | The East India Bank, London | |
| 1842 | F 1884 | The Oriental Bank Corporation (Earlier, Bank of Western India) | Bombay |
| 1842 | 1863 | The Agra Savings Fund | Agra |
| 1843 | M 1920 | Bank of Madras | Madras |
| 1844 | Unknown | Delhi Bank Corporation Ltd. | Delhi |
| 1844 | F 1850 | The Benares Bank | Banaras |
| 1844 | F 1893 | Simla Bank Ltd. | Simla |
| 1845 | F 1866 | The Commercial Bank of India | Bombay |
| 1845 | F 1851 | The Cownpore Bank | Kanpur |
| 1846 | M 1862 | Dacca Bank (merged into Bank of Bengal) | Dacca |
| 1846 | F 1894 | Uncovenanted Service | Agra Bank Ltd. |
| 1852 | Still Born | London Bank of Australia & India | Agra |
| 1852 | F 1855 | Chartered Bank of Asia | London |
| 1853 | Chartered Mercantile Bank of India, London & China | London | |
| 1853 | Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China | London | |
| 1854 | F 1857 | The London and Eastern Banking Corp. | London |
| 1854 | The Comptoir D'Escompte of Paris | Paris | |
| Sources: Cooke, Brunyate, Tandon, Maharashtra State Archives and RBI | |||
Indian Coinage
An Overview
India has been one of the earliest issuers of coins in the world (circa 6th Century BC). Few countries rival India for the sheer diversity of its coinage be it minting techniques, motifs, sizes, shapes, the metals used or for that matter the monetary history arising from the Monetary Standards India has experienced (Tri-metallism, Bi-metallism, the Silver Standard, the Gold Exchange Standard as well as fiat money).
In history, Indian coins have played a crucial role in documenting political and economic changes over time. Foreign coin hoards found in India throw light on Indian trade patterns in ancient, medieval, and late pre-colonial times. The Motifs on coins have been impacted upon by the cultural ethos of different regions at different time periods.
Our coinage pages attempt to give a sampler of Indian Coins down the ages and are by no means exhaustive. We propose to supplement the pages in the days to come. We welcome contributions of the public/viewers.
To identify these coins we invite you to browse through our pages.
India Paper Money A Retrospect : 1770-1998
Financial Instruments and 'Hundies' in India have a venerable history. Paper Money, in the modern sense, traces its origins to the late eighteenth century with the issues of private banks as well as semi-government banks (the Bank of Bengal, the Bank of Bombay and the Bank of Madras alluded to as the Presidency Banks).



Among the earliest issues were those by the Bank of Hindostan (1770-1832), the General Bank in Bengal and Bahar (1773-75, established by Warren Hastings), the Bengal Bank (1784-91), amongst others. Few of these notes survive.
The Paper Currency Act of 1861 conferred upon Government of India the monopoly of Note Issue bringing to an end note issues of Private and Presidency Banks. Paper currency in India owed much to the intellectual stimulus and personal dynamism of Sir James Wilson, the first Finance Member in the Executive Council of the Viceroy of India. With the early death of Sir James, the task of issuing Government Paper Money in India devolved upon his successor Samuel Laing who substantially modified Wilson's original proposals.
Government of India continued to issue currency notes till the Reserve Bank of India was established on 1st April, 1935. When the one rupee note was reintroduced as a war time measure in August, 1940, it was issued by Government of India with the status of a coin. Government of India continued to issue Rupee one notes till 1994.
The motifs appearing on Indian currency notes reflect the changing socio-cultural ethos and the world-view of the times: buccaneering mercantilism, colonial consolidation, domineering imperialism, the grandeur of empire, to the symbols of National Independence followed up by allegories of progress and finally in the latest series, reminiscing Gandhian values.
To understand these issues we invite you to browse through our pages.
Currency Timeline
Hundies
Hundis refer to financial instruments evolved on the Indian sub-continent used in trade and credit transactions. They were used
• as remittance instruments (to transfer funds from one place to another),
• as credit instruments (to borrow money [IOUs]),
• for trade transactions (as bills of exchange).
Technically, a Hundi is an unconditional order in writing made by a person directing another to pay a certain sum of money to a person named in the order. Hundis, being a part of the informal system have no legal status and are not covered under the Negotiable Instruments Act, 1881. Though normally regarded as bills of exchange, they were more often used as equivalents of cheques issued by indigenous bankers.
Hundis: Specimens







A Representative Darshani Hundi.
Early 20th Century
Nisani Hamare Gharu khate nam mandna.
Dastkhat Brijkishore Bhargava ke hundi likhe mujib sikar desi.
'SRI RAMJI
Sidh sri Patna subhastane chiranjeeva bhai Rikhabchand Bridhichan yog sri Jaipur se likhi Brijkishore Bhargava kee asis banchna, apranch hundi aik rupia 2,000 akshare rupia do hazar ke nime rupia aik hazar ka duna yahan rakha sah Sri Punamchandji Harakchandji pas miti Mangsir bad baras (12th) puga turat sah-jog rupia chalan ka dena. Sambat 1990, Miti Mangsir bad baras,
Rs.2,000
Neme Neme rupia panchsau ka chauguna pura do hazar kardejo.
'1' Chiranjeeva Rikhabchand Bridhichand, Patna.
Translation
Place it to the debit of our account.
Signature: Honour the Hundi written by Brijkishore Bhargava.
Greetings to Messrs. Rikhabchand Bridhichand, son of the fair city of Patna on whom the Hundi for Rs 2,000 (in words Rupees Two thousand only) is written by Brij Kishore Bhargava from Jaipur. Rupees one thousand if doubled make the sum of the hundi. The hundi has been drawn from here in favour of Messrs. Punamchand Harackchand on 12th Mangsir 1990, which please honour on presentation in the current money.
Rs.2,000
Four times of Rs. 500 make the sum of Rs. 2,000 for which the hundi is drawn.
Watermark on Hundis

