FAQ Page 1 - ربی - Reserve Bank of India
Biennial survey on Foreign Collaboration in Indian Industry (FCS)
Details of survey launch
Ans.: The RBI launches the FCS survey during the month of June every year with the last two financial year end-March as the reference date.
FAQs on Priority Sector Lending (PSL)
C. Adjustment for Weights in PSL Achievement
Clarification: If there is a decline in credit, the weighted incremental credit will be zero (0). The methodology as given below will be considered for all the districts for which data is reported in ADEPT and District-QPSA statement. Further, based on the methodology detailed below, banks are expected to monitor their own PSL achievement during the year taking into account the prescription of differential weights for credit in identified districts, for the purpose of trading in PSLCs.
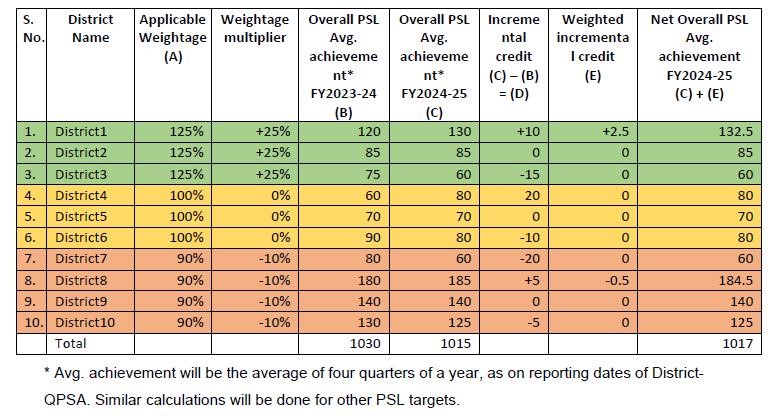
Clarification: For mapping a credit facility to a particular district, the ‘place of utilization of credit’ shall be the qualifying criteria.
Clarification: While calculating district-wise incremental credit for assigning weights, the organic credit i.e. only the credit directly disbursed by banks and for which the actual borrower/beneficiary wise details are maintained in the books of the bank, will be considered. Credit disbursed through the following inorganic routes shall not be considered for incremental weights.
- Investments by banks in securitised assets
- Transfer of Assets through Direct Assignment/Outright purchase
- Inter Bank Participation Certificates (IBPCs)
- Priority Sector Lending Certificates (PSLCs)
- Bank loans to MFIs (NBFC-MFIs, Societies, Trusts, etc.) for on-lending
- Bank loans to NBFCs for on-lending
Bank loans to HFCs for on-lending
D. Agriculture
Clarification: The PSL guidelines are activity and beneficiary specific and are not based on type of collateral. Therefore, bank loans given to individuals/ businesses for undertaking agriculture activities do not automatically become ineligible for priority sector classification, only on account of the fact that underlying asset is gold jewellery/ornament etc. It may, however, be noted that as per FIDD Circular dated December 6, 2024, it has been advised that banks may waive collateral security and margin requirements for agricultural loans upto ₹2 lakh. Therefore, bank should have extended the loan based on scale of finance and assessment of credit requirement for undertaking the agriculture activity and not solely based on available collateral in the form of gold. Further, as applicable to all loans under PSL, banks should put in place proper internal controls and systems to ensure that the loans extended under PSL are for approved purposes and the end use is continuously monitored.
Government Securities Market in India – A Primer
3.1 G-Secs are issued through auctions conducted by RBI. Auctions are conducted on the electronic platform called the E-Kuber, the Core Banking Solution (CBS) platform of RBI. Commercial banks, scheduled UCBs, Primary Dealers (a list of Primary Dealers with their contact details is given in Annex 2), insurance companies and provident funds, who maintain funds account (current account) and securities accounts (Subsidiary General Ledger (SGL) account) with RBI, are members of this electronic platform. All members of E-Kuber can place their bids in the auction through this electronic platform. The results of the auction are published by RBI at stipulated time (For Treasury bills at 1:30 PM and for GoI dated securities at 2:00 PM or at half hourly intervals thereafter in case of delay). All non-E-Kuber members including non-scheduled UCBs can participate in the primary auction through scheduled commercial banks or PDs (called as Primary Members-PMs). For this purpose, the UCBs need to open a securities account with a bank / PD – such an account is called a Gilt Account. A Gilt Account is a dematerialized account maintained with a scheduled commercial bank or PD. The proprietary transactions in G-Secs undertaken by PMs are settled through SGL account maintained by them with RBI at PDO. The transactions in G-Secs undertaken by Gilt Account Holders (GAHs) through their PMs are settled through Constituent Subsidiary General Ledger (CSGL) account maintained by PMs with RBI at PDO for its constituent (e.g., a non-scheduled UCB).
