 IST,
IST,
MONETARY AND CREDIT INFORMATION REVIEW
Volume II
Issue 11
May 2006
|
CONTENTS |
|
Service Charges to be displayed on Bank's Websites/at Branches |
UCBs permitted to market Mutual Fund Units
The Reserve Bank has decided to permit UCBs registered in states, which have signed memorandum of understanding and those registered under the Multi-State Co-operative Societies Act, 2002 to enter into agreements with mutual funds (MFs) for marketing their units. The permission to market MF units is, however, subject to the conditions indicated below -
(i) The bank should act as an agent of the customers, forwarding the investors’ application for purchase/sale of MF units to the mutual fund/Registrar/transfer agents.
(ii) The MF units should be purchased at the customers’ risk and without the bank guaranteeing any assured return.
(iii) The MF units should not be acquired from the secondary market.
(iv) The MF units should not be bought back from the customers.
(v) UCBs holding custody of MF
units on behalf of customers should ensure that their own investments and their
customers’ investments are kept distinct from each other.
(vi) Retailing of MF units should be confined to certain selected branches to
ensure better control.
(vii) The extant ‘know your customer’ (KYC)/anti-money laundering (AML) guidelines in respect of the applicants should be complied with.
UCBs have been further advised to report the details of the tie-up together with a copy of the agreement entered into with the mutual fund, to the Reserve Bank’s respective regional office within a period of ten days from the date of entering into the arrangement.
Regional rural banks (RRBs) have also been permitted to undertake marketing of units of mutual funds with the approval of their board of directors and subject to the conditions enumerated above.
The Reserve Bank has revised the eligibility norms for setting up of automated teller machines (ATMs) by UCBs. To be eligible to set up on-site/off-site ATMs, the UCB should have -
i) minimum deposits of Rs. 100 crore;
ii) complied with the prescribed capital
to risk weighted assets ratio (CRAR);
iii) net non-performing asset (NPA) of less than 10 per cent; and
iv) consistent record of profitability and compliance with cash reserve ratio
(CRR)/statutory liquidity ratio (SLR).
Accordingly, UCBs satisfying these eligibility norms may apply to the Reserve Bank’s regional office for prior approval for installing on-site and/or off-site ATMs. UCBs registered under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act may apply to the Reserve Bank’s regional office under the jurisdiction of which the registered/head office of the UCB is situated.
Scheduled UCBs, other than those classified as Grade II to IV, do not require the Reserve Bank’s prior approval for setting up on-site ATMs. UCBs should install off-site ATMs approved by the Reserve Bank, only within the area of their operation. Shifting and relocation of ATMs would require the Reserve Bank’s prior approval.
Scheduled and non-scheduled UCBs permitted to have ATMs, both under the automatic and approval route, may also issue ATM-cum-Debit Cards.
The Reserve Bank has further advised that UCBs now need not obtain the Reserve Bank’s prior approval to share/interlink with other banks, the ATMs/BTMs installed at their branches/ extension counters.
UCBs permitted to undertake Limited Transactions at ECs
UCBs are now allowed to undertake limited transactions at extension counters (ECs) as follows :
- Deposit/withdrawal transactions.
- Issue and encashment of drafts and mail transfers.
- Issue and encashment of travellers’ cheques.
- Collection of bills.
- Advances against fixed deposits of their customers (within the sanctioning power of the concerned officials at the extension counter).
- Disbursement of other loans (only for individuals) sanctioned by the head office/base branch up to a limit of Rs.10 lakh
RBI Instructions on Customer Service
The Reserve Bank has been, for the past couple of years, endeavouring towards having the banks to deliver quality service to their customers at a reasonable price. It has also taken several measures towards financial inclusion, so that basic banking facilities are made available to a larger Indian population. Some recent initiatives that the Reserve Bank has taken are : l With effect from January 1, 2006, the Reserve Bank has put in place a revised Banking Ombudsman Scheme for redressal of grievances of banking customers. The scope of the scheme has been enlarged to cover customer complaints in areas, such as, levying service charges without prior notice to the customer, non-adherence to the fair practices code as adopted by individual banks, credit card complaints, deficiencies in providing the services assured by banks and banks’ sales agents, etc.
The Monetary and Credit Information Review will, from this issue, regularly cover the Reserve Bank’s instructions useful to common bank customers.
Banks advised to display Service Charges
In order to ensure transparency in banking services, the Reserve Bank has advised banks to display and update, on their website, the details of various service charges levied by them for the services provided/products offered to their customers.
Banks have also been advised to display the charges relating to certain services (please see page 3) in their offices/ branches. These charges should also be displayed in the local language.
Banks are required to furnish the details of service charges presently applicable, to the Reserve Bank by May 31, 2006 to enable the Reserve Bank to place them on its website.
It may be recalled that the Reserve Bank has deregulated the levy of service charges by commercial banks and the decision to prescribe service charges has been left to the discretion of individual banks’ boards. While fixing service charges, banks have been advised to ensure that the charges are reasonable, consistent with the cost of providing these services and that customers with low value/volume of transactions are not penalised.
The Reserve Bank had been receiving representations from the public about the unreasonable and non-transparent service charges being levied by banks indicating that the existing institutional mechanism in this regard is not adequate.