Revenue Seals appearing on Hundis






GP Notes, Bonds & Shares





The Advent of Modern Banking in India: 1720 to 1850s
| Established | Failed (F) or Merged (M) | Bank | Place |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1720 | 1770 | Bank of Bombay | Bombay |
| 1770 | F 1832 | Bank of Hindostan | Calcutta |
| 1773 | F 1775 | General Bank of Bengal and Bihar | Calcutta |
| 1784 | F 1791 | Bengal Bank | Calcutta |
| 1786 | F 1791 | General Bank of India | Calcutta |
| 1788 | Unknown | The Carnatic Bank | Unknown |
| 1806 | M 1920 | Bank of Calcutta Bank of Bengal, 1808 | Calcutta |
| 1819 | F 1828 | The Commercial Bank | Calcutta |
| 1824 | F 1829 | The Calcutta Bank | Calcutta |
| 1828 | Unknown | Bank of India | |
| 1829 | F 1848 | The Union Bank | Calcutta |
| 1833 | Unknown | The Government Savings Bank | Calcutta |
| 1833 | F 1866 | The Agra & United Service Bank Ltd. (Earlier The Agra Bank and later The Agra and Masterman's Bank, London) | Agra |
| 1835 | F 1837 | The Bank of Mirzapore | Mirzapur |
| 1836 | Still Born | Bank of India (London) | |
| 1840 | F 1859 | North Western Bank of India | Mussoorie |
| 1840 | M 1920 | Bank of Bombay: Re-formed in 1868 | |
| 1841 | 1842 | Bank of Asia | London |
| 1841 | M 1849 | The Bank of Ceylon (Taken over by the Oriental Banking Corporation) | Colombo |
| 1842 | Still Born | The East India Bank, London | |
| 1842 | F 1884 | The Oriental Bank Corporation (Earlier, Bank of Western India) | Bombay |
| 1842 | 1863 | The Agra Savings Fund | Agra |
| 1843 | M 1920 | Bank of Madras | Madras |
| 1844 | Unknown | Delhi Bank Corporation Ltd. | Delhi |
| 1844 | F 1850 | The Benares Bank | Banaras |
| 1844 | F 1893 | Simla Bank Ltd. | Simla |
| 1845 | F 1866 | The Commercial Bank of India | Bombay |
| 1845 | F 1851 | The Cownpore Bank | Kanpur |
| 1846 | M 1862 | Dacca Bank (merged into Bank of Bengal) | Dacca |
| 1846 | F 1894 | Uncovenanted Service | Agra Bank Ltd. |
| 1852 | Still Born | London Bank of Australia & India | Agra |
| 1852 | F 1855 | Chartered Bank of Asia | London |
| 1853 | Chartered Mercantile Bank of India, London & China | London | |
| 1853 | Chartered Bank of India, Australia and China | London | |
| 1854 | F 1857 | The London and Eastern Banking Corp. | London |
| 1854 | The Comptoir D'Escompte of Paris | Paris | |
| Sources: Cooke, Brunyate, Tandon, Maharashtra State Archives and RBI | |||
Anecdotes (Update)

The selection of the Bank's common seal to be used as the emblem of the Bank on currency notes, cheques and publications, was an issue that had to be taken up at an early stage of the Bank's formation.
The general ideas on the seal were as follows:
1. The seal should emphasise the Governmental status of the Bank, but not too closely;
2. It should have something Indian in the design;
3. It should be simple, artistic and heraldically correct; and
4. The design should be such that it could be used without substantial alteration for letter heading, etc.
For this purpose, various seals, medals and coins were examined. The East India Company Double Mohur, with the sketch of the Lion and Palm Tree, was found most suitable; however, it was decided to replace the lion by the tiger, the latter being regarded as the more characteristic animal of India!
To meet the immediate requirements in connection with the stamping of the Bank's share certificates, the work was entrusted to a Madras firm. The Board, at its meeting on February 23, 1935, approved the design of the seal but desired improvement of the animal's appearance. Unfortunately it was not possible to make any major changes at that stage. But the Deputy Governor, Sir James Taylor, did not rest content with this. He took keen interest in getting fresh sketches prepared by the Government of India Mint and the Security Printing Press, Nasik. As a basis for good design, he arranged for a photograph to be taken of the statue of the tiger on the entrance gate at Belvedere, Calcutta. Something or the other went wrong with the sketches so that Sir James, writing in September I938, was led to remark:
...... s tree is all right but his tiger looks too like some species of dog, and I am afraid that a design of a dog and a tree would arouse derision among the irreverent. .....'s tiger is distinctly good but the tree has spoiled it. The stem is too long and the branches too spidery, but I should have thought that by putting a firm line under the feet of his tiger and making his tree stronger and lower we could get quite a good result from his design.
Later, with further efforts, it was possible to have better proofs prepared by the Security Printing Press, Nasik. However, it was eventually decided not to make any change in the existing seal of the Bank, and the new sketches came to be used as an emblem for the Bank's currency notes, letter-heads, cheques and publications issued by the Bank.
Source: 'History of the Reserve Bank of India' (Update)






 BROCHURE
(
BROCHURE
(