3.2 The RBI, in consultation with the Government of India, issues an indicative half-yearly auction calendar which contains information about the amount of borrowing, the range of the tenor of securities and the period during which auctions will be held. A Notification and a Press Communique giving exact particulars of the securities, viz., name, amount, type of issue and procedure of auction are issued by the Government of India about a week prior to the actual date of auction. RBI places the notification and a Press Release on its website (www.rbi.org.in) and also issues advertisements in leading English and Hindi newspapers. Auction for dated securities is conducted on Friday for settlement on T+1 basis (i.e. securities are issued on next working day i.e. Monday). The investors are thus given adequate time to plan for the purchase of G-Secs through such auctions. A specimen of a dated security in physical form is given at Annex 1. The details of all the outstanding dated securities issued by the Government of India are available on the RBI website at http://www.rbi.org.in/Scripts/financialmarketswatch.aspx. A sample of the auction calendar and the auction notification are given in Annex 3 and 4, respectively.
3.3 The Reserve Bank of India conducts auctions usually every Wednesday to issue T-bills of 91day, 182 day and 364 day tenors. Settlement for the T-bills auctioned is made on T+1 day i.e. on the working day following the trade day. The Reserve Bank releases a quarterly calendar of T-bill issuances for the upcoming quarter in the last week of the preceding quarter. e.g. calendar for April-June period is notified in the last week of March. The Reserve Bank of India announces the issue details of T-bills through a press release on its website every week.
3.4 Like T-bills, Cash Management Bills (CMBs) are also issued at a discount and redeemed at face value on maturity. The tenor, notified amount and date of issue of the CMBs depend upon the temporary cash requirement of the Government. The tenors of CMBs is generally less than 91 days. The announcement of their auction is made by Reserve Bank of India through a Press Release on its website. The non-competitive bidding scheme (referred to in paragraph number 4.3 and 4.4 under question No. 4) has not been extended to CMBs. However, these instruments are tradable and qualify for ready forward facility. Investment in CMBs is also reckoned as an eligible investment in G-Secs by banks for SLR purpose under Section 24 of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949. First set of CMB was issued on May 12, 2010.
3.5 Floatation of State Government Loans (State Development Loans)
In terms of Sec. 21A (1) (b) of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, the RBI may, by agreement with any State Government undertake the management of the public debt of that State. Accordingly, the RBI has entered into agreements with 29 State Governments and one Union Territory (UT of Puducherry) for management of their public debt. Under Article 293(3) of the Constitution of India (Under section 48A of Union territories Act, in case of Union Territory), a State Government has to obtain the permission of the Central Government for any borrowing as long as there is any outstanding loan that the State Government may have from the Centre.
Market borrowings are raised by the RBI on behalf of the State Governments to the extent of the allocations under the Market Borrowing Program as approved by the Ministry of Finance in consultation with the Planning Commission.
RBI, in consultation with State Governments announces, the indicative quantum of borrowing on a quarterly basis. All State Governments have issued General notifications which specify the terms and conditions for issue of SDL. Before every auction, respective state governments issue specific notifications indicating details of the securities being issued in the particular auction. RBI places a press release on its website and also issues advertisements in leading English and vernacular newspapers of the respective states.
Currently, SDL auctions are held generally on Tuesdays every week. As in case of Central Government securities, auction is held on the E-Kuber Platform. 10% of the notified amount is reserved for the retail investors under the non-competitive bidding.