Service
Charges to be displayed on Bank's Websites/at Branches
Minimum Information to be put on the Bank’s website
Savings Bank Account/No Frills Account
* Minimum balance
* Charges for non-maintenance
Savings Bank Account with Cheque Facility
* Minimum balance
* Charges for non-maintenance
Savings Bank Account without Cheque Facility
* Minimum balance
* Charges for non-maintenance
Other Savings Bank Account Facilities
* Issue of duplicate statement
* Issue of loose cheque leaves
* Issue of duplicate pass book
* Mode of calculation of minimum balance
Remittance Facilities through Own Bank
* DD - Issue, cancellation, duplicate and revalidation
* PO - Issue, cancellation, duplicate and revalidation
* TT - Issue, cancellation, duplicate and revalidation
* EFT - Inward and outward
* RTGS - Inward and outward
* Collection of Cheques
Remittance Facilities through other Bank
* DD - Issue, cancellation, duplicate and revalidation
* PO - Issue, cancellation, duplicate and revalidation
* TT - Issue, cancellation, duplicate and revalidation
* EFT - Inward and outward
* RTGS - Inward and outward
* Collection of Cheques
Foreign Exchange Transactions
* Remittance - Inward and outward
* TC - Selling, encashing and foreign currency
Cheque Collection
* Local
* Outstation through own bank
* Outstation through another bank
* Bouncing of cheque - local
* Bouncing of cheque - outstation - through own bank
* Bouncing of cheque - outstation - through another bank
Retail Loan
* Loan processing charges
* Pre-payment charges
* No due certificate
* Solvency certificate
* Late payment of EMI
* Changing from fixed to floating rates of interest
* Changing from float to fixed rates of interest
ATM Card
* Membership fee
* Annual fee
* Renewal charges
* Late payment charges
* Interest charges
* Replacement charges
* Transaction charge for partner banks
* Transaction charge for non-partner banks
Credit Card
* Membership fee
* Annual fee
* Renewal charges
* Late payment charges
* Interest charges
* Replacement charges
* Cash withdrawal
Debit Card
* Membership fee
* Annual fee
* Renewal charges
* Late payment charges
* Replacement charges
* Cash withdrawal
Miscellaneous
* Balance enquiry
* Balance certificate
* Interest certificate
* Account closure
* Use of fax/telephone/modem
* Photo attestation
* Signature attestation
* Stop payment charges
* Inoperative account
Minimum Information to be displayed at Bank Branches
A. Services rendered free of charge
B. Others
* Minimum balances to be maintained in savings bank account
* Charges for non-maintenance of minimum balance in savings bank account
* Charges for collection of outstation cheques
* Charges for issue of demand draft
* Charges for issue of cheque books, if any
* Charges for account statement
* Charges for account closure, if any
* Charges for deposit/withdrawal at ATM locations, if any
Limit for Overseas Branch Office Expenses raised
The remittance limits for incurring initial and recurring expenses of branch offices opened abroad have been raised to ten per cent and five per cent respectively, of average annual sales/income or turnover during the last two accounting years of the Indian entity. The earlier limits for such remittance were up to two and one per cent respectively.
Realisation of Export Proceeds
As a measure of further liberalisation, it has been decided that henceforth, authorised dealer banks may grant extension of time for realisation of export proceeds beyond the prescribed period from the date of export, up to the invoice value limit of USD 1 million. The earlier invoice value limit for such relaxation was USD 100,000.
Working Group for Distressed Farmers
The Reserve Bank has constituted a Working Group to Suggest measures to assist distressed farmers including provision of financial counselling services and introduction of a specific Credit Guarantee Scheme under the Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation of India (DICGC) Act for such farmers.
It may be recalled that paragraph 152 of the Annual Policy Statement 2006-07, observed that despite the spread of banking facilities in rural areas and availability of bank finance at reasonable rates, farmers in several areas are still in distress.
Commission Rates for Government Business revised
The rates of agency commission payable to banks for conduct of government business have been revised from July 1, 2005 as indicated below :
|
Existing Rates |
Revised Rates |
|
|
Receipts |
Rs.45/- per transaction |
No change |
|
Pension payments |
Rs.60/- per transaction |
No change |
|
Other payments |
Rs.50/- per transaction |
9 paise per |
|
Rs.100/- turnover |
The Reserve Bank had been receiving representations from agency banks that the rates of agency commission do not compensate the banks adequately and that there has been reduction in the commensurate commission receivable by them. The agency banks had particularly highlighted the fact that they remain out of funds for a few days on account of high value payments on behalf of the government.
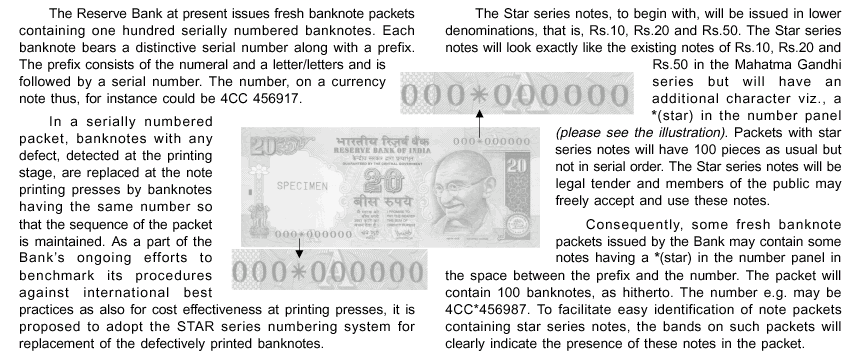
RBI to introduce Star Series Banknotes
Edited and published by Alpana Killawala for the Reserve Bank of India, Press Relations Division, Central Office, Shahid Bhagat Singh Marg, Mumbai - 400 001 and printed by her at Onlooker Press Ltd., 16, Sassoon Dock, Colaba, Mumbai - 400 005. For renewal and change of address please write to the Chief General Manager, Press Relations Division, Reserve Bank of India, Central Office Building, 12th floor, Fort, Mumbai - 400 001 without enclosing DD/cheque. MCIR is also available on Internet at www.mcir.rbi.org.in
పేజీ చివరిగా అప్డేట్ చేయబడిన తేదీ:

