Foreign Investment in India
Annual Return on Foreign Liabilities and Assets (FLA) under FEMA 1999
Eligible entities and requirements to submit the FLA return
Ans: Non-filing of the return on or before due date (July 15 of every year) will be treated as a violation of FEMA and penalty clause may be invoked for violation of FEMA. For further details on penalty clause, please see the below links:
Remittances (Money Transfer Service Scheme (MTSS) and Rupee Drawing Arrangement (RDA))
Rupee Drawing Arrangement (RDA)
FAQs on Non-Banking Financial Companies
Registration
Business restrictions imposed on Paytm Payments Bank Limited vide Press Releases dated January 31 and February 16, 2024
Bank Accounts with Paytm Payments Bank
Yes. Refunds, cashbacks, sweep-in from partner banks or interest are permitted credits into your account even after March 15, 2024
Framework for Compromise Settlements and Technical Write-offs
A. COMPROMISE SETTLEMENT IN WILFUL DEFAULT AND FRAUD CASES
No. The cooling period has been introduced as a general prescription for normal cases of compromise settlements, without prejudice to the penal measures applicable in respect of borrowers classified as fraud or wilful defaulter as per the Master Directions on Frauds dated July 1, 2016 and the Master Circular on Wilful Defaulters dated July 1, 2015, respectively, as mentioned at (2) above.
External Commercial Borrowings (ECB) and Trade Credits
A. BASIC QUERIES
Borrowings from overseas have to be in compliance with the applicable ECB guidelines / provisions contained in the Foreign Exchange Management (Borrowing and Lending in Foreign Exchange) Regulations, 2018 issued vide Notification No. FEMA 3 (R)/2018-RB dated December 17, 2018, as amended from time to time.
Domestic Deposits
I. Domestic Deposits
Retail Direct Scheme
Scheme related queries
-
Government of India Treasury Bills (T-Bills)
-
Government of India dated securities (dated G-Sec)
-
State Development Loans (SDLs)
-
Sovereign Gold Bonds (SGB)
Targeted Long Term Repo Operations (TLTROs)
Ans: There is no maturity restriction on the specified securities to be acquired under TLTRO scheme. However, the outstanding amount of specified securities in bank’s HTM portfolio should not fall below the level of amount availed under TLTRO scheme.
Housing Loans
All you wanted to know about NBFCs
A. Definitions
Banks and NBFCs are different entities subject to different statutory and regulatory requirements. However, NBFCs lend and make investments and hence these activities are akin to that of banks. The major differences between banks and NBFCs are given below:
i. NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits;
ii. NBFCs do not form part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue cheques drawn on itself;
iii. Deposit insurance facility of Deposit Insurance and Credit Guarantee Corporation (DICGC) is not available to depositors of deposit taking NBFCs.
Core Investment Companies
A. Definitions:
Ans: Net assets have been defined in Master Direction DoR(NBFC).PD.003/03.10.119/2016-17 dated August 25, 2016 (para3(1) (xviii)) specifically for the purpose of defining a CIC. As such they will only include the items specifically mentioned therein, irrespective of whether any of these qualify as operating assets or not.
The 10% of net assets which CIC’s can hold outside the group may include real estate or other fixed assets which are required for effective functioning of a company but should not include other financial investments/loans in non-group companies.
Indian Currency
A) Basics of Indian Currency/Currency Management
Bank notes are printed at four currency presses, two of which are owned by the Government of India through its Corporation, Security Printing and Minting Corporation of India Ltd. (SPMCIL) and two are owned by the Reserve Bank, through its wholly owned subsidiary, Bharatiya Reserve Bank Note Mudran Private Ltd. (BRBNMPL). The currency presses of SPMCIL are at Nasik (Western India) and Dewas (Central India). The two presses of BRBNMPL are at Mysuru (Southern India) and Salboni (Eastern India).
Coins are minted in four mints owned by SPMCIL. The mints are located at Mumbai, Hyderabad, Kolkata and NOIDA. The coins are issued for circulation only through the Reserve Bank in terms of Section 38 of the RBI Act.

















